Java编程中的NIO,俗称new I/O,是在JDK1.4版本之后开始引入的,在JDK1.4之前,Java服务端大多使用同步阻塞式来处理网络请求,在低流量、低并发情况还能抗住,在如今互联网时代,信息量很明显差远了,在没有NIO之前,服务器端通信模块基本被C/C++占据着,它们可以利用操作系统的原生API来处理非阻塞事件,随着java的nio类库发布,经过不断发展完善,性能也逐渐与c++媲美了,加上JAVA很多优秀的开源类库,使用更广泛了,现在,来了解一下nio的原理,做一个感官上的认识。
使用NIO,必须记住如下3个核心概念,编程实现就是围绕他们的关系的:
1. 缓冲区Buffer: 在nio编程中,读写都在基于缓冲区的,区别于之前的基于流的,根据用途,可以使用字节缓冲区、字符缓冲区等
2. 通道Channel: 在Buffer里的数据通过Channel与网络交互,是全双工的,而流数单工操作的
3. 多路复用器Selector: 管理Channel,最基本的就是读写Channel,一个线程使用Selector来轮询读写Channel,通道上有事件发生时,就会进行处理,类似一个函数指针集合,在BLE开发的底层OS上也是这样处理的,增加一个模块,只要写好模块函数,然后把函数指针放到功能数组就可以了,后面就轮询这个注册了的函数,有置位就调用指针进行操作。这种模式可以实现单线程就能支持上千万并发连接。
下面新建一个工程来测试一下:
1. 新建一个TestNIO工程,目录结构设为如下:

2. 实现服务器端,代码如下:
package cn.linjk.testnio.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Created by LinJK on 19/11/2016.
*/
public class NioServer {
private static final int serverPort = 8889;
public static void main(String[] argc) {
//启动一个线程来处理Selector
HelloServer helloServer = new HelloServer(serverPort);
if (!helloServer.getInitResult()) {
System.out.println("Init Error");
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("Hello Server listening on localhost:" + serverPort);
new Thread(helloServer).start();
}
}
class HelloServer implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
private ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite;
private boolean contrustorFlag;
public HelloServer(int port) {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
contrustorFlag = true;
}
catch (Exception e) {
contrustorFlag = false;
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public boolean getInitResult() {
return contrustorFlag;
}
public void stop() {
stop = true;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
try {
selector.select(1000); //1秒轮询周期,可以按需修改
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey selectionKey = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = it.next();
it.remove();
try {
//handle event
handleIncomeEvent(selectionKey);
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (selectionKey != null) {
selectionKey.cancel();
if (selectionKey.channel() != null) {
selectionKey.channel().close();
}
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//User set stop listening, clear something
if (selector != null) {
try {
selector.close();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void handleIncomeEvent(SelectionKey key) {
if (key.isValid()) {
//连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel)key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//监听到了连接事件,原有基础上注册监听读取用户端数据事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//读到客户端数据事件
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBufferRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int readCnt = socketChannel.read(byteBufferRead);
if (readCnt > 0) {
byteBufferRead.flip();//刷新缓冲区,然后从缓冲区读取数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBufferRead.remaining()];
byteBufferRead.get(bytes);
String request = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("Server receive: " + request);
//say hello to client
byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(20);
byteBufferWrite.put("[<<-]Hello".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();//刷新数据到缓冲区
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
//避免缓冲区已满,造成写数据不全现象,注册写事件,轮询是否所有数据已写完
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
else if (readCnt < 0) {
key.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
}
else {
//
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
while (byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()){
//.....
}
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Input key unvalid");
}
}
}
3. 实现客户端,测试功能,有些异常没有写全,也没实现重连服务器机制,只把框架写了,代码如下:
package cn.linjk.testnio.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Created by LinJK on 19/11/2016.
*/
public class NioClient {
private static Selector selector;
private static SocketChannel socketChannel;
private static volatile boolean stop;
public static void main(String[] argc) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//connect to server
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8889))) {
//注册监听服务器返回事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//send request to server
ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
byteBufferWrite.put("I am Jim".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
if (!byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Send Finish.");
}
}
else {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
while (!stop) {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey selectionKey = null;
while (it.hasNext()) {
selectionKey = it.next();
it.remove();
if (selectionKey.isValid()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel();
if (selectionKey.isConnectable()) {
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//send data
ByteBuffer byteBufferWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
byteBufferWrite.put("I am Jim".getBytes());
byteBufferWrite.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBufferWrite);
if (!byteBufferWrite.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println("Send Finish.");
}
}
}
//收到服务器返回数据事件
if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer byteBufferRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
int readCnt = socketChannel.read(byteBufferRead);
if (readCnt > 0) {
byteBufferRead.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBufferRead.remaining()];
byteBufferRead.get(bytes);
System.out.println("Receive from server: " + new String(bytes, "UTF-8"));
stop = true;
}
else if (readCnt < 0){
selectionKey.channel();
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
}
if (selector != null) {
selector.close();
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
//资源清理....
System.exit(1);
}
}
}).start();
}
}
4. 代码分析:
对比服务端和客户端的代码逻辑,有如下两点相似:
a. 程序启动后创建一个线程来管理Selctor
b. 都配置为非阻塞操作,然后注册SelctionKey到SocketChanell,然后在线程的run()函数里轮询哪个事件发生了再进行操作
流程都相似,稍微有点不一样,看代码并运行一下就明白了。
5. 运行结果:
先运行Server端,然后运行Client端,二者输出分别如下:
Server:

Client:
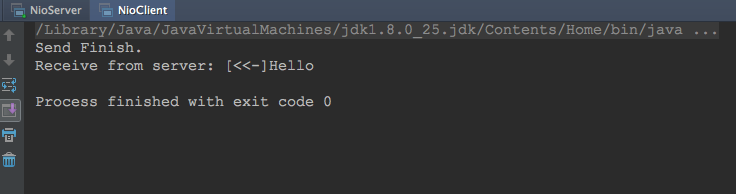
6. 总结:
NIO和IO直接最大区别就是,NIO是面向缓冲区的,IO是面向流的,面向缓冲区数据处理比较灵活,数据处理速度与吞吐量更大,同时保证数据完整性比较重要,前面提到缓冲区满时,需要检测"半包"也是这个意思,使用NIO的非阻塞避免了因网络情况阻塞造成的高并发环境下时延问题,在高并发通讯情况下,可以使用它来处理通信还是很好的。