numpy基础
import numpy as np
定义array
In [156]: np.ones(3)
Out[156]: array([1., 1., 1.])
In [157]: np.ones((3,5))
Out[157]:
array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
In [158]:
In [158]: np.zeros(4)
Out[158]: array([0., 0., 0., 0.])
In [159]: np.zeros((2,5))
Out[159]:
array([[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
In [160]:
In [146]: a = np.array([[1,3,5,2],[4,2,6,1]])
In [147]: print(a)
[[1 3 5 2]
[4 2 6 1]]
In [148]:
In [161]: np.arange(10)
Out[161]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In [162]: np.arange(3,13)
Out[162]: array([ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
In [163]: np.arange(3,13).reshape((2,5))
Out[163]:
array([[ 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]])
In [164]:
In [169]: np.arange(2,25,2)
Out[169]: array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24])
In [170]: np.arange(2,25,2).reshape(3,4)
Out[170]:
array([[ 2, 4, 6, 8],
[10, 12, 14, 16],
[18, 20, 22, 24]])
In [171]:
In [176]: np.linspace(1,10,4)
Out[176]: array([ 1., 4., 7., 10.])
In [177]:
array基本运算
In [7]: a = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
In [8]: b = np.arange(5,9).reshape((2,3))
In [10]: print(a)
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
In [11]: print(b)
[[5 6]
[7 8]]
In [12]:
In [12]: a+b
Out[12]:
array([[ 6, 8],
[10, 12]])
In [13]: a-b
Out[13]:
array([[-4, -4],
[-4, -4]])
In [14]: a*b # 对应元素相乘
Out[14]:
array([[ 5, 12],
[21, 32]])
In [17]: a/b
Out[17]:
array([[0, 0],
[0, 0]])
In [18]:
In [18]: a**2
Out[18]:
array([[ 1, 4],
[ 9, 16]])
In [19]:
In [15]: np.dot(a,b) # 矩阵乘法
Out[15]:
array([[19, 22],
[43, 50]])
In [16]: a.dot(b)
Out[16]:
array([[19, 22],
[43, 50]])
In [17]:
In [54]: print(a)
[[ 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13]]
In [55]: np.sum(a)
Out[55]: 90
In [56]: np.min(a)
Out[56]: 2
In [57]: np.max(a)
Out[57]: 13
In [58]:
In [58]: np.sum(a,axis=1)
Out[58]: array([14, 30, 46])
In [59]: np.sum(a,axis=0)
Out[59]: array([18, 21, 24, 27])
In [60]:
# 三角函数结合random生成一组随机数据
In [74]: N = 10
In [75]: t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, N)
In [76]: print(t)
[0. 0.6981317 1.3962634 2.0943951 2.7925268 3.4906585
4.1887902 4.88692191 5.58505361 6.28318531]
In [77]: y = np.sin(t) + 0.02*np.random.randn(N)
In [78]: print(y)
[-0.00947902 0.64196198 0.96567468 0.89394571 0.33830193 -0.3015316
-0.86943758 -0.95954123 -0.62526393 0.02872202]
In [79]: M = 3
In [80]: for ii, vv in zip(np.random.rand(M)*N, np.random.randn(M)):
...: y[int(ii):] += vv
...:
In [81]: print(y)
[-0.00947902 0.64196198 1.47685437 1.55309848 0.99745469 0.35762117
-0.21028481 -0.30038846 -0.29746375 0.35652221]
In [82]:
In [101]: a = np.arange(2,14).reshape((3,4))
In [102]: print(a)
[[ 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9]
[10 11 12 13]]
In [103]: print(np.argmin(a)) # 最小值的索引
0
In [104]: print(np.argmax(a)) # 最大值的索引
11
In [105]: np.cumsum(a) # 从0元素开始的累计和
Out[105]: array([ 2, 5, 9, 14, 20, 27, 35, 44, 54, 65, 77, 90])
In [106]: np.cumprod(a) # 从1元素开始的累计乘
Out[106]:
array([ 2, 6, 24, 120, 720,
5040, 40320, 362880, 3628800, 39916800,
479001600, 6227020800])
In [107]:
In [129]: a
Out[129]:
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13]])
In [130]: np.cumsum(a,axis=1)
Out[130]:
array([[ 2, 5, 9, 14],
[ 6, 13, 21, 30],
[10, 21, 33, 46]])
In [131]: np.cumsum(a,axis=0)
Out[131]:
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 8, 10, 12, 14],
[18, 21, 24, 27]])
In [132]:
In [133]: np.cumprod(a,axis=1)
Out[133]:
array([[ 2, 6, 24, 120],
[ 6, 42, 336, 3024],
[ 10, 110, 1320, 17160]])
In [134]: np.cumprod(a,axis=0)
Out[134]:
array([[ 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 12, 21, 32, 45],
[120, 231, 384, 585]])
In [135]:
In [146]: a = np.array([[1,3,5,2],[4,2,6,1]])
In [147]: print(a)
[[1 3 5 2]
[4 2 6 1]]
In [148]: a.shape
Out[148]: (2, 4)
In [149]: a.ndim
Out[149]: 2
In [150]: a.size
Out[150]: 8
In [151]: np.diff(a) # 累差运算
Out[151]:
array([[ 2, 2, -3],
[-2, 4, -5]])
In [152]: np.diff(a,axis=1)
Out[152]:
array([[ 2, 2, -3],
[-2, 4, -5]])
In [153]: np.diff(a,axis=0)
Out[153]: array([[ 3, -1, 1, -1]])
In [154]:
In [108]: a = np.array([10,7,11,9,8,13,12,9])
In [109]: a.ndim
Out[109]: 1
In [110]: a.shape
Out[110]: (8,)
In [111]: a.size
Out[111]: 8
In [112]: a.mean() # 均值
Out[112]: 9.875
In [113]: a.var() # 方差
Out[113]: 3.609375
In [114]: a.std() # 标准差
Out[114]: 1.899835519196333
In [115]:
In [117]: np.median(a) # 中位数
Out[117]: 9.5
In [118]:
In [138]: z = (a-a.mean())/a.std() # z-score
In [139]: print(z)
[ 0.06579517 -1.5132889 0.59215653 -0.46056619 -0.98692754 1.64487924
1.11851788 -0.46056619]
In [140]:
In [198]: a = np.arange(-3,3).reshape((2,3))
In [199]: a
Out[199]:
array([[-3, -2, -1],
[ 0, 1, 2]])
In [200]: np.nonzero(a) # 查找非0元素
Out[200]: (array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1]), array([0, 1, 2, 1, 2]))
In [201]: print(np.nonzero(a))
(array([0, 0, 0, 1, 1]), array([0, 1, 2, 1, 2]))
In [202]:
In [207]: a = np.arange(14,2,-1).reshape((3,4))
In [208]: print(a)
[[14 13 12 11]
[10 9 8 7]
[ 6 5 4 3]]
In [209]: np.sort(a) # 排序
Out[209]:
array([[11, 12, 13, 14],
[ 7, 8, 9, 10],
[ 3, 4, 5, 6]])
In [210]:
In [210]: np.sort(a,axis=1)
Out[210]:
array([[11, 12, 13, 14],
[ 7, 8, 9, 10],
[ 3, 4, 5, 6]])
In [211]: np.sort(a,axis=0)
Out[211]:
array([[ 6, 5, 4, 3],
[10, 9, 8, 7],
[14, 13, 12, 11]])
In [212]:
# 矩阵的转置
In [212]: a = np.arange(14,2,-1).reshape((3,4))
In [213]: print(a)
[[14 13 12 11]
[10 9 8 7]
[ 6 5 4 3]]
In [214]:
In [215]: print(np.transpose(a))
[[14 10 6]
[13 9 5]
[12 8 4]
[11 7 3]]
In [216]: a.T
Out[216]:
array([[14, 10, 6],
[13, 9, 5],
[12, 8, 4],
[11, 7, 3]])
In [217]:
In [220]: a.T.dot(a) # 先转置,再进行矩阵乘法
Out[220]:
array([[332, 302, 272, 242],
[302, 275, 248, 221],
[272, 248, 224, 200],
[242, 221, 200, 179]])
In [221]:
# 矩阵的clip,处理最大值和最小值
In [221]: print(a)
[[14 13 12 11]
[10 9 8 7]
[ 6 5 4 3]]
In [222]: np.clip(a,5,11)
Out[222]:
