.animate()
.stop()
.finish()
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
.animate()
参数:(target, duration, easing, callback)
target: 到达的目标点, 例如{ width : '+=100', height: '+=100'} 选择器选中的元素的宽和高,加上100。值 可以写 数字 100, 可以写 字符串的 '100px' 也可以写计算 '+=100'
duration: 运动过程的时间, 如果你需要 这个动画 过程 1秒, 那么就填 1000,(毫秒) 这个动画会 1秒内 执行完。 3000,就是3秒完成这个动画。
easing: 过度动画的效果, 例如jquery 自身提供的 两个, linear 匀速运动,swing 先慢后快,再快,再慢, 不写默认是 swing , jquery支持的动画插件( jQuery Easing Plugin) 记得在jquery 引入后 再引入 此插件
链接: https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery-easing/1.4.1/jquery.easing.min.js

callback: 回调函数,动画结束后执行的函数。
下面来看实际使用:
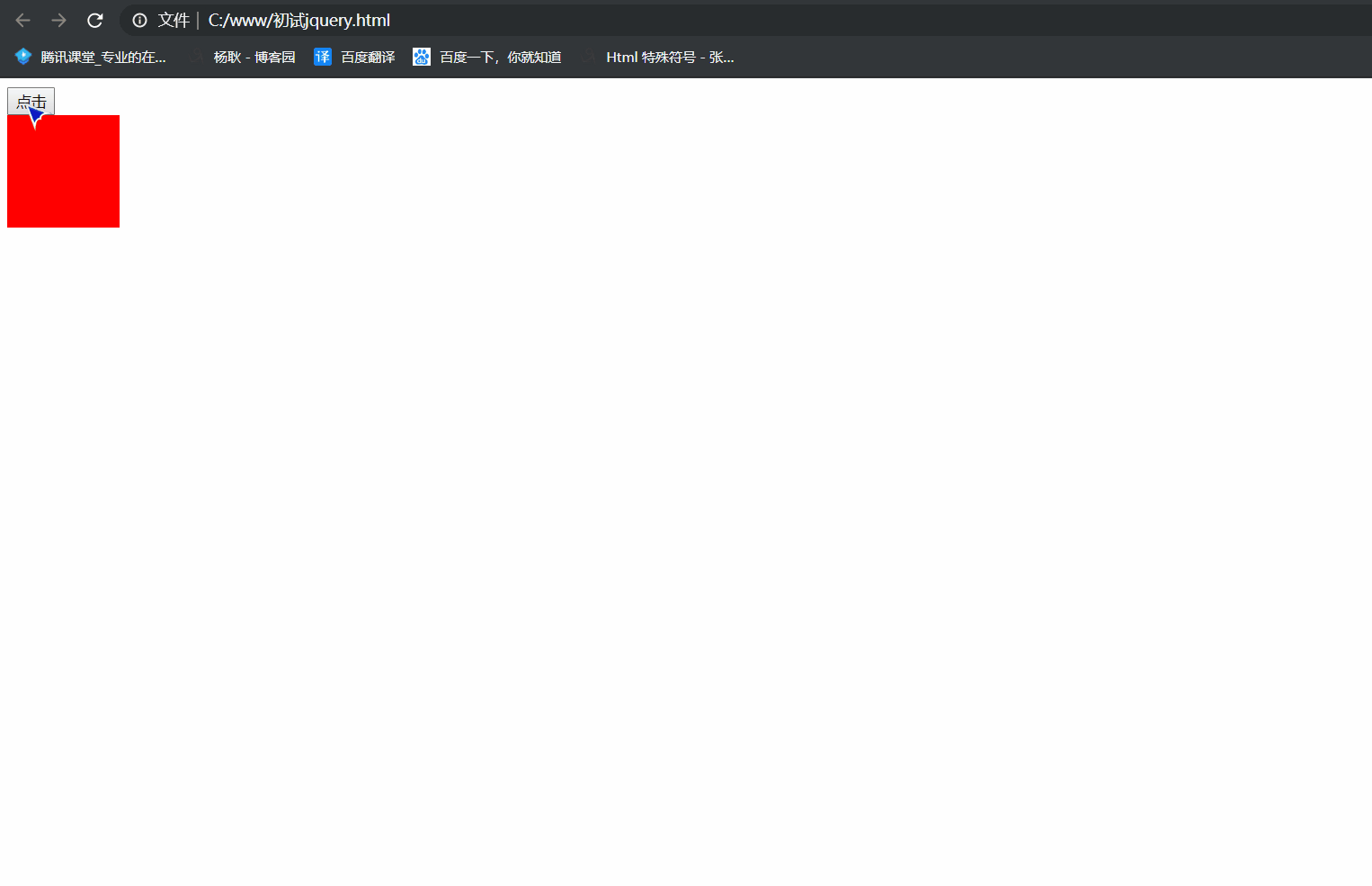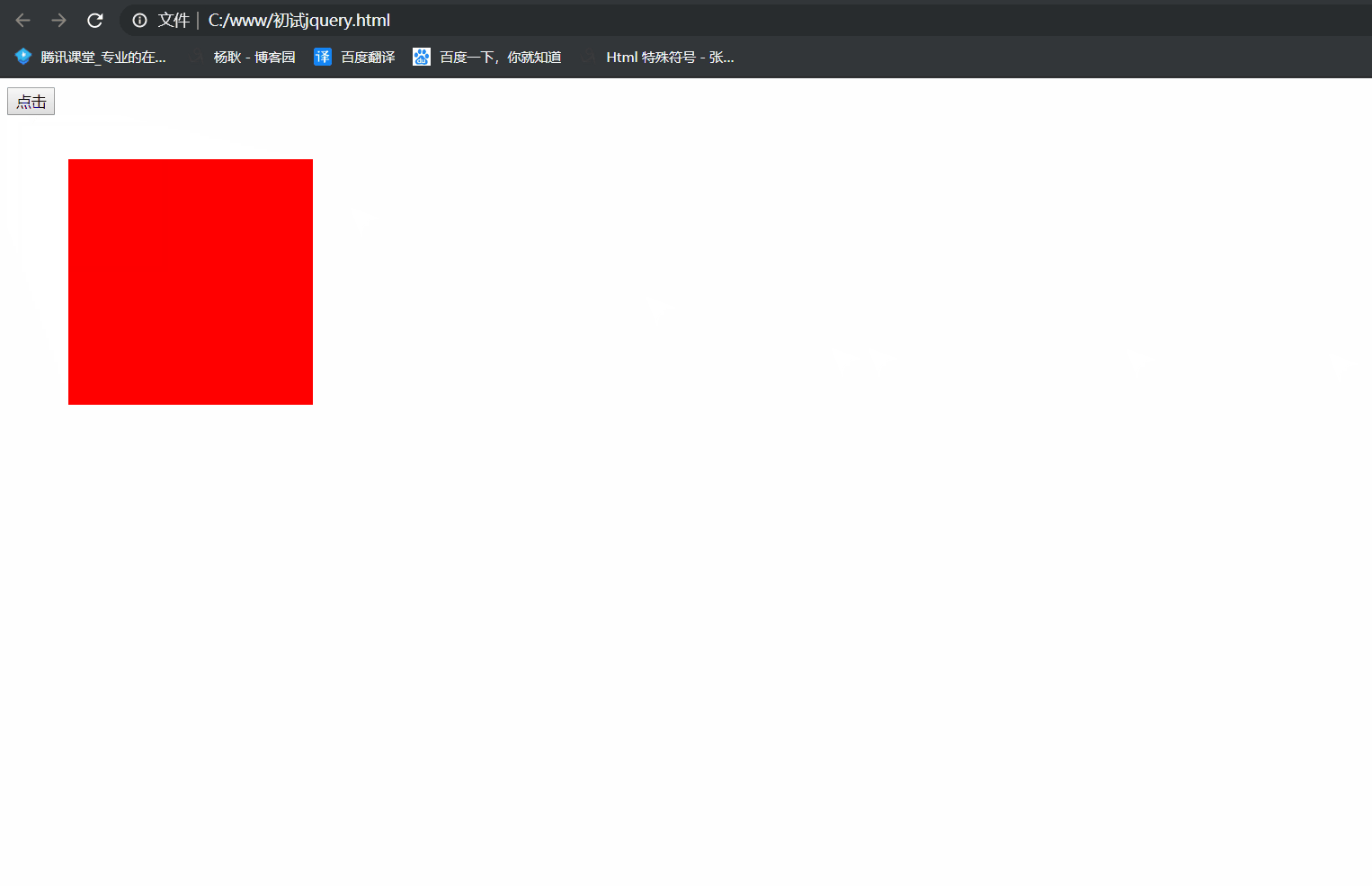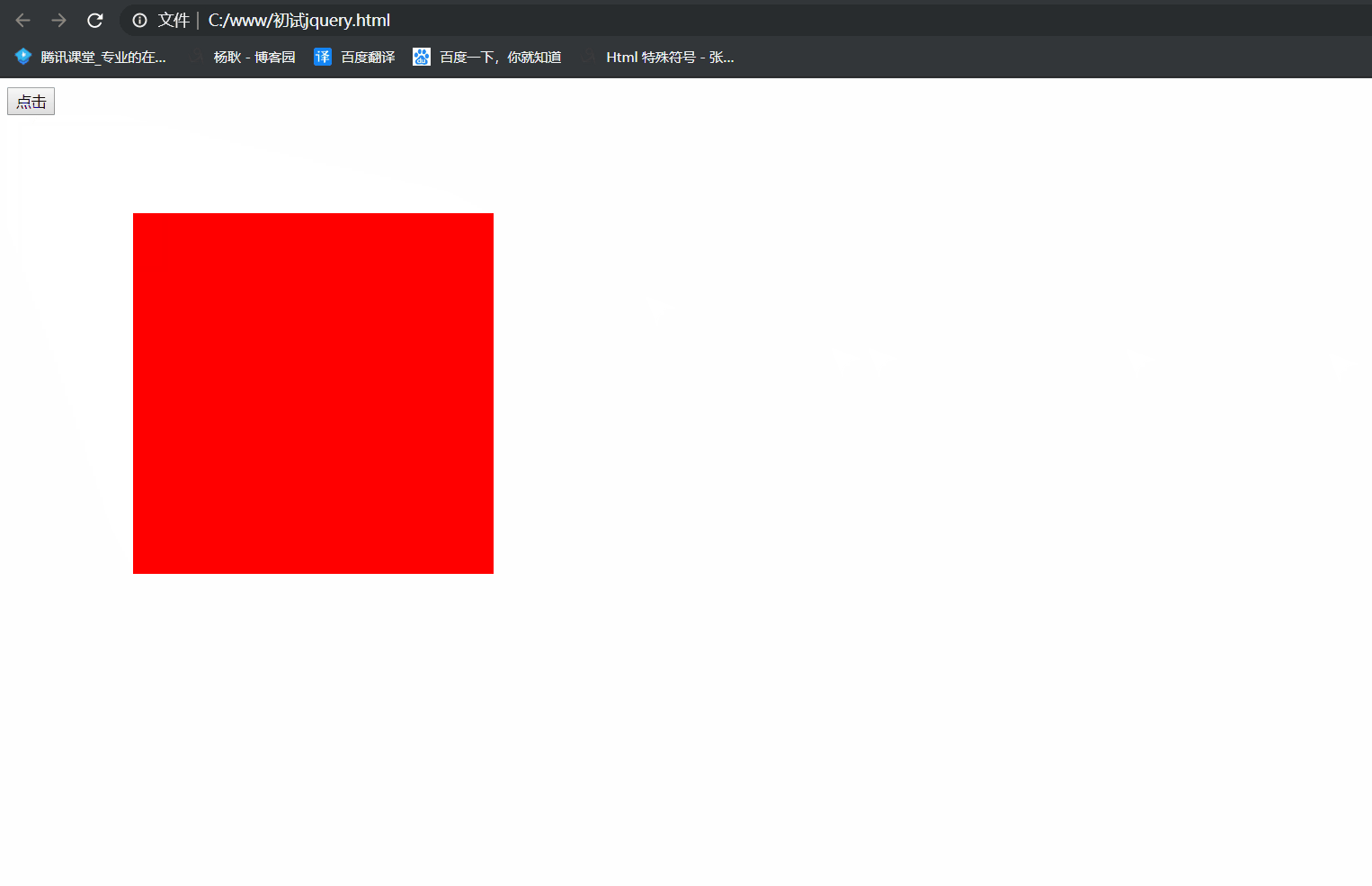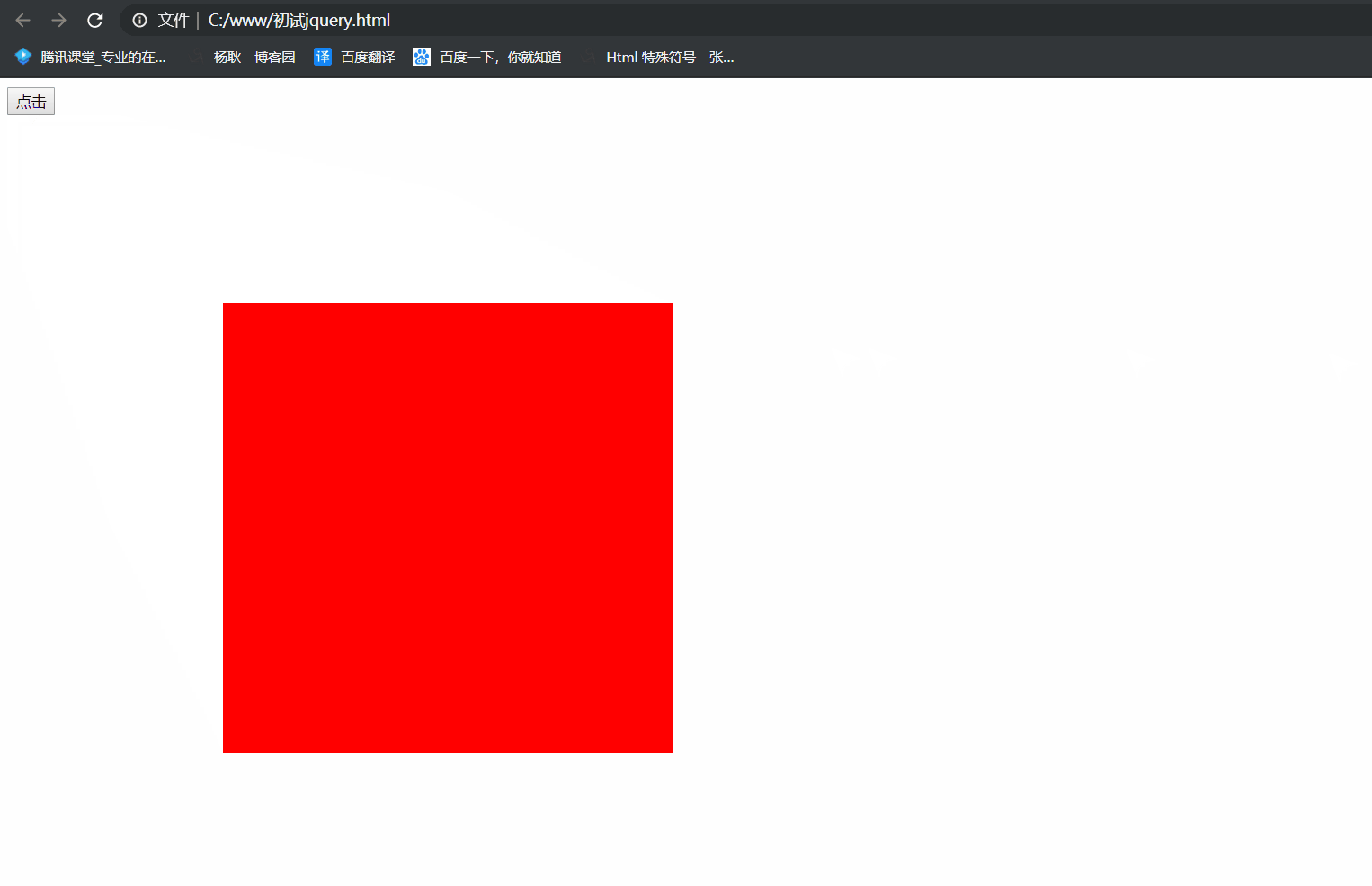
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> 7 <title>Document</title> 8 </head> 9 <body> 10 <button>点击</button> 11 <div class="box" style="position: absolute; 100px; height: 100px; background: red"></div> 12 13 <script src="./jquery/jquery.js"></script> 14 <script> 15 $('button').click(function(){ 16 $('.box').animate({ 300, height: 300, left: 100, top: 100},2000, function(){ 17 $('.box').animate({ '+=100', height: '+=100', left: '+=100', top: '+=100'},2000) 18 }) 19 }) 20 //先让他运动到 width 300px, height 300px left 100px top 100px ,运动完后, 执行回调函数, 再 21 // 