0113
进度条
<ProgressBar>
两种风格
水平进度条
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal"
android:max="200"进度条最大设置为200.不写这条语句默认下是100
或者在代码里面设置
firstBar.setMax(200);
圆圈
style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle"
android:visibility="gone"当前不可见,由程序让它改为可视的状态
------------------------------------------
对进度条的操作响应
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(i==0)
{
firstBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
secondBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
if(i<firstBar.getMax())
{
firstBar.setProgress(i);
firstBar.setSecondaryProgress(i+10);
secondBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
else
{
firstBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
secondBar.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
i=i+10;
}
----------------------------------------------------------
Activity08
1 package com.example.mars_activity08; 2 3 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.app.Activity; 6 import android.view.Menu; 7 import android.view.View; 8 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 9 import android.widget.Button; 10 import android.widget.ProgressBar; 11 12 public class ProgressBarTest extends Activity { 13 14 private ProgressBar firstBar; 15 private ProgressBar secondBar; 16 private Button myButton; 17 private int i=0; 18 @Override 19 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 20 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 21 setContentView(R.layout.main); 22 //根据控件的ID开获取控件的对象 23 firstBar=(ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.firstBar); 24 secondBar=(ProgressBar)findViewById(R.id.secondBar); 25 myButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.myButton); 26 myButton.setOnClickListener(new ButtonListener()); 27 28 29 } 30 class ButtonListener implements OnClickListener 31 { 32 33 @Override 34 public void onClick(View arg0) { 35 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 36 37 if(i==0) 38 { 39 firstBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); 40 secondBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); 41 42 } 43 if(i<firstBar.getMax()) 44 { 45 firstBar.setProgress(i); 46 firstBar.setSecondaryProgress(i+10); 47 secondBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); 48 49 50 } 51 else 52 { 53 firstBar.setVisibility(View.GONE); 54 secondBar.setVisibility(View.GONE); 55 } 56 i=i+10; 57 } 58 } 59 60 61 62 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <ProgressBar 8 android:id="@+id/firstBar" 9 style="?android:attr/progressBarStyleHorizontal" 10 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 11 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 12 android:visibility="gone" 13 /> 14 <ProgressBar 15 android:id="@+id/secondBar" 16 style="?android:attr/progressBarStyle" 17 android:layout_width="100dp" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 19 android:visibility="gone" 20 /> 21 22 23 <Button 24 android:id="@+id/myButton" 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 27 android:text="begin" 28 29 /> 30 31 32 </LinearLayout>
------------------------------------------------------------
ListView 控件的用法
点击可以达到选中整个一横行的效果
这个Activity实现的是ListActivity 是Activity的子类
ArrayList的运用
Activity09.java
