园子里头看到了一些最基础的 keras 入门指导, 用一层网络,可以训练一个简单的线性回归模型。
自己学习了一下,按照教程走下来,结果不尽如人意,下面是具体的过程。
第一步: 生成随机数据,绘出散点图
import numpy as np from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 生产随机数据 np.random.seed(123) # 指定种子,使得每次生成的随机数保持一致 x = np.linspace(-1,1,200) # 生成一个长度为 200 的 list,数值大小在 [-1,1] 之间 np.random.shuffle(x) #随机排列传入 list y = 0.5 * x + 2 + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, (200,)) # 添加正态分布的偏差值
#测试数据 与 训练数据
x_train, y_train = x[:160], y[:160]
x_test, y_test = x[160:], y[160:0]
#绘出散点图: plt.scatter(x,y) plt.show()
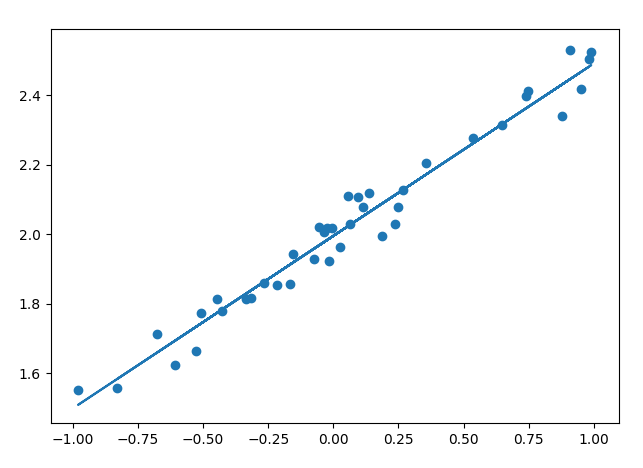
散点图如下:

二、创建网络模型
# 创建模型 model = Sequential() # 添加全连接层,输入维度 1, 输出维度 1 model.add(Dense(output_dim = 1, input_dim= 1))
三、模型编译
# 模型编译 # 损失函数:二次方的误差, 优化器:随机梯度随机梯度下降,stochastic gradient descent model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='sgd')
四、模型训练
# 训练模型,就跑一次 print('start train model:') for step in range(300): cost = model.train_on_batch(x_train, y_train) if step % 50 == 0: print('cost:', cost)
五、测试模型
#看测试数据损失又多少 print('start test:') cost = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, batch_size=40) print('the loss is:', cost) # 查看函数参数 w,b = model.layers[0].get_weights() print('weights =',w, ' biases = ', b) # 用模型预测测试值 y_pred = model.predict(x_test) # 画出测试散点图 plt.scatter(x_test, y_test) # 画出回归线 plt.plot(x_test, y_pred) plt.show()
输出结果:

此次训练所得模型:
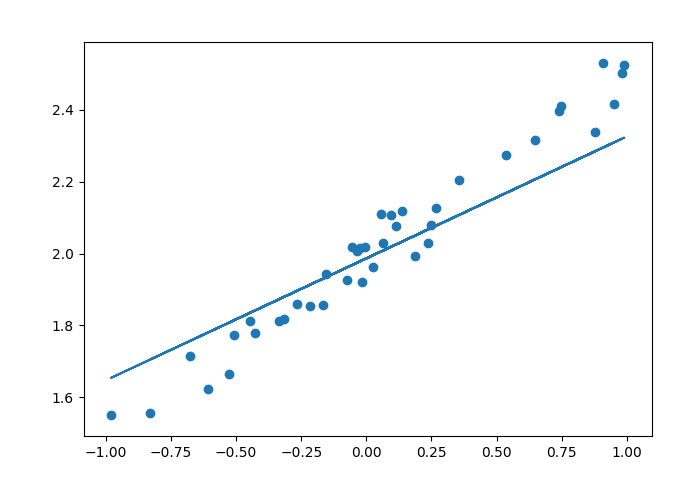
从图中可以看出,模型没有很好的满足我们的需求,进行调整,看下结果:
减小batch_size, 增加训练次数。
batch_size: 单一批训练样本数量
epochs : 将全部样本训练都跑一遍为 1 个 epoch, 10 个 epochs 就是全部样本都训练 10 次
# 调整模型训练过程 model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=5,epochs=60)
最终所得模型图为:
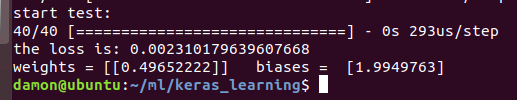
曲线为: