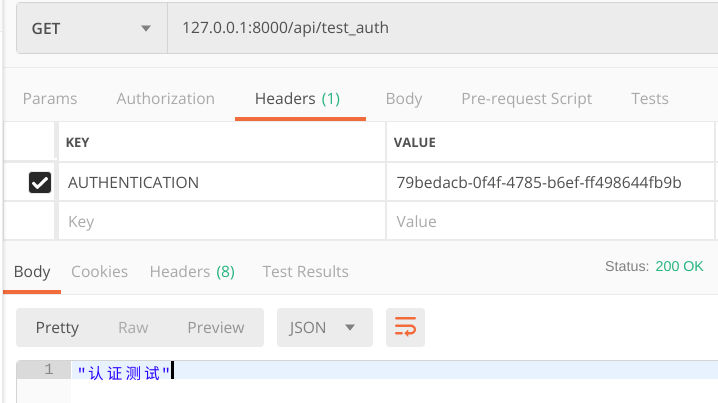
认证
任何的项目都需要认证,当用户输入了用户名和密码,验证通过,代表用户登录成功
那HTTP请求是无状态的,下次这个用户再请求,是不可能识别这个用户是否登录的
就要有自己的方式来实现这个认证,用户登录成功以后,生成一个随机字符串,以后这个用户再请求,都要携带这个随机字符串。
就可以根据这个字符串进行判断这个用户是否登录,目的是前端发送请求的时候带过来就可以,以前的cookie,session是的一种解决方案,认证的时候也用过token的这种解决方案。
token
用户登录成功后,生成一个随机字符串token给前端返回
那么前端以后都携带这个token来访问这样只需要鉴别这个token来做认证
前端如果发送请求把token放在请求头中看下的认证要怎么写
序列化注册数据
测试的时候用的重写create方法,真正开发前端传过来的就是加密后的密文密码

from rest_framework import serializers from Course.models import Account import hashlib class RegisterSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = Account fields = "__all__" def create(self, validated_data): pwd = validated_data["pwd"] pwd_salt = "luffy_password" + pwd # 加盐处理 md5_str = hashlib.md5(pwd_salt.encode()).hexdigest() user_obj = Account.objects.create(username=validated_data["username"], pwd=md5_str) return user_obj
注册,登录的视图

from rest_framework.views import APIView from rest_framework.response import Response from .serializers import RegisterSerializer from utils.base_response import BaseResponse from Course.models import Account from utils.redis_pool import POOL import redis import uuid from utils.my_auth import LoginAuth from utils.geetest import GeetestLib from django.http import HttpResponse import json # Create your views here. class RegisterView(APIView): def post(self, request): res = BaseResponse() # 实例化响应类 # 用序列化器做校验 ser_obj = RegisterSerializer(data=request.data) if ser_obj.is_valid(): ser_obj.save() res.data = ser_obj.data else: res.code = 1020 res.error = ser_obj.errors return Response(res.dict) class LoginView(APIView): def post(self, request): res = BaseResponse() username = request.data.get("username", "") pwd = request.data.get("pwd", "") user_obj = Account.objects.filter(username=username, pwd=pwd).first() if not user_obj: res.code = 1030 res.error = "用户名或密码错误" return Response(res.dict) # 用户登录成功生成一个token写入redis # 写入redis token : user_id conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=POOL) # 从连接池获取一个连接 try: token = uuid.uuid4() conn.set(str(token), user_obj.id, ex=10000) # conn.set(str(token), user_obj.id) # str(token) 用作key res.data = token except Exception as e: print(e) res.code = 1031 res.error = "创建令牌失败" return Response(res.dict)

class BaseResponse(object): """ 封装响应的类 """ def __init__(self): self.code = 1000 self.data = None self.error = None @property def dict(self): return self.__dict__ # 返回字典
认证器
http头部发送的字段信息 key:value
在服务器接受时,需要加上前缀(并且大写)例如 HTTP_KEY ,通过 request.META.get(HTTP_KEY) 获取值

import redis from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed from .redis_pool import POOL from Course.models import Account CONN = redis.Redis(connection_pool=POOL) class LoginAuth(BaseAuthentication): def authenticate(self, request): # 从请求头中获取前端带过来的token。或者跟前端商量好 token = request.META.get("HTTP_AUTHENTICATION", "") # print(request.META) # print(token) if not token: raise AuthenticationFailed("没有携带token") # 去redis比对 user_id = CONN.get(str(token)) # get没有的值返回 None if user_id == None: raise AuthenticationFailed("token过期") # 重新登录设置token user_obj = Account.objects.filter(id=user_id).first() return user_obj, token
用到的redis连接池

import redis POOL = redis.ConnectionPool(host="127.0.0.1", port=6379, decode_responses=True, max_connections=10)
注册用户测试
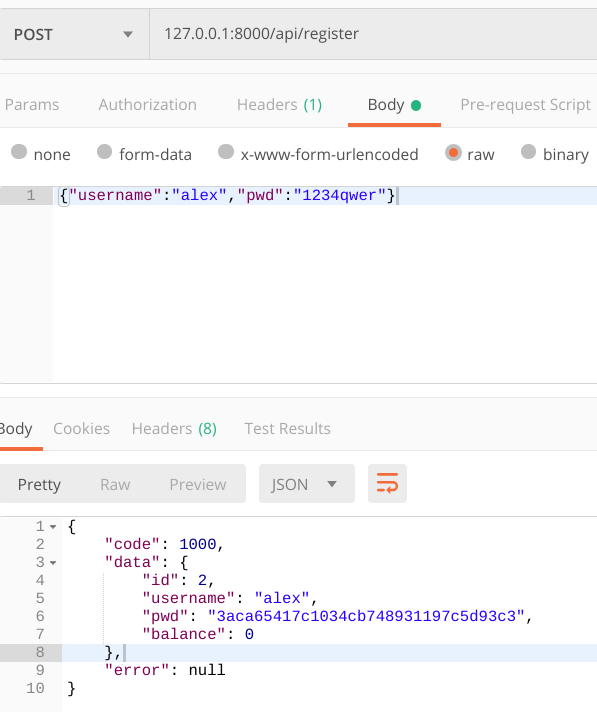
测试发送密码时为密文。前端传过来,后端加密后再与数据库中的比对

以token为key存放在redis中,登录成功后返回生成的token数据(有有效期的),下次登录时携带上。后端以传过来的token 去reids中找,能找到就拿到用户信息,不能就说明过期需要重新登录,或者token不存在.