KVM stands for Kernel Based Virtual Machine, is a virtualization software which provides ability to run a multiple guest operating systems with the help of hardware virtualization extensions. It supports wide variety of guest operating system’s such as Linux, Windows, Solaris, Haiku, REACT OS and much more. This guide shows you how to install KVM on Fedora 22.
KVM can be managed using command line or available graphical tools. Virt-Manager (Virtual Machine Manager) is the most widely used application for managing KVM based virtual machines, it supports creating, editing, starting, and stopping KVM-based virtual machines, as well as live or cold migration of guest machines between hosts.
Pre-requisites:
As said earlier, KVM will work only if the CPU has a support of hardware virtualization, either Intel VT or AMD-V. To find whether your cpu supports VT features, run the following command.
# egrep '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo |
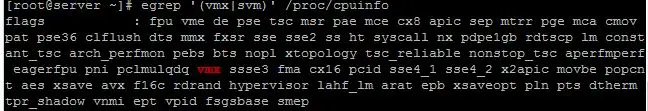 CentOS 7 – Intel VT Support
CentOS 7 – Intel VT Support
If the above commands returns with any output showing vmx or svm then your hardware supports VT else it does not.
Installing KVM:
Issue the following command to install latest qemu package and also virt-manager which provides graphical interface to manage virtual machines.
# dnf groupinstall "Virtualization" # dnf install qemu-img libvirt libvirt-python libvirt-client |
- qemu-kvm = QEMU emulator
- qemu-img = QEMU disk image manager
- virt-install = Command line tool to create virtual machines.
- libvirt = Provides libvirtd daemon that manages virtual machines and controls hypervisor.
- libvirt-client = provides client side API’s for accessing servers and also provides virsh utility which provides command line tool to manage virtual machines.
- virt-viewer – Graphical console
Creating Virtual Machine:
Once you have installed KVM and other tools, it is all set to start creating virtual machines. We will look be looking at creating virtual machines in both command line and graphical mode.
Command Line Mode:
virt-install is used to create virtual machines using command line, this command needs multiple inputs from us to create a virtual machine such as CPU,Memory, disk, network, installation media location, os variant and more.
# virt-install --name=itzgeekguest --ram=1024 --vcpus=1 --cdrom=/tmp/CentOS-6.5-x86_64-minimal.iso --os-type=linux --os-variant=rhel6 --network bridge=br0 --graphics=spice --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/itzgeekguest.dsk,size=4
Note: The above command uses bridged networking “br0” for allowing virtual machines to communicate with outside network, you can find a tutorial on creating bridged networking on Fedora 22.
–name – Name of the Virtual machine
–ram – Memory size in MB
–vcpus – Virtal cpu’s in numbers
–cdrom – Location of the ISO image
–os-type – OS type like Linux, Windows and Unix
–os-variant – OS variant like rhel 6, solaris
–network – Networking
–graphics – Guest display settings
–disk path – Location of the disk with size of 4 GB
Once you’ve issued the above command, virt-install will create a virtual machine and starts virt viewer console for OS installation.
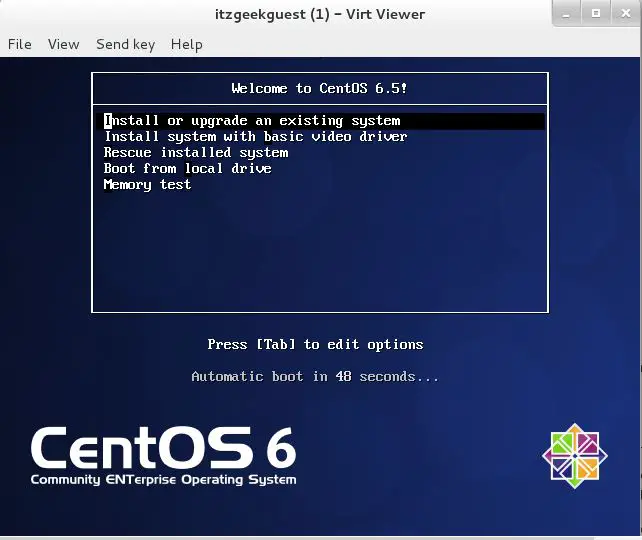 Fedora 22 – Guest Installation command Line Virt Viewer
Fedora 22 – Guest Installation command Line Virt Viewer
Graphical Mode:
Type the following command in terminal in GUI mode.
# virt-manager |
or
Activities –> Search –> Virtual Machine Manager.
You may be asked to enter password, if you don’t have root access.
