目的:
1.Java注解简介
2.Java元注解(重点)
3.自定义注解
案例一(获取类与方法上的注解值)
案例二(获取类属性上的注解属性值)
案例三(获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值)
4.Aop自定义注解的应用(重点)
Java注解简介
1. Java注解(Annotation)
Java注解是附加在代码中的一些元信息,用于一些工具在编译、
运行时进行解析和使用,起到说明、配置的功能。
注解相关类都包含在java.lang.annotation包中。
2. Java注解分类
2.1 JDK基本注解
2.2 JDK元注解
2.3 自定义注解
3. JDK基本注解
3.1 @Override
重写
3.2 @Deprecated
已过时
3.3 @SuppressWarnings(value = "unchecked")
压制编辑器警告
Java元注解
作用:元注解用于修饰其他的注解
- @Retention:定义注解的保留策略
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) //注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) //默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得,
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
@Target:指定被修饰的Annotation可以放置的位置(被修饰的目标)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) //接口、类
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) //属性
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) //方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) //构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE) //局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) //注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) //包
注:可以指定多个位置,例如:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}),也就是此注解可以在方法和类上面
@Inherited:指定被修饰的Annotation将具有继承性
@Documented:指定被修饰的该Annotation可以被javadoc工具提取成文档.
案例一(获取类与方法上的注解值):
TranscationModel
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; /** * enum枚举 */ public enum TranscationModel { Read, ReadWrite, Write }
MyAnnotation1
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * MyAnnotation1注解可以用在类、接口、属性、方法上 * 注解运行期也保留 * 不可继承 */ @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyAnnotation1 { String name(); }
MyAnnotation2
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * MyAnnotation2注解可以用在方法上 * 注解运行期也保留 * 不可继承 */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface MyAnnotation2 { TranscationModel model() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite; }
MyAnnotation3
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * MyAnnotation3注解可以用在方法上 * 注解运行期也保留 * 可继承 */ @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Inherited @Documented public @interface MyAnnotation3 { TranscationModel[] models() default TranscationModel.ReadWrite; }
Dome1
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; /** * 获取类与方法上的注解值 */ @MyAnnotation1(name = "abc") public class Demo1 { @MyAnnotation1(name = "xyz") private Integer age; @MyAnnotation2(model = TranscationModel.Read) public void list() { System.out.println("list"); } @MyAnnotation3(models = {TranscationModel.Read, TranscationModel.Write}) public void edit() { System.out.println("edit"); } }
Demo1Test
package com.hmc.annotation.P1; import org.junit.Test; public class Demo1Test { @Test public void list() throws Exception { // 获取类上的注解 MyAnnotation1 annotation1 = Demo1.class.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation1.class); System.out.println(annotation1.name());//abc // 获取方法上的注解 MyAnnotation2 myAnnotation2 = Demo1.class.getMethod("list").getAnnotation(MyAnnotation2.class); System.out.println(myAnnotation2.model());//Read } @Test public void edit() throws Exception { MyAnnotation3 myAnnotation3 = Demo1.class.getMethod("edit").getAnnotation(MyAnnotation3.class); for (TranscationModel model : myAnnotation3.models()) { System.out.println(model);//Read,Write } } }

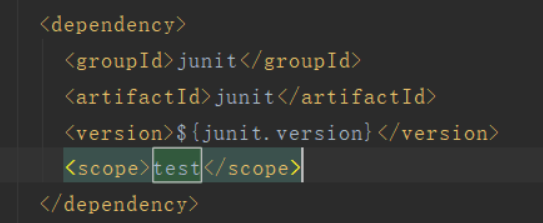
注意:
jar包的运用中最好不要出现test,把《scope》《/scope》删除即可
案例二(获取类属性上的注解属性值)
TestAnnotation
复制代码 package com.hmc.annotation.P2; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; //@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target(ElementType.FIELD) public @interface TestAnnotation { String value() default "默认value值"; String what() default "这里是默认的what属性对应的值"; }
Dome2
package com.hmc.annotation.P2; /** * 获取类属性上的注解属性值 */ public class Demo2 { @TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值_msg1", what = "这就是what对应的值_msg1") private static String msg1; @TestAnnotation("这就是value对应的值1") private static String msg2; @TestAnnotation(value = "这就是value对应的值2") private static String msg3; @TestAnnotation(what = "这就是what对应的值") private static String msg4; }