让他运动, '+=100', height: '+=100', left: '+=100', top: '+=100' 所以你能明显的在中间看到有停顿 22 </script> 23 </body> 24 </html>
这样写,你会发现,如果回调函数多了, 看起来不直观, 所以animate() 有内置队列, 允许你 以下的 写法。
<script> $('button').click(function(){ $('.box').animate({ 300, height: 300, left: 100, top: 100},2000) .animate({ '+=100', height: '+=300', left: '+=100', top: '+=100'},2000) }) </script>
不用写回调函数, 直接在后面链式调用即可
什么是内置队列呢, 第一个进去, 会第一个出, 所以,往后添加,会变成一个队列。

.stop()
停止当前动画。
参数:null true true,true
不填参数: 只有一段动画, 直接停止。 但是如果你当前有两段动画,就是你有一段动画,而且回调函数,又有一段动画。 执行了.stop() 会停止当前段的动画,并且开始 第二段的动画。
.stop(true): 停止动画, 无论你后面有多少段动画, 执行.stop(true), 就停在当前位置了。
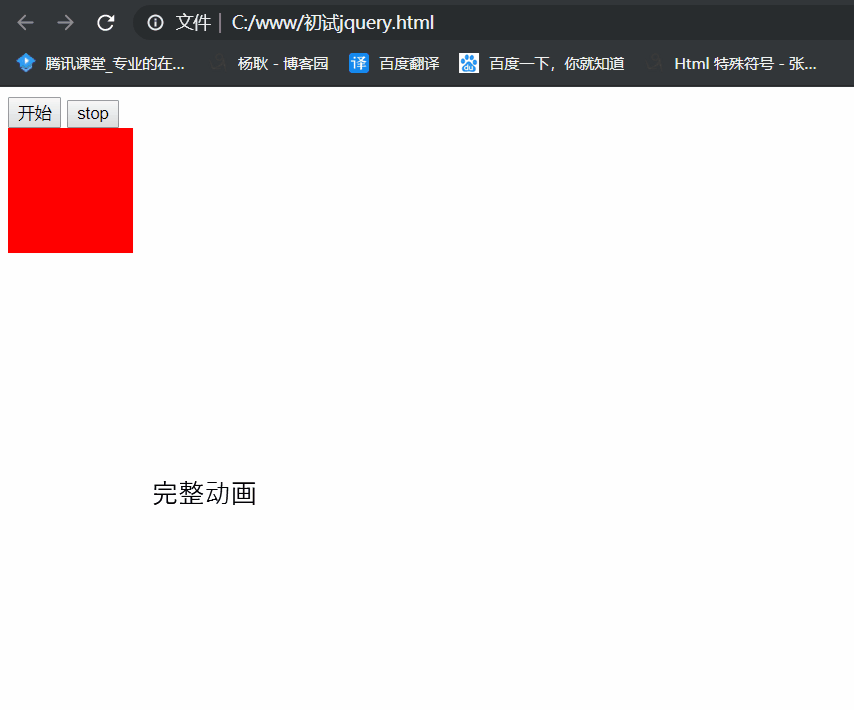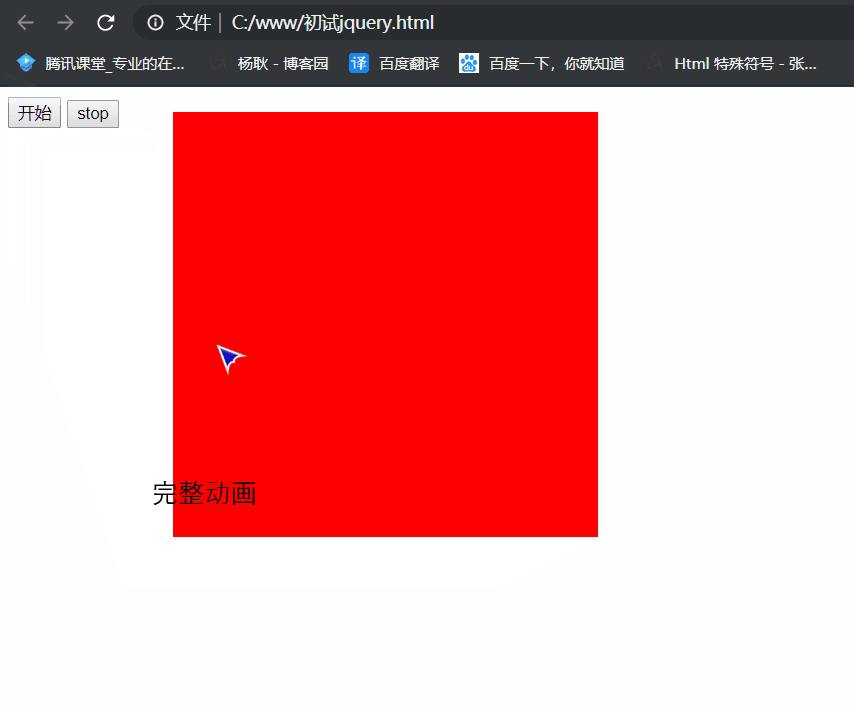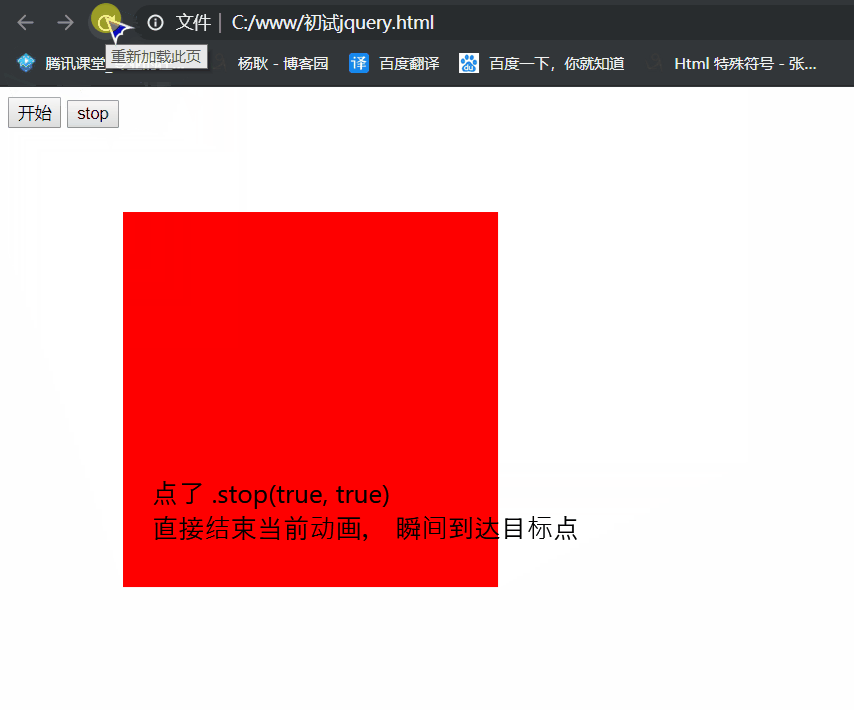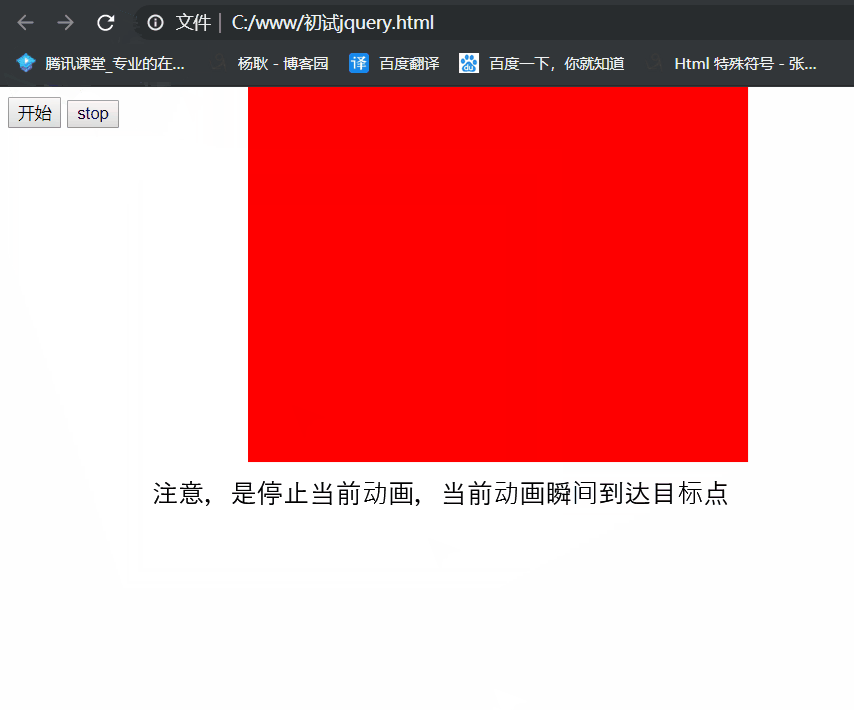
.stop(true,true): 停止当前动画, 并且,瞬间到达目标点。
.stop() 不带参数

.stop(true)
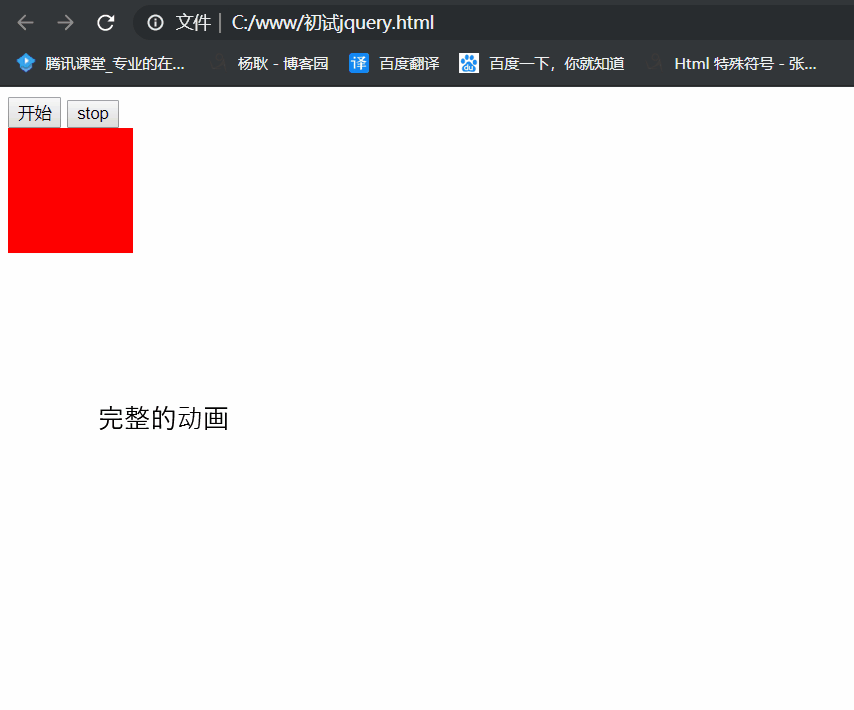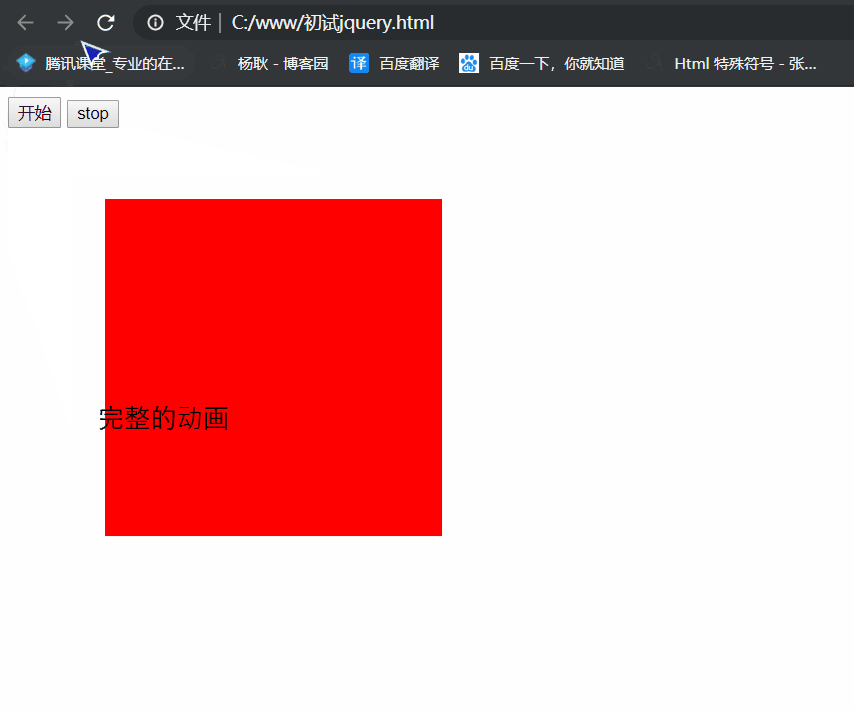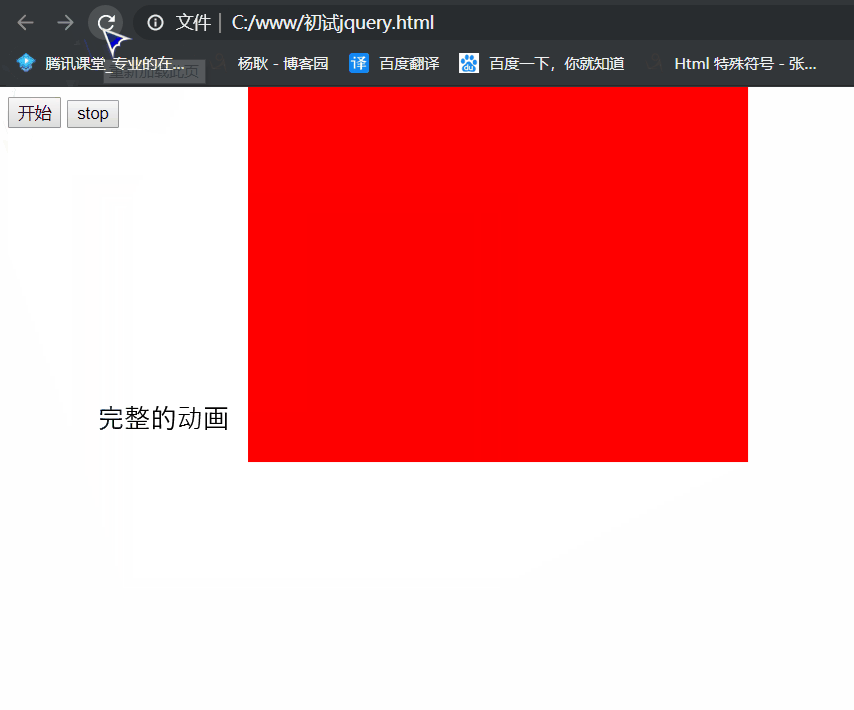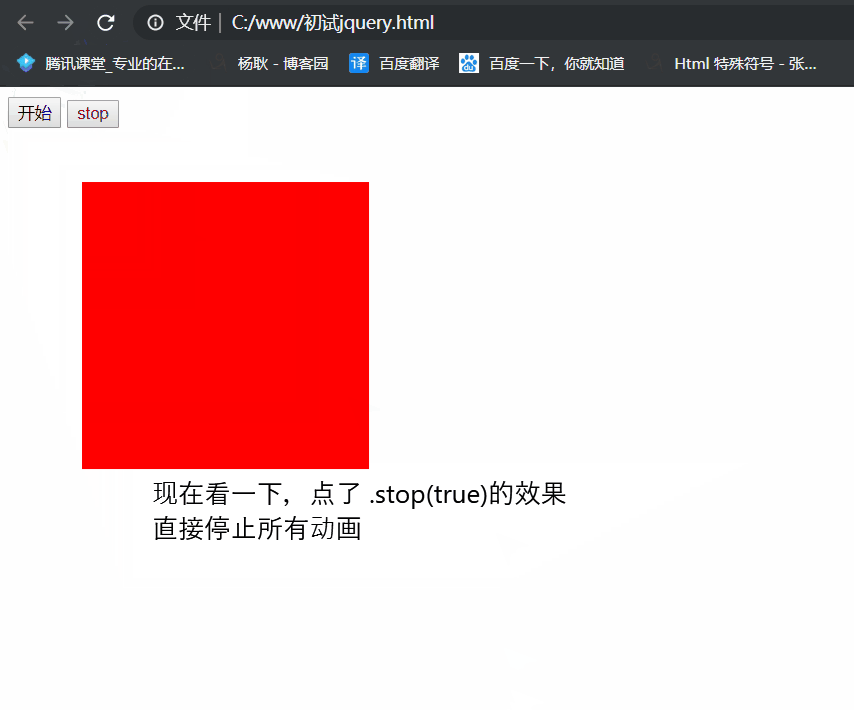
.stop(true, true)
.finish()
跳过动画,直接到达目标点
没有参数可以传
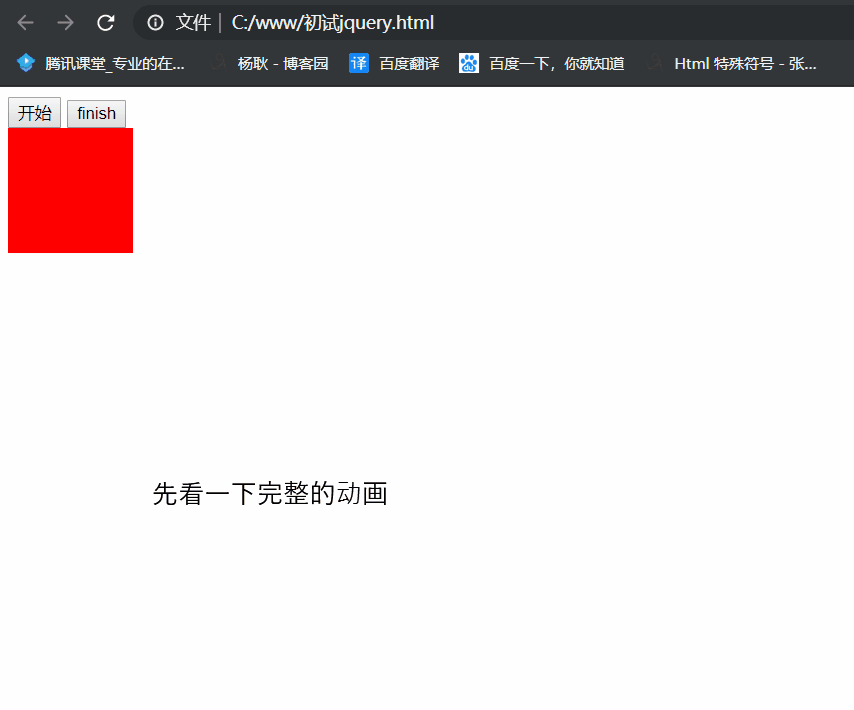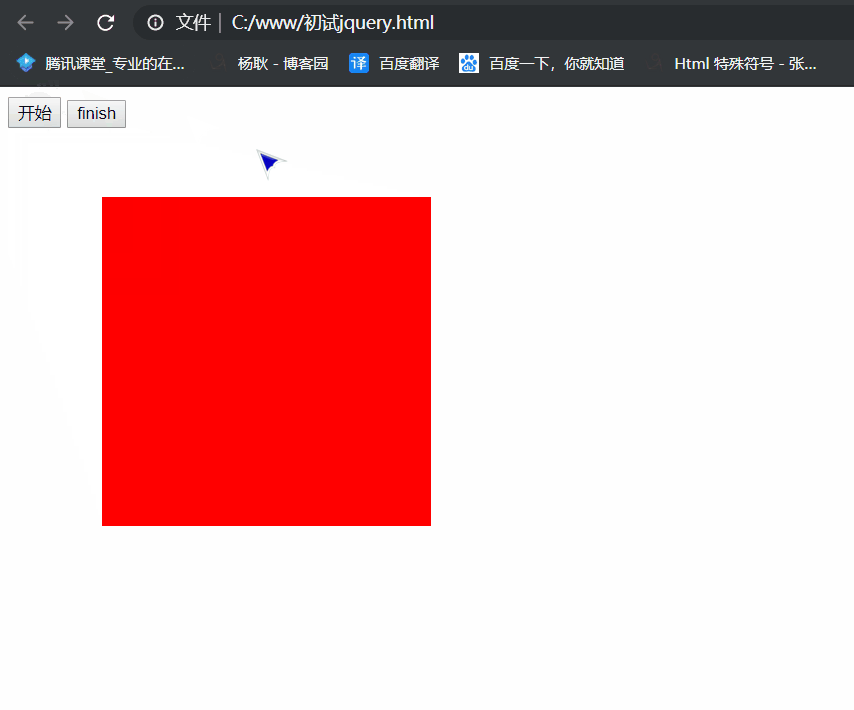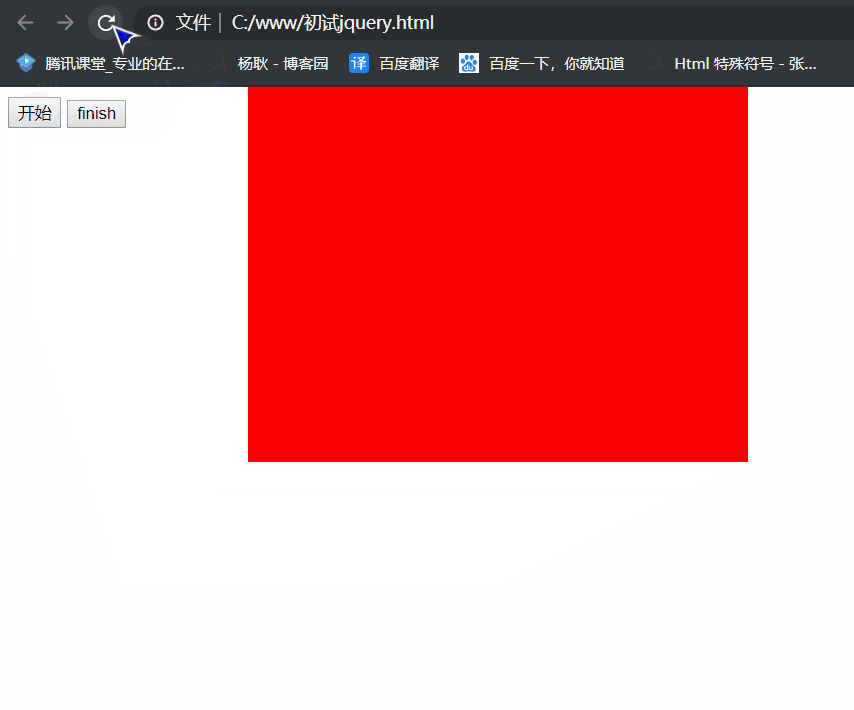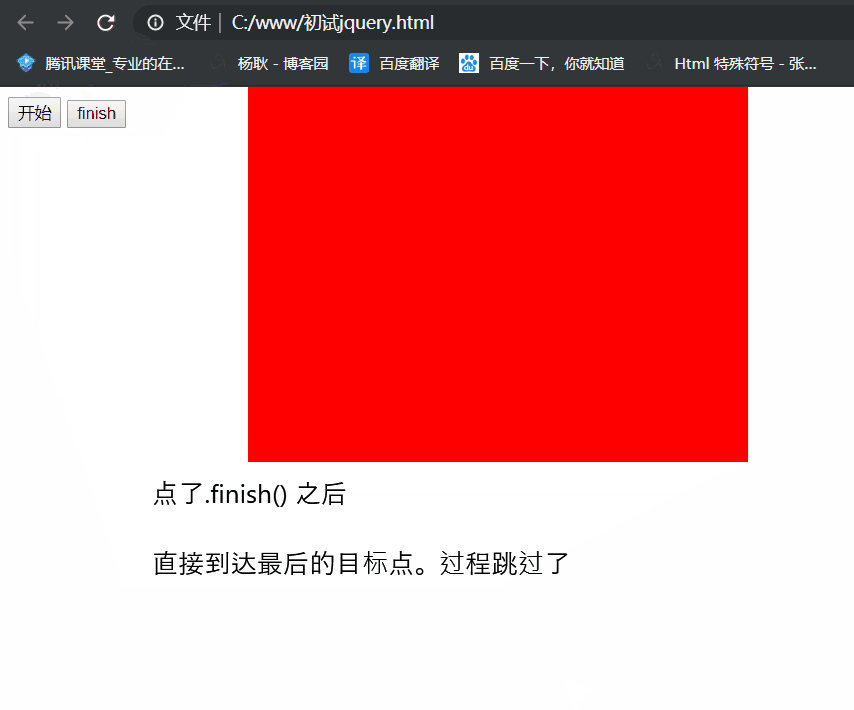
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> 7 <title>Document</title> 8 </head> 9 <body> 10 <button class="init">开始</button> 11 <button class="finish">finish</button> 12 <div class="box" style="position: absolute; 100px; height: 100px; background: red"></div> 13 14 <script src="./jquery/jquery.js"></script> 15 <script> 16 $('.init').click(function(){ 17 $('.box') 18 .animate({ 300, height: 300, left: 100, top: 100},2000) 19 .animate({ '+=100', height: '+=100', left: '+=100', top: '-100'},2000) 20 }) 21 22 $('.finish').on('click', function(){ 23 $('.box').finish(); 24 }) 25 26 </script> 27 </body> 28 </html>
.animate() 原理 39行
1 jQuery.prototype.myDelay = function(duration){ 2 this.myqueue('fx',function(next){ 3 setTimeout(function(){ 4 next(); 5 },2000) 6 }) 7 return this; 8 } 9 10 jQuery.prototype.myqueue = function(){ 11 var myqueueName = arguments[0] || 'fx'; 12 var myqueueFun = arguments[1] || null; 13 14 if(arguments.length == 1){ 15 return this[0][myqueueName]; 16 } 17 18 this[0][myqueueName] == undefined ? this[0][myqueueName] = [myqueueFun] : this[0][myqueueName].push(myqueueFun); 19 20 return this; 21 } 22 23 jQuery.prototype.mydequeue = function(type){ 24 var self = this; 25 var mydequeueName = type || 'fx'; 26 var myqueueArr = this.myqueue(mydequeueName); 27 var currFun = myqueueArr.shift(); 28 if(currFun == undefined){ 29 return; 30 } 31 var next = function(){ 32 self.mydequeue(mydequeueName); 33 } 34 currFun(next); 35 36 return this; 37 } 38 39 jQuery.prototype.myAnimate = function(obj, callback){ 40 var len = this.length; 41 var self = this; 42 43 var baseFunc = function(next){ 44 var times = 0; 45 for(var i = 0; i < len; i ++){ 46 startMove(self[i], obj, function(){ 47 times ++; 48 if(times == len){ 49 callback && callback(); 50 next(); 51 } 52 }); 53 } 54 } 55 56 this.myqueue('fx', baseFunc); 57 if(this.myqueue('fx').length == 1){ 58 this.mydequeue('fx'); 59 } 60 61 62 function startMove(dom, attrObj, callback) { 63 clearInterval(dom.timer); 64 dom.timer = setInterval(function () { 65 var speed = null, iCur = null; 66 var bStop = true; 67 68 for (var attr in attrObj) { 69 if (attr == "opacity") { 70 iCur = parseFloat(getStyle(dom, attr)) * 100; 71 } else { 72 iCur = parseInt(getStyle(dom, attr)); 73 } 74 speed = (attrObj[attr] - iCur) / 9; 75 speed = speed > 0 ? Math.ceil(speed) : Math.floor(speed); 76 77 if (attr == "opacity") { 78 dom.style.opacity = (speed + iCur) / 100; 79 } else { 80 dom.style[attr] = speed + iCur + 'px'; 81 } 82 83 if (attrObj[attr] !== iCur) { 84 bStop = false; 85 } 86 } 87 if (bStop) { 88 clearInterval(dom.timer); 89 callback(); 90 } 91 }, 20) 92 } 93 94 function getStyle(elem, prop){ 95 if(window.getComputedStyle){ 96 return window.getComputedStyle(elem, null)[prop]; 97 }else{ 98 return elem.currentStyle[prop]; 99 } 100 } 101 102 return this; 103 }