1 package com.example.mars_activity09; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.HashMap; 5 import java.lang.Integer; 6 import android.os.Bundle; 7 import android.app.Activity; 8 import android.app.ListActivity; 9 import android.view.Menu; 10 import android.view.View; 11 import android.widget.ListView; 12 import android.widget.SimpleAdapter; 13 14 public class Activity09 extends ListActivity { 15 16 @Override 17 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 18 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 19 setContentView(R.layout.main); 20 //创建存储HashMap这样数据结构的ArrayList对象,其中HashMap是存储键值对的 21 ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> list =new ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>>(); 22 //对ArrayLsit中的HashMap创建对象,HashMap是存储键值对的 23 HashMap<String,String> map1=new HashMap<String,String>(); 24 HashMap<String,String> map2=new HashMap<String,String>(); 25 HashMap<String,String> map3=new HashMap<String,String>(); 26 //在HashMap中存储键值对 27 map1.put("user_name"," kangyuxin");//第一个是键 第二个是值 28 map1.put("user_ip", "192.168.1.1"); 29 map2.put("user_name", "zhangsan"); 30 map2.put("user_ip","222.123.22.1" ); 31 map3.put("user_name", "lisi"); 32 map3.put("user_ip", "1.123.20.1"); 33 //将HashMap放入ArrayList 34 list.add(map1); 35 list.add(map2); 36 list.add(map3); 37 //An easy adapter to map static data to views defined in an XML file. 38 SimpleAdapter listAdapter= new SimpleAdapter(this, 39 list,R.layout.user,new String[]{"user_name","user_ip"},//如果两个就是两列,与map的键值一致 40 //存string类型数据 username和userip是一个键 41 new int[]{R.id.user_name,R.id.user_ip});//用此控件显示//此顺序决定显示顺序 42 //到map中找username所对应的键所对应的值,username的值就是在map中所对应的值 43 44 //注意String和 int数组 是{} 45 //在ListAdapter里面必须调用setListAdpater这个方法,此方法继承ListActivity 46 //ArrayList展现出来需要创建一个适配器 47 //Adapter是连接后端数据和前端显示的适配器接口,是数据和UI(View)之间一个重要的纽带。 48 setListAdapter(listAdapter); 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 }
user.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="horizontal" > 6 <TextView 7 android:id="@+id/user_name" 8 android:layout_width="200dip" 9 android:layout_height="30dip" 10 android:textSize="10pt" 11 android:singleLine="true" 12 13 /> 14 15 <TextView 16 android:id="@+id/user_ip" 17 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 19 android:gravity="left" 20 android:textSize="10pt" 21 /> 22 23 24 </LinearLayout>
main.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 4 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 <LinearLayout 7 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 8 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 9 > 10 <ListView 11 android:id="@id/android:list" 12 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 13 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 14 android:scrollbars="vertical" 15 /> 16 17 </LinearLayout> 18 19 </LinearLayout> 20 21 22 23
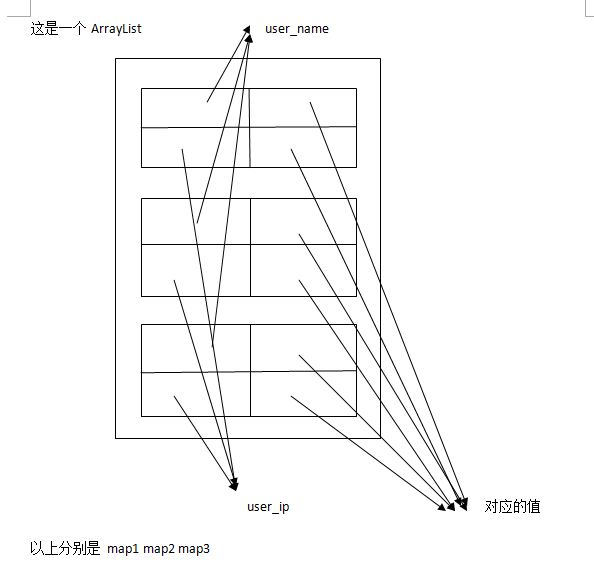
什么是ArrayList ArrayList就是传说中的动态数组,用MSDN中的说法,就是Array的复杂版本,它提供了如下一些好处:
- 动态的增加和减少元素
- 实现了ICollection和IList接口
- 灵活的设置数组的大小
- Add、AddRange、Remove、RemoveAt、RemoveRange、Insert、InsertRange
这几个方法比较类似
Add方法用于添加一个元素到当前列表的末尾
AddRange方法用于添加一批元素到当前列表的末尾
Remove方法用于删除一个元素,通过元素本身的引用来删除
RemoveAt方法用于删除一个元素,通过索引值来删除
RemoveRange用于删除一批元素,通过指定开始的索引和删除的数量来删除
Insert用于添加一个元素到指定位置,列表后面的元素依次往后移动
InsertRange用于从指定位置开始添加一批元素,列表后面的元素依次往后移动

listView是产生点击可以选中一行的效果,但具体那一行怎么显示由user.xml决定,
user.xml是规定每一行怎么显示
将数据存储在ArrayList里面
通过Adapter将数据与UI相互连接
Adapter是连接后端数据和前端显示的适配器接口,是数据和UI(View)之间一个重要的纽带。在常见的View(ListView,GridView)等地方都需要用到Adapter
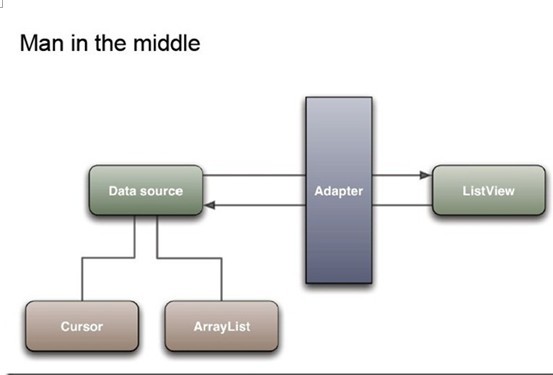
Adapter负责将整理好的ArrayList显示出来