Demo2Test
package com.hmc.annotation.P2; import org.junit.Test; public class Demo2Test { @Test public void test1() throws Exception { TestAnnotation msg1 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg1").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); System.out.println(msg1.value()); System.out.println(msg1.what()); } @Test public void test2() throws Exception{ TestAnnotation msg2 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg2").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); System.out.println(msg2.value()); System.out.println(msg2.what()); } @Test public void test3() throws Exception{ TestAnnotation msg3 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg3").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); System.out.println(msg3.value()); System.out.println(msg3.what()); } @Test public void test4() throws Exception{ TestAnnotation msg4 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("msg4").getAnnotation(TestAnnotation.class); System.out.println(msg4.value()); System.out.println(msg4.what()); } }

案例三(获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值):
IsNotNull
package com.hmc.annotation.P3; import java.lang.annotation.*; /** * 非空注解:使用在方法的参数上,false表示此参数可以为空,true不能为空 */ @Documented @Target({ElementType.PARAMETER}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface IsNotNull { boolean value() default false; }
Demo3
package com.hmc.annotation.P3; /** * 获取参数修饰注解对应的属性值 */ public class Demo3 { public void hello1(@IsNotNull(true) String name) { System.out.println("hello:" + name); } public void hello2(@IsNotNull String name) { System.out.println("hello:" + name); } }
Demo3Test
package com.hmc.annotation.P3; import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Parameter; public class Demo3Test { @Test public void hello1() throws Exception { Demo3 demo3 = new Demo3(); for (Parameter parameter : demo3.getClass().getMethod("hello1", String.class).getParameters()) { IsNotNull annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(IsNotNull.class); if(annotation != null){ System.out.println(annotation.value());//true } } } @Test public void hello2() throws Exception { Demo3 demo3 = new Demo3(); for (Parameter parameter : demo3.getClass().getMethod("hello2", String.class).getParameters()) { IsNotNull annotation = parameter.getAnnotation(IsNotNull.class); if(annotation != null){ System.out.println(annotation.value());//false } } } }
Aop自定义注解的应用
MyLog
package com.hmc.annotation.Aop; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface MyLog { String desc(); }
MyLogAspect
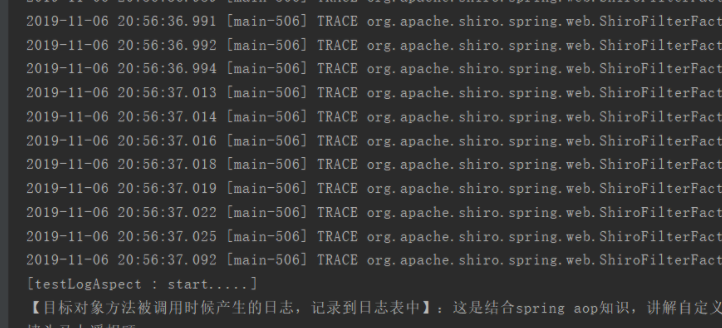
package com.hmc.annotation.Aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Aspect public class MyLogAspect { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyLogAspect.class); /** * 只要用到了com.huangting.annotation.Aop.MyLog这个注解的,就是目标类 */ @Pointcut("@annotation(com.hmc.annotation.Aop.MyLog)") private void MyValid() { } @Before("MyValid()") public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); MyLog myLog = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(MyLog.class); System.out.println("[" + signature.getName() + " : start.....]"); System.out.println("【目标对象方法被调用时候产生的日志,记录到日志表中】:"+myLog.desc()); } }
BaseTestCase
package com.hmc.annotation.Aop; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) public class BaseTestCase { }
LogController
package com.hmc.annotation.Aop; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class LogController { @MyLog(desc = "这是结合spring aop知识,讲解自定义注解应用的一个案例") public void testLogAspect(){ System.out.println("墙头马上遥相顾"); } }
LogControllerTest
package com.hmc.annotation.Aop; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; public class LogControllerTest extends BaseTestCase { @Autowired private LogController logController; @Test public void testLogAspect(){ logController.testLogAspect(); } }