学习内容:
1.File类:
(1)三种构造方式:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d:\test\test.txt"); File parent = new File("d:\test"); File child = new File(parent,"test.txt"); File pc = new File("d:\test","test.txt"); } }
绝对路径问题:File file = new File("..\io");//基于当前java文件的位置
(2)常用方法:
create.exists(),判断路径是否存在
createNewFile(),创建一个文件
mkdirs(),创建多级目录的文件夹
delete(),删除文件,如果是删除文件夹,则只能删除空文件夹
isDirectory(),判断是否是文件夹
getAbsolutePath(),获取绝对路径
getPath(),获取绝对路径
getParentFile(),获取父级File,返回的是File对象!
getParent(),获取父级路径名,返回String
getCanonicalPath(),获取绝对路径
getName(),获取文件名
exists(),判断路径是否存在
lastModified(),最后修改时间,返回毫秒值
listFiles(),以文件数组的形式,返回当前文件夹下的所有文件(不包含子文件及子文件夹)
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d:\test\test.txt"); try { File create = new File("d:\test\study.txt"); if(!create.exists()) { create.createNewFile(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { File cfile = new File("d:\study"); if(!cfile.exists()) { System.out.println(cfile.mkdirs());//创建多级目录 //cfile.mkdir() 创建单级目录 } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { File delete = new File("d:\study"); //System.out.println(delete.delete());//只能删除空文件夹 System.out.println(delete.isDirectory());//是否是文件夹 System.out.println(delete.getAbsolutePath());//获取绝对路径 System.out.println(delete.getCanonicalPath());//获取相对路径 System.out.println(delete.getName());//获取文件名 System.out.println(delete.lastModified());//返回最后修改时间,毫秒值 // 以文件数组的形式,返回当前文件夹下的所有文件(不包含子文件及子文件夹) File[] fs = delete.listFiles(); for(File all:fs) { System.out.println(all); } File fl= new File("D:\study"); File[] fls = fl.listFiles(new MyFilter());//文件名过滤器 for(File ff:fls) { if(ff.isDirectory()) { System.out.println(ff); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(3)FileFilter接口
该接口提供accept方法,返回布尔值,可在调用listFiles方法时添加过滤规则,如果true,则向File数组添加元素,反之不添加。
public class MyFilter implements FileFilter{ @Override public boolean accept(File pathname) { String s = pathname.getName(); if(s.endsWith("txt")) { return true; }else { return false; } } }
2.递归
在方法内调用当前方法,可以用来代替for循环,但是要注意,使用递归一定要注意设置跳出循环的条件,不然会造成栈溢出错误!
public class Test { static int a=0; static int sum = 0; public static void test() { a++; if(a<=10) { sum+=a; test(); }else{ System.out.println(sum); System.out.println("over"); } } public static int test2(int n) { if(n==1) { return 1; }else { return n+test2(n-1); } } public static int test3(int n) { if(n==1) { return 1; }else { return n*test3(n-1); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //test(); //System.out.println(test2(10)); //System.out.println(test3(5)); } }
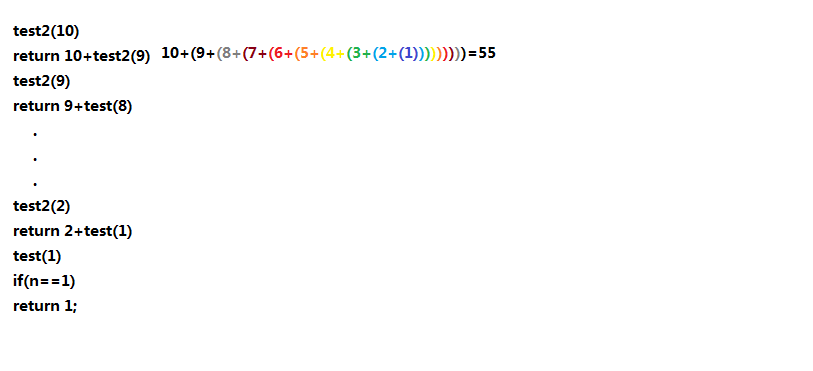
3.字节流
字节流分为输入流和输出流,即inputstream和outputstream,通过输入输出流来操作外部文件。
(1)输出流
调用write方法来写数据,一次读取一个字节
构造方法:
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);//如果路径文件存在,执行覆盖,如果File路径不存在,直接创建路径
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f,true);//不覆盖原文件,可继续写入内容
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d:\test\test.txt"); try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(f);){//如果路径文件存在,执行覆盖,如果File路径不存在,直接创建路径文件,
//注意,如果输入的是文件夹地址会报错! //FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(f,true);//不覆盖文件,继续添加 byte[] in = {-48,-49,-50,-51,-20,-91};//如果是负数,则传入汉字,一个汉字两个字节 fos.write(in);//传入一个byte数组 fos.write(50);//传入单个字节值 fos.write(in, 0, 2);//左开右闭 byte[] word = "hello".getBytes(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
(2)输入流
调用read方法来读取数据,一次读取一个字节
package edu.java.io; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d:\test\test.txt"); try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f)){ byte[] read = new byte[(int)f.length()]; int a = fis.read(read);//返回有效字节个数,和f.length()相同 for(byte b:read) { System.out.print(b);//输出单个字节 System.out.println((char)b);//输出单个字符 } String str = new String(read,0,read.length);//直接生成一个String System.out.println(str); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("文件读取错误!"); } } }
注意: new String(read,0,read.length)的构造方法:三个参数分别为byte数组名,起始下标,字节个数,例如new String(read,0,2),读取从下标0开始的2个字符
4.IO异常处理:
输入输出流必须被正确关闭,可以用try with resource(JDK1.7特性)即 try()方式关闭,或者在finally中关闭
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("d:\test\test.txt"); //IO异常一般不能处理,只能打印错误信息或者抛出运行时异常 FileOutputStream fos =null;//注意作用域,定义在try catch 外部 try { fos = new FileOutputStream(f,true); String str = "JAVA是世界上最好的语言"; byte[] s= str.getBytes(); fos.write(s); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); throw new RuntimeException("文件写入失败,请重试!"); } finally { if(fos!=null) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e3) { e3.printStackTrace(); } } } try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);){ byte[] b = new byte[(int)f.length()]; fis.read(b); for(byte r:b) { System.out.println(r); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }