最近编程经常遇到需要 排列&&组合(求子集) 的问题:遂整理一下。
1. 数字的排列与组合(递归):O(n!),O(nC(n,k)) * O(n)
#include <stdio.h> int arr[100]; void init(int N) { for(int i = 0; i < N; ++i) arr[i] = i+1; } void print(int a[], int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%d ", a[i]); printf(" "); } void permutation(int arr[], int begin, int end) { if(begin == end) { print(arr, end); return; } for(int start = begin; start < end; ++start) { int t = arr[begin]; arr[begin] = arr[start]; arr[start] = t; permutation(arr, begin+1, end); arr[start] = arr[begin]; arr[begin] = t; } } void combination(int endNum, int curNum, int begin, int end, int a[]) { if(curNum == endNum) { print(a, endNum); return; } for(int i = begin; i <= end; ++i) { a[curNum] = i; combination(endNum, curNum+1, i+1, end, a); } } int main() { int N; scanf("%d", &N); printf("Combination: "); int a[30] = {0}; for(int numberOfElem = 1; numberOfElem <= N; ++numberOfElem) combination(numberOfElem, 0, 1, N, a); init(N); printf("Permutation: "); permutation(arr, 0, N); return 0; }
2. 字符的排列组合
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> char s[] = "ABC"; void print(const char a[], int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf("%c ", a[i]); printf(" "); } void permutation(char s[], int begin, int end) { if(begin == end) { print(s, end); return; } for(int start = begin; start < end; ++start) { char t = s[begin]; s[begin] = s[start]; s[start] = t; permutation(s, begin+1, end); s[start] = s[begin]; s[begin] = t; } } void combination(int endNum, int curNum, int begin, int end, char a[], const char s[]) { if(curNum == endNum) { print(a, endNum); return; } for(char i = begin; i < end; ++i) { a[curNum] = s[i]; combination(endNum, curNum+1, i+1, end, a, s); } } int main() { int N = strlen(s); printf("Combination: "); char a[30] = {0}; for(int members = 1; members <= N; ++members) combination(members, 0, 0, N, a, s); printf("Permutation: "); permutation(s, 0, N); return 0; }
3.数字的组合(非递归)Θ(n2n) * O(n):
#include <stdio.h> unsigned long long count = 1; int main() { int n, k, i, j, c; scanf("%d", &n); for(k = 1; k <= n; ++k) { for (i=0; i<(1<<n); i++) { for (j=0,c=0; j<32; j++) if (i & (1<<j)) c++; if (c == k) { for (j=0;j<32; j++) if (i & (1<<j)) printf ("%i ", j+1); printf (" "); ++count; } } } printf("total: %d ", count); }
另外:http://www.cnblogs.com/autosar/archive/2012/04/08/2437799.html 写的不错,可以学习一下。
8月29号。
忽然想起来小时候经常玩的快算 24.
试着利用全排列算法,写了个快算24的小程序。效果还不错。
思想:1、4个数字全排列,对每一个排列,从头到尾计算一遍。共 4!* 43次计算 。 2、 取出所有的两两组合,2 * C(4,2) 种方案, 共 2 * C(4,2) * 43次计算;但是利用全排列,对于每一个排列,取前两个和后两个组合整好是 2 * C(4,2) = 4!种方案。 故总计算复杂度为: 4! * 43 = 42 * 64 = 2688 次(* 2)。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int v = 24;
int A[4];
const char ch[4] = { '+', '-', '*', '/'};
bool has_answer = false;
int compute(const char ch, int v1, int v2) {
switch(ch) {
case '+': return v1+v2;
case '-': return v1 > v2 ? v1-v2 : -10000;
case '*': return v1*v2;
default:
{
if(v2 == 0) return -10000;
float tem = (float)(v1)/v2;
int tem2 = v1 / v2;
if(abs(tem-tem2) > 0) return -10000;
return tem2;
};
}
}
bool compute24() {
int l, m, n;
for(l = 0; l < 4; ++l) {
int v2 = compute(ch[l], A[0], A[1]);
for(m = 0; m < 4; ++m) {
int v3 = compute(ch[m], v2, A[2]);
for(n = 0; n < 4; ++n) {
if(has_answer) return true;
if(compute(ch[n], v3, A[3]) == v) {
cout << "[ [" << A[0] << ' ' << ch[l] << ' ' << A[1] << "] " << ch[m] << ' '
<< A[2] << " ] " << ch[n] << ' ' << A[3] << " = " << v << endl;
return has_answer = true;
}
else if(compute(ch[m], v2, compute(ch[n], A[2], A[3])) == v) {
cout << "[ " << A[0] << ' ' << ch[l] << ' ' << A[1] << " ] " << ch[m] << " [ "
<< A[2] << ' ' << ch[n] << ' ' << A[3] << " ] = " << v << endl;
return has_answer = true;
}
}
}
}
return has_answer;
}
void permutation(int begin) {
if(begin == 4) {
compute24();
return;
}
for(int start = begin; start < 4; ++ start) {
int tem = A[start];
A[start] = A[begin];
A[begin] = tem;
permutation(begin+1);
A[begin] = A[start];
A[start] = tem;
}
}
int main() {
while(true) {
has_answer = false;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
cin >> A[k];
}
permutation(0);
if(!has_answer) cout << "No solution." << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
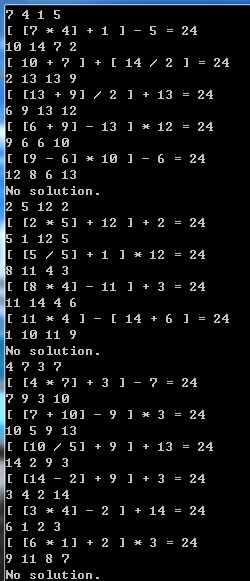
准备的测试用例: {9, 10, 5, 2}, {5, 6, 7, 9}, {5, 5, 5, 5}, {7, 11, 9, 13}, {3, 7, 11, 3}, {9, 5, 6, 2}, {5, 6, 9, 11}, {10, 11, 2, 2}

使用随机数生成:
/* modify the function main(), as follows: */
int main() {
while(true) {
has_answer = false;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for(int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
A[k] = rand() % 14 + 1;
cout << A[k] << ' ';
}
cout << endl; Sleep(10000);
permutation(0);
if(!has_answer) cout << "No solution." << endl;
Sleep(10000);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}