网站需要定时执行不同的任务,比如清理无效的数据、定时发送mail等,Nop的这个定时任务设计比较好,简单的说就是将所有任务相同的属性持久化,具体的执行通过继承接口来实现。
持久化对象:ScheduleTask
ScheduleTask定义了Seconds,Type等属性,分别记录执行周期和任务类型。

public class ScheduleTask:BaseEntity { public string Name { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the run period (in seconds) /// </summary> public int Seconds { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the type of appropriate ITask class /// </summary> public string Type { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the value indicating whether a task is enabled /// </summary> public bool Enabled { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the value indicating whether a task should be stopped on some error /// </summary> public bool StopOnError { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the machine name (instance) that leased this task. It's used when running in web farm (ensure that a task in run only on one machine). It could be null when not running in web farm. /// </summary> public string LeasedByMachineName { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the datetime until the task is leased by some machine (instance). It's used when running in web farm (ensure that a task in run only on one machine). /// </summary> public DateTime? LeasedUntilTime { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the datetime when it was started last time /// </summary> public DateTime? LastStartTime { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the datetime when it was finished last time (no matter failed ir success) /// </summary> public DateTime? LastEndTime { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the datetime when it was sucessfully finished last time /// </summary> public DateTime? LastSuccessTime { get; set; } }
比如定义一个deleteGuestTask,即2小时删除一次guest。
var deleteGuestTask = new ScheduleTask { Name = "Delete Guest Task", Seconds = 7200, Type = "Portal.Services.Users.DeleteGuestTask,Portal.Services", StopOnError = true, LeasedByMachineName = "0", Enabled = true, };
对数据库的基本操作就交给了ScheduleTaskService。ScheduleTaskService继承IScheduleTaskService。

public partial interface IScheduleTaskService { void DeleteTask(ScheduleTask task); ScheduleTask GetTaskById(int taskId); ScheduleTask GetTaskByType(string type); IList<ScheduleTask> GetAllTasks(bool showHidden = false); void InsertTask(ScheduleTask task); void UpdateTask(ScheduleTask task); }
面向接口ITask
ITask接口只有一个方法:
public partial interface ITask { /// <summary> /// Execute task /// </summary> void Execute(); }
Nop实现了多个任务
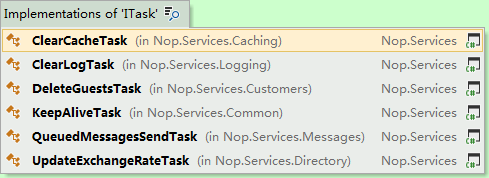
例如DeleteGuestTask:

public class DeleteGuestTask:ITask { private readonly IUserService _userService; public DeleteGuestTask(IUserService userService) { _userService = userService; } public void Execute() { //60*24 = 1 day var olderThanMinutes = 1440; _userService.DeleteGuestUsers(null, DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(-olderThanMinutes), true); } }
而ScheduleTask如何和ITask关联的任务就交给了Task类。

public partial class Task { /// <summary> /// Ctor for Task /// </summary> private Task() { this.Enabled = true; } /// <summary> /// Ctor for Task /// </summary> /// <param name="task">Task </param> public Task(ScheduleTask task) { this.Type = task.Type; this.Enabled = task.Enabled; this.StopOnError = task.StopOnError; this.Name = task.Name; } private ITask CreateTask(ILifetimeScope scope) { ITask task = null; if (this.Enabled) { var type2 = System.Type.GetType(this.Type); if (type2 != null) { object instance; if (!EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.TryResolve(type2, scope, out instance)) { //not resolved instance = EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.ResolveUnregistered(type2, scope); } task = instance as ITask; } } return task; } /// <summary> /// Executes the task /// </summary> /// <param name="scope"></param> /// <param name="throwException">A value indicating whether exception should be thrown if some error happens</param> /// <param name="dispose">A value indicating whether all instances hsould be disposed after task run</param> public void Execute(ILifetimeScope scope=null,bool throwException = false, bool dispose = true) { this.IsRunning = true; //background tasks has an issue with Autofac //because scope is generated each time it's requested //that's why we get one single scope here //this way we can also dispose resources once a task is completed if (scope == null) { scope = EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.Scope(); } var scheduleTaskService = EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.Resolve<IScheduleTaskService>("", scope); var scheduleTask = scheduleTaskService.GetTaskByType(this.Type); try { var task = this.CreateTask(scope); if (task != null) { this.LastStartUtc = DateTime.UtcNow; if (scheduleTask != null) { //update appropriate datetime properties scheduleTask.LastStartTime = this.LastStartUtc; scheduleTaskService.UpdateTask(scheduleTask); } //execute task task.Execute(); this.LastEndUtc = this.LastSuccessUtc = DateTime.UtcNow; } } catch (Exception exc) { this.Enabled = !this.StopOnError; this.LastEndUtc = DateTime.UtcNow; //log error if (throwException) throw; } if (scheduleTask != null) { //update appropriate datetime properties scheduleTask.LastEndTime = this.LastEndUtc; scheduleTask.LastSuccessTime = this.LastSuccessUtc; scheduleTaskService.UpdateTask(scheduleTask); } //dispose all resources if (dispose) { scope.Dispose(); } this.IsRunning = false; } /// <summary> /// A value indicating whether a task is running /// </summary> public bool IsRunning { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Datetime of the last start /// </summary> public DateTime? LastStartUtc { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Datetime of the last end /// </summary> public DateTime? LastEndUtc { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Datetime of the last success /// </summary> public DateTime? LastSuccessUtc { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// A value indicating type of the task /// </summary> public string Type { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// A value indicating whether to stop task on error /// </summary> public bool StopOnError { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Get the task name /// </summary> public string Name { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// A value indicating whether the task is enabled /// </summary> public bool Enabled { get; set; } }
CreateTask方法用Autofac Resolve(相当于反射)出了对应的任务类型。
private ITask CreateTask(ILifetimeScope scope) { ITask task = null; if (this.Enabled) { var type2 = System.Type.GetType(this.Type); if (type2 != null) { object instance; if (!EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.TryResolve(type2, scope, out instance)) { //not resolved instance = EngineContext.Current.ContainerManager.ResolveUnregistered(type2, scope); } task = instance as ITask; } } return task; }
而Task的Execute方法,调用的是各自任务的Execute。
TaskManager统一管理,TaskThread真正执行
TaskManager统一加载和执行任务,在Global中调用。
protected void Application_Start() { //... TaskManager.Instance.Initialize(); TaskManager.Instance.Start(); }
这里说一下TaskThread,它包含一个Timer和Dictionary<string, Task> _tasks;