array([[11, 11, 11, 11],
[10, 9, 8, 7],
[ 6, 5, 5, 5]])
In [223]:
卷积运算
numpy.convolve(weights,array)
weight = [a,b,c]
array = [i,j,k,m,n]
Result:[ai, bi+aj, ci+bj+ak, cj+bk+am, ck+bm+an, cm+bn, cn][N-1:-N+1]
针对移动平均算法来预测下一个数据,越接近待预测点的数据权重越大,
那么就需要让 i, j, k, m, n 的系数逐渐增大即可;即让 a > b > c ,并且 a+b+c=1 。
示例:
In [223]: weight = np.ones(3)/3
In [224]: print(weight)
[0.33333333 0.33333333 0.33333333]
In [225]: arr = np.array([8,11,9,7,10])
In [226]: np.convolve(weight,arr)
Out[226]:
array([2.66666667, 6.33333333, 9.33333333, 9. , 8.66666667,
5.66666667, 3.33333333])
In [227]:
In [227]: weight = np.array([0.8,0.1,0.1])
In [228]: np.convolve(weight,arr)
Out[228]: array([6.4, 9.6, 9.1, 7.6, 9.6, 1.7, 1. ])
In [229]:
random常用操作
# 生成随机浮点数,范围是在0.0~1.0之间
In [19]: a = np.random.random((2,3))
In [20]: print(a)
[[0.02185901 0.69585563 0.04555439]
[0.37331857 0.32903986 0.62448246]]
In [21]:
# 生成随机整数,可指定起止范围
In [48]: np.random.randint(3)
Out[48]: 2
In [49]: np.random.randint(low=3,high=9)
Out[49]: 6
In [50]: np.random.randint(low=3,high=9,size=(3,4))
Out[50]:
array([[5, 6, 7, 8],
[8, 7, 3, 8],
[5, 4, 5, 5]])
In [51]:
In [68]: np.random.randint(low=-5,high=2,size=(3,4))
Out[68]:
array([[-4, -4, -2, 1],
[ 1, 0, 0, 1],
[-4, -3, 1, -5]])
In [69]:
# 生成正态分布,又名高斯分布(Gaussian distribution)随机数
In [64]: np.random.normal()
Out[64]: -0.5399414561419419
In [65]: np.random.normal(loc=0,scale=1,size=(2,3))
Out[65]:
array([[-0.50318082, -0.38614219, 0.30450427],
[ 0.41711087, 0.29990928, -0.7843322 ]])
In [66]:
In [66]: np.random.normal(loc=2,scale=3,size=(2,3))
Out[66]:
array([[ 3.37067379, 6.23517315, 2.3267659 ],
[ 6.46832646, -2.76363304, 5.77883853]])
In [67]:
# 生成标准正态分布("standard normal" distribution)随机数,标准正态分布的平均值为0,方差为1,服从u(0,1)分布。
In [83]: np.random.randn()
Out[83]: 0.502482341264108
In [84]: np.random.randn(3,4)
Out[84]:
array([[ 0.34507555, -0.26868132, -0.56103417, 0.86176617],
[-0.16535555, -0.38045904, 0.48176385, -1.09005206],
[-0.60780266, 1.74113117, -0.72427329, -0.51232408]])
In [85]:
# 生成[0, 1)间随机数
In [99]: np.random.rand()
Out[99]: 0.607701127768974
In [100]: np.random.rand(3,4)
Out[100]:
array([[0.73020695, 0.53993878, 0.46693879, 0.82611629],
[0.76117076, 0.16522599, 0.85129611, 0.74448772],
[0.6450236 , 0.49994053, 0.04115063, 0.30081311]])
In [101]:
array索引
# 一维数组的索引和list类似 略 # 二维数组的索引 In [13]: import numpy as np In [14]: a = np.arange(3,15).reshape((3,4)) In [15]: print(a) [[ 3 4 5 6] [ 7 8 9 10] [11 12 13 14]] In [16]: a[1] Out[16]: array([ 7, 8, 9, 10]) In [17]: a[1,2] Out[17]: 9 In [18]: a[1][2] # 等价于 a[1,2] Out[18]: 9 In [19]: In [19]: a[1,1:-1] # 获取第二行,除去首尾元素 Out[19]: array([8, 9]) In [20]: a[1,1:2] # 获取第二行第二个元素 Out[20]: array([8]) In [21]: In [24]: a[1:-1,2] # 获取第二列,除去首尾元素 Out[24]: array([9]) In [26]: a[:,2] # 获取第二列元素 Out[26]: array([ 5, 9, 13]) In [27]:
迭代array
# 迭代行
In [27]: print(a)
[[ 3 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9 10]
[11 12 13 14]]
In [28]: for row in a:
...: print(row)
...:
[3 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9 10]
[11 12 13 14]
In [29]:
# 迭代列
In [29]: print(a.T)
[[ 3 7 11]
[ 4 8 12]
[ 5 9 13]
[ 6 10 14]]
In [30]: for column in a.T:
...: print(column)
...:
[ 3 7 11]
[ 4 8 12]
[ 5 9 13]
[ 6 10 14]
In [31]:
# 二维矩阵,多行转换成一行,迭代每一个item
In [31]: print(a)
[[ 3 4 5 6]
[ 7 8 9 10]
[11 12 13 14]]
In [32]: print(a.flat)
<numpy.flatiter object at 0x7f392e3545c0>
In [33]: print(a.flatten())
[ 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]
In [34]: for item in a.flat:
...: print(item)
...:
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
In [35]:
合并array
In [39]: a = np.array([1,2,3]) In [40]: b = np.array([2,2,2]) In [41]: c = np.vstack((a,b)) # vertical stack,上下合并 In [42]: print(c) [[1 2 3] [2 2 2]] In [43]: c.shape Out[43]: (2, 3) In [44]: c.ndim Out[44]: 2 In [45]: c.size Out[45]: 6 In [46]: In [47]: d = np.hstack((a,b)) # horizontal stack,左右合并 In [48]: print(d) [1 2 3 2 2 2] In [49]: d.shape Out[49]: (6,) In [50]: d.ndim Out[50]: 1 In [51]: d.size Out[51]: 6 In [52]: # newaxis改变数组维度 In [54]: print(a) [1 2 3] In [55]: e = a[np.newaxis,:] In [56]: print(e) [[1 2 3]] In [57]: f = a[:,np.newaxis] In [58]: print(f) [[1] [2] [3]] In [59]: In [59]: a = np.array([1,2,3])[:,np.newaxis] In [60]: b = np.array([2,2,2])[:,np.newaxis] In [61]: print(a) [[1] [2] [3]] In [62]: print(b) [[2] [2] [2]] In [63]: c = np.vstack((a,b)) In [64]: print(c) [[1] [2] [3] [2] [2] [2]] In [65]: d = np.hstack((a,b)) # 合并两个array In [66]: print(d) [[1 2] [2 2] [3 2]] In [67]: In [74]: d = np.hstack((a,b,b,a)) # 合并多个array In [75]: print(d) [[1 2 2 1] [2 2 2 2] [3 2 2 3]] In [76]: # concatenate 常用来合并多个矩阵或序列,axis可以方便的指定维度 In [76]: a = np.array([1,2,3]) In [77]: b = np.array([2,2,2]) In [78]: a = a[:,np.newaxis] In [79]: b = b[:,np.newaxis] In [80]: c = np.concatenate((a,b,b,a),axis=0) In [81]: print(c) [[1] [2] [3] [2] [2] [2] [2] [2] [2] [1] [2] [3]] In [82]: c = np.concatenate((a,b,b,a),axis=1) In [83]: print(c) [[1 2 2 1] [2 2 2 2] [3 2 2 3]] In [84]:
分割array
In [92]: a = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
In [93]: print(a)
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
In [94]: c = np.split(a,2,axis=1) # 等项分割
In [95]: len(c)
Out[95]: 2
In [96]: c[0]
Out[96]:
array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]])
In [97]: c[1]
Out[97]:
array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])
In [98]:
In [98]: print(c)
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])]
In [99]:
In [99]: d = np.array_split(a,3,axis=1) # 不等项分割
In [100]: len(d)
Out[100]: 3
In [101]: print(d)
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2],
[ 6],
[10]]), array([[ 3],
[ 7],
[11]])]
In [102]: d[0]
Out[102]:
array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]])
In [103]: d[1]
Out[103]:
array([[ 2],
[ 6],
[10]])
In [104]: d[2]
Out[104]:
array([[ 3],
[ 7],
[11]])
In [105]:
In [111]: print(a)
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
