接口
接口的关键字是interface,接口名首字母大写,写法是interface 类名(){};
创建一个接口:
1 public interface NewFeat { 2 String a="NewFeat"; 3 //视频播放 4 public void video(); 5 6 //音频播放 7 public void audio(); 8 }
接口的实现:
1 //实现NewFeat接口 2 public class NewFeatImp implements NewFeat{ 3 4 @Override 5 public void video() { 6 System.out.print("我能播放视频!"); 7 } 8 @Override 9 public void audio() { 10 System.out.print("我能播放音频!"); 11 } 12 13 }
什么是接口:
①概念性的接口,系统对外提供的所有服务
②实在的接口,使用interface关键字所修饰的类
接口的特性和使用:
①接口不可以被实例化,也没有构造方法
②实现类必须实现接口的所有方法
③实现类可以实现多个接口
用implements关键字,多个接口使用逗号隔开
④接口中的变量都是静态常量(public static final)
⑤接口中的方法默认都是公共抽象方法(public abstract)
⑥接口不能实现其他接口,但是可以继承多个其他接口,用extends关键字,多个接口用逗号隔开
接口和抽象类的区别:
相同点:
都代表系统的抽象层
都不能被实例化 都能包含抽象方法 用于描述系统提供的服务,不必提供具体实现
不同点:
在抽象类中可以为部分方法提供默认实现,而接口中只能包含抽象方法
抽象类便于复用,接口便于代码维护
一个类只能继承一个直接的父类,但可以实现多个接口
异常
异常是指在程序的运行过程中所发生的不正常的事件,它会中断正在运行的程序。
Java的异常处理是通过5个关键字来实现的:try、catch、 finally、throw、throws
try-catch-finally结构:
不论是否有异常,finally块中的语句都会执行。
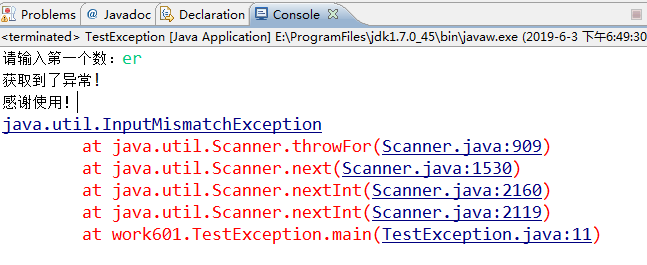
1 public class TestException { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); 4 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 5 try{ 6 int n1=in.nextInt(); 7 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 8 int n2=in.nextInt(); 9 System.out.println("两数之商为:"+(n1/n2)); 10 }catch(InputMismatchException e){ 11 System.out.println("获取到了异常!"); 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 //退出虚拟机 14 //System.exit(1); 15 }finally{ 16 System.out.println("感谢使用!"); 17 } 18 } 19 }
运行结果:
注: try-catch-finally结构中try语句块是必须的,catch、finally语句块均可选,但两者至少出现之一
当finnally前面有System.exit(1)时,finally块中的语句不执行。
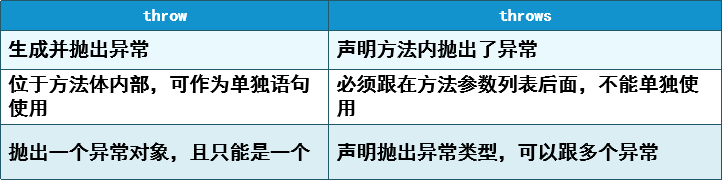
throw和throws:
实例:
1 public class Persion { 2 private int age; 3 public int getAge() { 4 return age; 5 } 6 public void setAge(int age) throws Exception { 7 if(1<=age&&age<=100){ 8 this.age = age; 9 }else{ 10 //异常抛出 11 throw new Exception("年龄输入错误!"); 12 } 13 14 } 15 16 }
创建测试类,
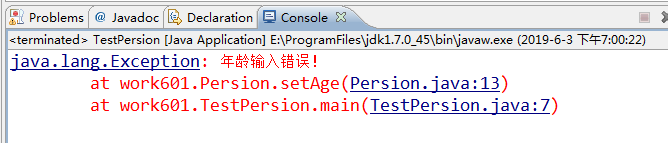
1 public class TestPersion { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 Persion p=new Persion(); 4 //获取异常并进行处理 5 try{ 6 p.setAge(209); 7 System.out.print("年龄是:"+p.getAge()); 8 }catch(Exception e){ 9 //输出异常 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 13 } 14 15 }
输出结果:
异常链:
异常链创建了新的异常但却保留了原有异常的信息
创建一个用户类:
1 public class User { 2 private String name;//用户名 3 private String password;//用户密码 4 public String getName() { 5 return name; 6 } 7 public void setName(String name) { 8 this.name = name; 9 } 10 public String getPassword() { 11 return password; 12 } 13 public void setPassword(String password) { 14 this.password = password; 15 }
创建一个登陆类:
1 public class Login { 2 private String lname;//登录名 3 private String lpassword;//登录密码 4 5 public String getLname() { 6 return lname; 7 } 8 public void setLname(String lname) { 9 this.lname = lname; 10 } 11 public String getLpassword() { 12 return lpassword; 13 } 14 public void setLpassword(String lpassword) { 15 this.lpassword = lpassword; 16 } 17 18 }
自定义两个异常:
1 public class RegFalseException extends Exception{ 2 3 public RegFalseException(){} 4 5 public RegFalseException(String message, Throwable cause) { 6 super(message, cause); 7 } 8 public RegFalseException(String masg){ 9 super(masg); 10 } 11 12 }
1 public class LogFalseException extends Exception{ 2 3 public LogFalseException() { 4 super(); 5 } 6 public LogFalseException(String message, Throwable cause) { 7 super(message, cause); 8 } 9 10 public LogFalseException(String message) { 11 super(message); 12 } 13 14 }
创建测试类:
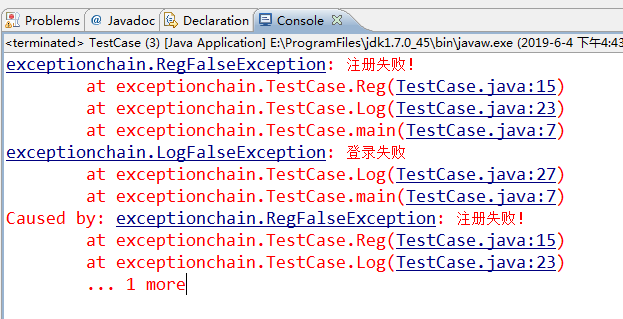
1 public class TestCase { 2 public static void main(String[] args){ 3 User use=new User(); 4 try { 5 Log(use); 6 } catch (LogFalseException e) { 7 e.printStackTrace(); 8 } 9 } 10 //用户注册方法 11 public static void Reg(User use) throws RegFalseException{ 12 if(use.getName()==null){ 13 throw new RegFalseException("注册失败!"); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.print("注册成功!"); 16 } 17 } 18 //用户登录方法 19 public static void Log(User use) throws LogFalseException{ 20 try{ 21 Reg(use); 22 System.out.print("登录成功!"); 23 }catch(RegFalseException e){ 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 throw new LogFalseException("登录失败",e); 26 } 27 } 28 29 }
运行结果:两种异常都输出了