public partial class TaskThread : IDisposable { private Timer _timer; private bool _disposed; private readonly Dictionary<string, Task> _tasks; internal TaskThread() { this._tasks = new Dictionary<string, Task>(); this.Seconds = 10 * 60; } private void Run() { if (Seconds <= 0) return; this.StartedUtc = DateTime.Now; this.IsRunning = true; foreach (Task task in this._tasks.Values) { task.Execute(Scope,false,false); } this.IsRunning = false; } private void TimerHandler(object state) { this._timer.Change(-1, -1); this.Run(); if (this.RunOnlyOnce) { this.Dispose(); } else { this._timer.Change(this.Interval, this.Interval); } } /// <summary> /// Disposes the instance /// </summary> public void Dispose() { if ((this._timer != null) && !this._disposed) { lock (this) { this._timer.Dispose(); this._timer = null; this._disposed = true; } } } private ILifetimeScope Scope { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Inits a timer /// </summary> public void InitTimer(ILifetimeScope scope) { Scope = scope; if (this._timer == null) { this._timer = new Timer(new TimerCallback(this.TimerHandler), null, this.Interval, this.Interval); } } /// <summary> /// Adds a task to the thread /// </summary> /// <param name="task">The task to be added</param> public void AddTask(Task task) { if (!this._tasks.ContainsKey(task.Name)) { this._tasks.Add(task.Name, task); } } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets the interval in seconds at which to run the tasks /// </summary> public int Seconds { get; set; } /// <summary> /// Get or sets a datetime when thread has been started /// </summary> public DateTime StartedUtc { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Get or sets a value indicating whether thread is running /// </summary> public bool IsRunning { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// Get a list of tasks /// </summary> public IList<Task> Tasks { get { var list = new List<Task>(); foreach (var task in this._tasks.Values) { list.Add(task); } return new ReadOnlyCollection<Task>(list); } } /// <summary> /// Gets the interval at which to run the tasks /// </summary> public int Interval { get { return this.Seconds * 1000; } } /// <summary> /// Gets or sets a value indicating whether the thread whould be run only once (per appliction start) /// </summary> public bool RunOnlyOnce { get; set; } }
在Run方法中执行所有包含的任务。这里其实是相同周期的任务。
TaskManager有一个_taskThreads集合,而Initialize方法的主要任务是从数据库加载ScheduleTask.然后将相同周期的任务组装成同一个TaskThread.还区分了只执行一次的任务。
public void Initialize() { this._taskThreads.Clear(); var taskService = EngineContext.Current.Resolve<IScheduleTaskService>(); var scheduleTasks = taskService .GetAllTasks() .OrderBy(x => x.Seconds) .ToList(); //group by threads with the same seconds foreach (var scheduleTaskGrouped in scheduleTasks.GroupBy(x => x.Seconds)) { //create a thread var taskThread = new TaskThread { Seconds = scheduleTaskGrouped.Key }; foreach (var scheduleTask in scheduleTaskGrouped) { var task = new Task(scheduleTask); taskThread.AddTask(task); } this._taskThreads.Add(taskThread); } var notRunTasks = scheduleTasks .Where(x => x.Seconds >= _notRunTasksInterval) .Where(x => !x.LastStartTime.HasValue || x.LastStartTime.Value.AddSeconds(_notRunTasksInterval) < DateTime.UtcNow) .ToList(); //create a thread for the tasks which weren't run for a long time if (notRunTasks.Count > 0) { var taskThread = new TaskThread { RunOnlyOnce = true, Seconds = 60 * 5 //let's run such tasks in 5 minutes after application start }; foreach (var scheduleTask in notRunTasks) { var task = new Task(scheduleTask); taskThread.AddTask(task); } this._taskThreads.Add(taskThread); } }
在Star中执行任务。
public void Start() { foreach (var taskThread in this._taskThreads) { taskThread.InitTimer(); } }
在后台管理任务的情况,可以立即执行。
public ActionResult RunNow(int id) { var scheduleTask = _taskService.GetTaskById(id); if (scheduleTask == null) return View("NoData"); var task = new Task(scheduleTask); task.Enabled = true; task.Execute(null,false,false); return RedirectToAction("Index"); }
个人感觉还是值得借鉴的,我已经用到自己的项目中,可以方便的扩展到自己的其他任务。