Once it is opened, right-click on localhost(QEMU) and Click on New. Virtual Machine Manager will start a new wizard for creating virtual machine, you will find no difficulty in using this graphical mode.
Step 1: You would require to name your virtual machine, in the same window, you would be asked to choose how would you like to install the operating system. Here i chose to install it from ISO image or CD-ROM.
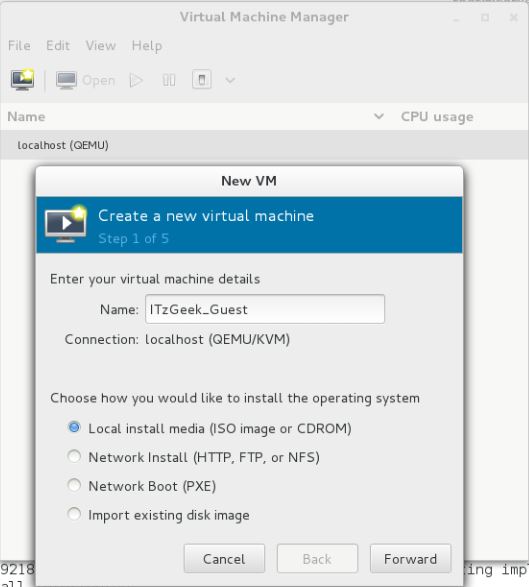 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Create VM
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Create VM
Step 2: Enter the location of ISO image or use physical CD-ROM, do not forget to choose operating system type and version.
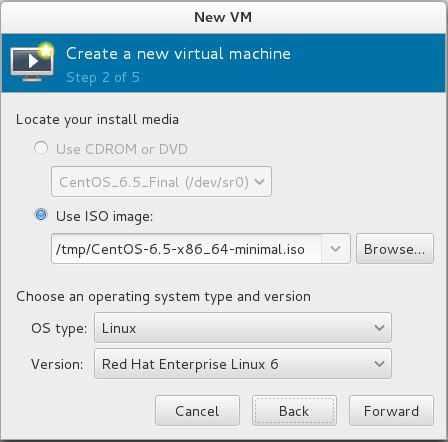 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Installation Media
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Installation Media
Step 3: Configure CPU and memory for virtual machine.
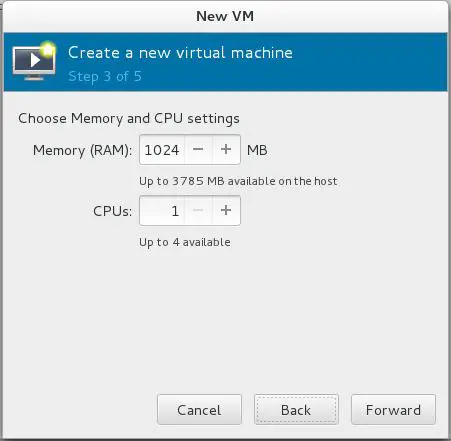 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Memory and CPU
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Memory and CPU
Step 4: You have to mention the amount of storage that you want to assign to a virtual machine, Un check on “Allocate entire disk now”, this will prevent from allocating full disk at the VM creation. Disk size will be allocated dynamically depending on the virtual machine usage.
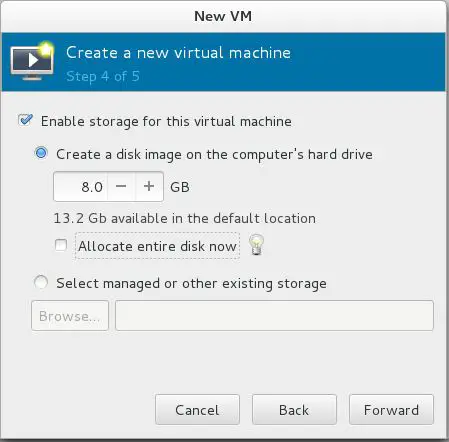 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Allocating Storage
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Allocating Storage
Step 5: Summary of all the settings, click on advanced settings to select bridged networking in order to allow virtual machine to communicate outside network. Click on Finish.