In [112]: b = np.hsplit(a,2) # horizontal split,水平分割
In [113]: print(b)
[array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]]), array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])]
In [114]: b[0]
Out[114]:
array([[0, 1],
[4, 5],
[8, 9]])
In [115]: b[1]
Out[115]:
array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11]])
In [116]:
In [116]: c = np.vsplit(a,3) # vertical split,垂直分割
In [117]: len(c)
Out[117]: 3
In [118]: print(c)
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]), array([[4, 5, 6, 7]]), array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])]
In [119]: c[0]
Out[119]: array([[0, 1, 2, 3]])
In [120]: c[1]
Out[120]: array([[4, 5, 6, 7]])
In [121]: c[2]
Out[121]: array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
In [122]:
Numpy.copy()
In [150]: a = np.arange(4) In [151]: print(a) [0 1 2 3] In [152]: b = a In [153]: b is a Out[153]: True In [154]: a[0] = 99 In [155]: print(b) [99 1 2 3] In [156]: In [156]: c = a.copy() # deep copy In [157]: c is a Out[157]: False In [159]: print(a) [99 1 2 3] In [160]: a[1:3] = [7,8] In [161]: print(a) [99 7 8 3] In [163]: print(b) [99 7 8 3] In [164]: print(c) [99 1 2 3] In [165]:
Numpy其他
In [169]: a = np.array([-9,7,12,-4,-3,6,2]) In [170]: print(a) [-9 7 12 -4 -3 6 2] In [171]: np.abs(a) Out[171]: array([ 9, 7, 12, 4, 3, 6, 2]) In [172]: np.where(np.abs(a)>6) Out[172]: (array([0, 1, 2]),) In [173]:
numpy参考:http://pda.readthedocs.io/en/latest/chp4.html
Pandas基础
import pandas as pd
Series
In [173]: import pandas as pd In [174]: import numpy as np In [175]: s = pd.Series([1,3,6,np.nan,44,1]) # 定义pandas.Series In [176]: print(s) 0 1.0 1 3.0 2 6.0 3 NaN 4 44.0 5 1.0 dtype: float64 In [177]:
Base Time Series Frequencies

Aggragate for duplicate Indices
In [157]: dates = pd.DatetimeIndex(['1/1/2000', '1/2/2000', '1/2/2000', '1/2/2000','1/3/2000','1/3/2000'])
In [158]: dates
Out[158]:
DatetimeIndex(['2000-01-01', '2000-01-02', '2000-01-02', '2000-01-02',
'2000-01-03', '2000-01-03'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
In [159]: dup_ts = pd.Series(np.arange(6), index=dates)
In [160]: dup_ts
Out[160]:
2000-01-01 0
2000-01-02 1
2000-01-02 2
2000-01-02 3
2000-01-03 4
2000-01-03 5
dtype: int64
In [161]: dup_ts.index.is_unique
Out[161]: False
In [162]: dup_ts['2000-01-01']
Out[162]: 0
In [163]: dup_ts['2000-01-02']
Out[163]:
2000-01-02 1
2000-01-02 2
2000-01-02 3
dtype: int64
In [164]: dup_ts['2000-01-03']
Out[164]:
2000-01-03 4
2000-01-03 5
dtype: int64
In [165]:
In [165]: grouped = dup_ts.groupby(level=0)
In [166]: grouped.mean()
Out[166]:
2000-01-01 0.0
2000-01-02 2.0
2000-01-03 4.5
dtype: float64
In [167]: grouped.count()
Out[167]:
2000-01-01 1
2000-01-02 3
2000-01-03 2
dtype: int64
In [168]: grouped.sum()
Out[168]:
2000-01-01 0
2000-01-02 6
2000-01-03 9
dtype: int64
In [169]:
Group by month or weekday by passing a function that accesses those fields on the time series’s index.
