一、前言
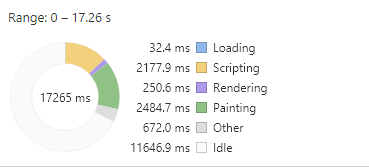
如上图,页面在渲染和画图时,耗时还是比较多的,这就对我们的编写要求愈加严格。
我们有很多方法来减少上图所示的页面加载耗时的,比如
但是更多的还是在于平时的编写规范,我们需要了解浏览器,让他更加便捷快速的理解(加载)我们的代码。
另外,在编写页面时,如果内容较多,相应的css也会变得更多、更加复杂。
或许会你会想着拆分css成2个或更多的文件,然而这并不是好的方法,会增加向服务器请求的次数,进而延长了页面加载完成的时间。
基于以上两点考虑,规范化的编写代码,不仅仅能够减少页面加载的耗时,提升用户体验,还可以使得代码更易于理解,增加可读性。
二、正文
2.1 属性书写顺序
[建议] 同一 rule set 下的属性在书写时,应按功能进行分组,并以 Formatting Model(布局方式、位置) > Box Model(尺寸) > Typographic(文本相关) > Visual(视觉效果) 的顺序书写,以提高代码的可读性。
解释:
- Formatting Model 相关属性包括:
position/top/right/bottom/left/float/display/overflow等 - Box Model 相关属性包括:
border/margin/padding/width/height等 - Typographic 相关属性包括:
font/line-height/text-align/word-wrap等 - Visual 相关属性包括:
background/color/transition/list-style等
另外,如果包含 content 属性,应放在最前面。
示例:相关的属性声明按照给定的顺序做分组处理,组之间需要有一个空行。
.sidebar { /* formatting model: positioning schemes / offsets / z-indexes / display / ... */ position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 0; overflow-x: hidden; /* box model: sizes / margins / paddings / borders / ... */ width: 200px; padding: 5px; border: 1px solid #ddd; /* typographic: font / aligns / text styles / ... */ font-size: 14px; line-height: 20px; /* visual: colors / shadows / gradients / ... */ background: #f5f5f5; color: #333; -webkit-transition: color 1s; -moz-transition: color 1s; transition: color 1s; }
2.2 命名规范
- 类名使用小写字母,以中划线分隔
- id采用驼峰式命名
- scss中的变量、函数、混合、placeholder采用驼峰式命名
/* class */ .element-content { ... } /* id */ #myDialog { ... } /* 变量 */ $colorBlack: #000; /* 函数 */ @function pxToRem($px) { ... } /* 混合 */ @mixin centerBlock { ... } /* placeholder */ %myDialog { ... }
2.3 属性简写
属性简写需要你非常清楚属性值的正确顺序,而且在大多数情况下并不需要设置属性简写中包含的所有值,所以建议尽量分开声明会更加清晰;
margin 和 padding 相反,需要使用简写;
常见的属性简写包括:
fontbackgroundtransitionanimation
/* not good == 不需要设置属性简写中包含的所有值时,建议不要简写*/ .element { transition: opacity 1s linear 2s; } /* good */ .element { transition-delay: 2s; transition-timing-function: linear; transition-duration: 1s; transition-property: opacity; } /* not good == 对于margin、padding需要使用简写*/ .element { padding-top: 2rem; padding-right: 0; padding-bottom: 2rem; padding-left: 0; } /* good */ .element { padding: 2rem 0; }
2.4 媒体查询
尽量将媒体查询的规则靠近与他们相关的规则,不要将他们一起放到一个独立的样式文件中,或者丢在文档的最底部,这样做只会让大家以后更容易忘记他们。
.element { ... } .element-avatar{ ... } @media (min- 480px) { .element { ... } .element-avatar { ... } }
2.5 杂项
- 不允许有空的规则;
- 元素选择器用小写字母;
- 去掉小数点前面的0;
去掉数字中不必要的小数点和末尾的0;
属性值'0'后面不要加单位; - 同个属性不同前缀的写法需要在垂直方向保持对齐,具体参照后面的写法;
无前缀的标准属性应该写在有前缀的属性后面; - 不要在同个规则里出现重复的属性,如果重复的属性是连续的则没关系;
不要在一个文件里出现两个相同的规则; - 用
border: 0;代替border: none;; - 选择器不要超过4层(在scss中如果超过4层应该考虑用嵌套的方式来写);
- 发布的代码中不要有
@import; - 尽量少用'*'选择器。
/* not good == 不允许有空的规则;*/ .element { } /* not good == 元素选择器用小写字母*/ LI { ... } /* good */ li { ... } /* not good == 去掉小数点前面的0;*/ .element { color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5); } /* good */ .element { color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5); } /* not good == 去掉数字中不必要的小数点和末尾的0;*/ .element { width: 50.0px; } /* good */ .element { width: 50px; } /* not good == 属性值'0'后面不要加单位;*/ .element { width: 0px; } /* good */ .element { width: 0; } /* not good *== 同个属性不同前缀的写法需要在垂直方向保持对齐,具体参照后面的写法; *== 无前缀的标准属性应该写在有前缀的属性后面; */ .element { border-radius: 3px; -webkit-border-radius: 3px; -moz-border-radius: 3px; background: linear-gradient(to bottom, #fff 0, #eee 100%); background: -webkit-linear-gradient(top, #fff 0, #eee 100%); background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #fff 0, #eee 100%); } /* good */ .element { -webkit-border-radius: 3px; -moz-border-radius: 3px; border-radius: 3px; background: -webkit-linear-gradient(top, #fff 0, #eee 100%); background: -moz-linear-gradient(top, #fff 0, #eee 100%); background: linear-gradient(to bottom, #fff 0, #eee 100%); } /* not good == 不要在同个规则里出现重复的属性,如果重复的属性是连续的则没关系;*/ .element { color: rgb(0, 0, 0); width: 50px; color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5); } /* good */ .element { color: rgb(0, 0, 0); color: rgba(0, 0, 0, .5); } /* not good == 选择器不要超过4层(在scss中如果超过4层应该考虑用嵌套的方式来写);*/ .container . main div ul .element { ... } /* good */ .container . main .element { ... }
三、结语
具体的规范可以参照大厂的规范文档,如下链接: