HashMap是线程不安全的
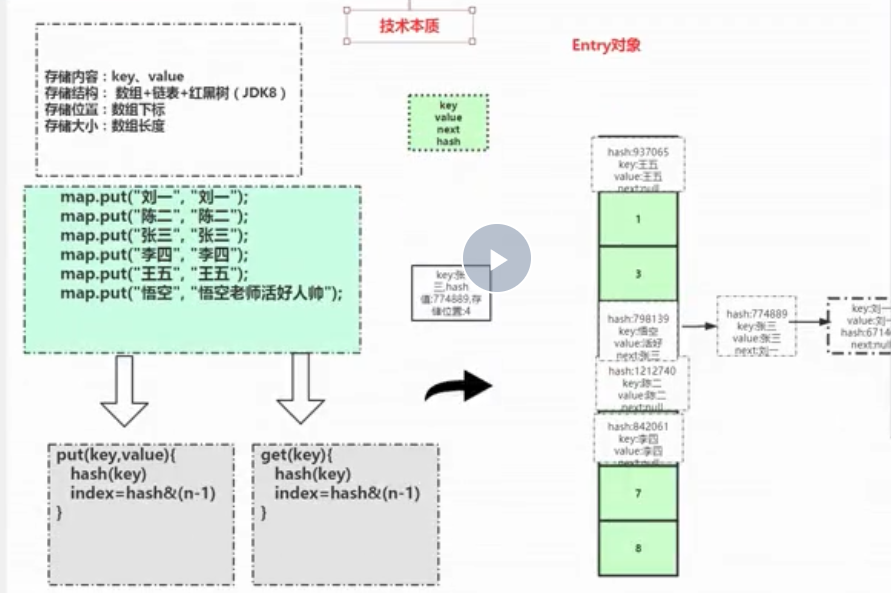
HashMap中存储的内容: key ,value
HashMap中存储结构:数组+链表+红黑树(jdk8)
HashMap中存储位置:数组下标
HashMap中存储大小:数组长度
数组的定义
Integer [] integer=new Integer[10];
对于数组,指定下标的时,时间复杂度是O(1),但是,对于插入和删除,不指定下标时,时间复杂度是O(n)
链表:
public class Node{
public Node next;
public Object data;
}
对于链表,插入和删除的时间复杂度是O(1),查找的时间复杂度是O(n);
HashMap中存放的Entry 对象
put:如果存储的index值一样,会采用链表的存储结构,链表的next的值是上一次放入该索引的值-----但是,若果,该索引上的值太多,会导致链表很长,所以使用红黑树(平衡二叉树)
get:如果一个位置上存放了多个value值,会比较hash值
手写HashMap实现:
自定义map
public interface Map<K,V> {
public V put(K k,V v);
public V get(K k);
public int size();
public interface Entry<K,V>{
public K getKey();
public V getValue();
}
}
自定义hashMap
public class hashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V>{
public Entry<K,V> [] table=null;
public static int defalutLength=16;
public int size=0;
public hashMap(){
table=new Entry[defalutLength];
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) {
//hash
int index=hash(k);
Entry entry=table[index];
if(null==entry){ //在数组的基础上存储
table[index]=new Entry<K,V>(k,v,null,index);
size++;
}else{ //如果在该数组的位置上有个值,就采用链表存储
table[index]=new Entry<K,V>(k,v,entry,index);
}
//数组的长度 index值,下标的位置
//通过这个位置找到我们的table对应的entry对象
return table[index].getValue();
}
private int hash(K k){
int index=k.hashCode()%(defalutLength-1);
return Math.abs(index);
}
@Override
public V get(K k) {
if(size==0){
return null;
}
int index=hash(k);
Entry<K,V> entry=getEntry(k,index);
return entry==null?null:entry.getValue();
}
private Entry<K,V> getEntry(K k,int index){
for(Entry e=table[index];e!=null;e=e.next){
//在获取值的时候,如果在index位置存在多个,则需要比较hash值
if(e.hash==index&&(k==e.getKey()||k.equals(e.getKey()))){
return e;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public int size() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return size;
}
class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K, V>{
private K k;
private V v;
private Entry<K,V> next;
private int hash;
public Entry(K k,V v,Entry<K,V> next,int hash){
this.k=k;
this.v=v;
this.next=next;
this.hash=hash;
}
@Override
public K getKey() {
return k;
}
@Override
public V getValue() {
return v;
}
}
}