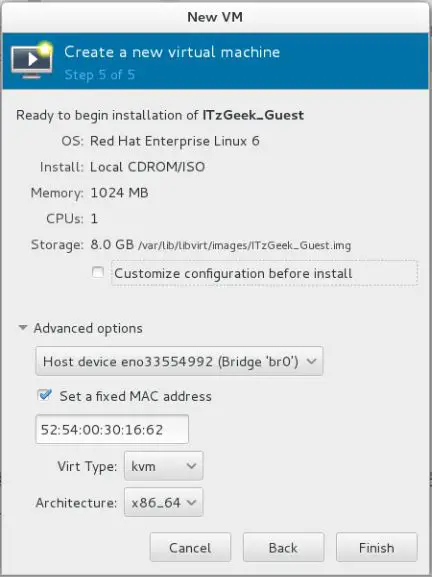 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Summary
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Summary
Step 6: KVM will start to create a virtual machine depends on our input, once vm is created. Virt manager will start a console for OS installation. The following screen shows the installation screen of CentOS 6.
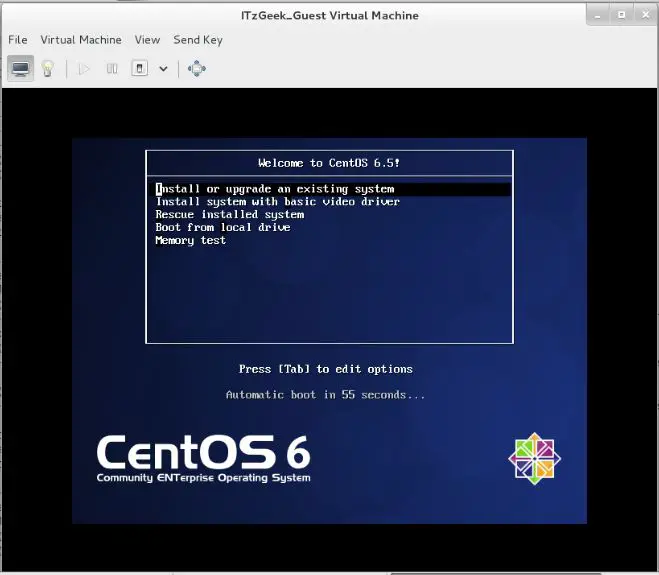 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – VM Console
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – VM Console
Managing Virtual Machine:
With the Virtual Machine Manger, you can perform vm’s life cylcle actions such as start, power off, reset, clone and migration by right clicking on selected virtual machine.
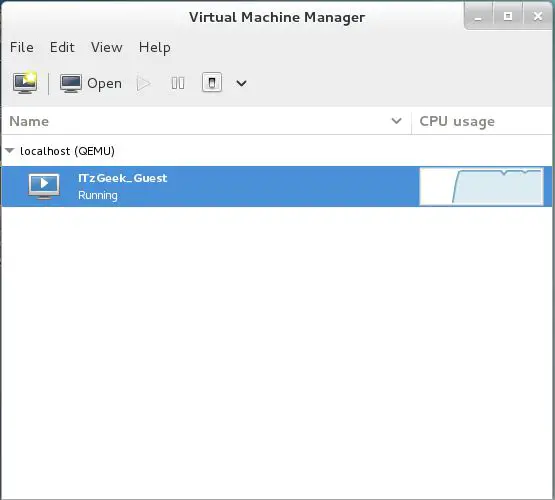 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager
Managing virtual machine using virt manager is very simple, you can just click on “bulp” icon in the vm console. Here you can add, modify and remove devices.
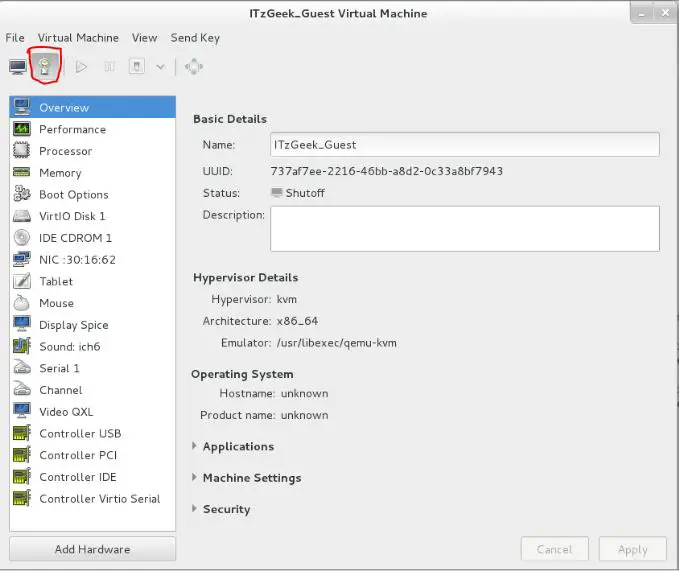 Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Managing VM
Fedora 22 – Virt Manager – Managing VM
That’s All.