题目
去年的Lucas非常喜欢数论题,但是一年以后的Lucas却不那么喜欢了。
在整理以前的试题时,发现了这样一道题目“求Sigma(f(i)),其中1<=i<=N”,其中 表示i的约数个数。他现在长大了,题目也变难了。
求如下表达式的值:
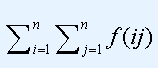
其中 表示ij的约数个数。
他发现答案有点大,只需要输出模1000000007的值。
输入格式
第一行一个整数n。
输出格式
一行一个整数ans,表示答案模1000000007的值。
输入样例
2
输出样例
8
提示
对于100%的数据n <= 10^9。
题解
这题推导和SDOI2015约数个数和那道题是一样的
只不过计算的方式有差别
这道题没有多组询问,而且n特别大【不能O(n)实现】,要用杜教筛
最后推出式子:
[ans=sumlimits_{d=1}^{n} mu(d) (sumlimits_{i=1}^{lfloor frac{n}{d}
floor} lfloor frac{lfloor frac{n}{d}
floor}{i}
floor)^2
]
如果我们记
[sum(n) = sumlimits_{i=1}^{n}lfloor frac{n}{i}
floor
]
那么式子可以写成:
[ans=sumlimits_{d=1}^{n} mu(d) sum(lfloor frac{n}{d}
floor)^2
]
显然可以分块计算
因为(n<=10^9),所以对于(mu)的前缀和我们采用杜教筛,时间复杂度(O(n^{frac{2}{3}}logn))
对于(sum(n)),我们内部也分块计算,时间复杂度(O(int_{0}^{sqrt{n}} x^{frac{1}{2}} dx) = O(frac{2}{3} n^{frac{3}{4}}) = O(n^{frac{3}{4}}))
所以总的复杂度(O(n^{frac{2}{3}}logn + n^{frac{3}{4}}))
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define LL long long int
#define Redge(u) for (int k = h[u],to; k; k = ed[k].nxt)
#define REP(i,n) for (int i = 1; i <= (n); i++)
#define BUG(s,n) for (int i = 1; i <= (n); i++) cout<<s[i]<<' '; puts("");
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000005,maxm = 100005,INF = 1000000000,P = 1000000007;
typedef map<LL,LL> Map;
Map _mu;
Map::iterator it;
LL p[maxn],pi,mu[maxn],N,n;
int isn[maxn];
void init(LL n){
N = (LL)pow(n,2.0 / 3.0);
mu[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++){
if (!isn[i]) p[++pi] = i,mu[i] = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= pi && i * p[j] < N; j++){
isn[i * p[j]] = true;
if (i % p[j] == 0){
mu[i * p[j]] = 0;
break;
}
mu[i * p[j]] = -mu[i];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) mu[i] = (mu[i - 1] + mu[i]) % P;
}
LL sum(LL x){
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = 1,nxt; i <= x; i = nxt + 1){
nxt = x / (x / i);
ans = (ans + (nxt - i + 1) * (x / i) % P) % P;
}
return ans;
}
LL S(LL n){
if (n < N) return mu[n];
if ((it = _mu.find(n)) != _mu.end())
return it->second;
LL ans = 1;
for (int i = 2,nxt; i <= n; i = nxt + 1){
nxt = n / (n / i);
ans = (ans - (nxt - i + 1) * S(n / i) % P) % P;
}
return _mu[n] = ans;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
init(n);
LL ans = 0;
for (int i = 1,nxt; i <= n; i = nxt + 1){
nxt = n / (n / i);
LL tmp = sum(n / i);
tmp = tmp * tmp % P;
ans = ans + (S(nxt) - S(i - 1)) % P * tmp % P;
}
ans = (ans % P + P) % P;
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}