In [90]: rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=100, freq='D')
In [91]: ts = pd.Series(np.arange(100), index=rng)
In [92]: ts.groupby(lambda x: x.month).mean()
Out[92]:
1 15
2 45
3 75
4 95
dtype: int64
In [93]: ts.groupby(lambda x: x.month).sum()
Out[93]:
1 465
2 1305
3 2325
4 855
dtype: int64
In [94]: ts.groupby(lambda x: x.month).max()
Out[94]:
1 30
2 59
3 90
4 99
dtype: int64
In [95]: ts.groupby(lambda x: x.weekday).mean()
Out[95]:
0 47.5
1 48.5
2 49.5
3 50.5
4 51.5
5 49.0
6 50.0
dtype: float64
In [96]: ts.groupby(lambda x: x.weekday).sum()
Out[96]:
0 665
1 679
2 693
3 707
4 721
5 735
6 750
dtype: int64
In [97]:
Resample method arguments
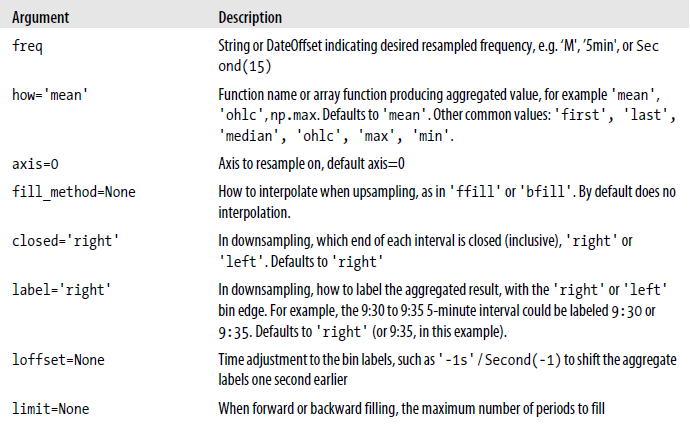

Resampling and Frequency Conversion
In [50]: rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=100, freq='D')
In [51]: ts = pd.Series(np.random.randn(len(rng)), index=rng)
In [52]: ts
Out[52]:
2000-01-01 0.030631
2000-01-02 -2.087034
2000-01-03 1.238687
2000-01-04 -1.297059
2000-01-05 -1.341296
2000-01-06 -0.353311
2000-01-07 -0.854693
2000-01-08 0.426789
...
2000-03-27 1.262705
2000-03-28 -0.646236
2000-03-29 -0.349658
2000-03-30 -1.093438
2000-03-31 -0.254758
2000-04-01 0.146417
2000-04-02 1.774502
2000-04-03 -0.712635
2000-04-04 -1.552352
2000-04-05 0.303172
2000-04-06 -0.023492
2000-04-07 -1.418930
2000-04-08 0.789877
2000-04-09 1.767594
Freq: D, Length: 100, dtype: float64
In [53]:
In [53]: ts.resample('M').mean()
Out[53]:
2000-01-31 0.003531
2000-02-29 0.030067
2000-03-31 -0.106783
2000-04-30 0.119350
Freq: M, dtype: float64
In [54]: ts.resample('M',kind='period').mean()
Out[54]:
2000-01 0.003531
2000-02 0.030067
2000-03 -0.106783
2000-04 0.119350
Freq: M, dtype: float64
In [55]:
Aggregate this data into five-minute chunks or bars by taking the sum of each group.
In [71]: rng = pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=24, freq='T')
In [72]: rng
Out[72]:
DatetimeIndex(['2000-01-01 00:00:00', '2000-01-01 00:01:00',
'2000-01-01 00:02:00', '2000-01-01 00:03:00',
'2000-01-01 00:04:00', '2000-01-01 00:05:00',
'2000-01-01 00:06:00', '2000-01-01 00:07:00',
'2000-01-01 00:08:00', '2000-01-01 00:09:00',
'2000-01-01 00:10:00', '2000-01-01 00:11:00',
'2000-01-01 00:12:00', '2000-01-01 00:13:00',
'2000-01-01 00:14:00', '2000-01-01 00:15:00',
'2000-01-01 00:16:00', '2000-01-01 00:17:00',
'2000-01-01 00:18:00', '2000-01-01 00:19:00',
'2000-01-01 00:20:00', '2000-01-01 00:21:00',
'2000-01-01 00:22:00', '2000-01-01 00:23:00'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='T')
In [73]: ts = pd.Series(np.arange(24), index=rng)
In [74]: ts
Out[74]:
2000-01-01 00:00:00 0
2000-01-01 00:01:00 1
2000-01-01 00:02:00 2
2000-01-01 00:03:00 3
2000-01-01 00:04:00 4
2000-01-01 00:05:00 5
2000-01-01 00:06:00 6
2000-01-01 00:07:00 7
2000-01-01 00:08:00 8
2000-01-01 00:09:00 9
2000-01-01 00:10:00 10
2000-01-01 00:11:00 11
2000-01-01 00:12:00 12
2000-01-01 00:13:00 13
2000-01-01 00:14:00 14
2000-01-01 00:15:00 15
2000-01-01 00:16:00 16
2000-01-01 00:17:00 17
2000-01-01 00:18:00 18
2000-01-01 00:19:00 19
2000-01-01 00:20:00 20
2000-01-01 00:21:00 21
2000-01-01 00:22:00 22
2000-01-01 00:23:00 23
Freq: T, dtype: int64
In [75]: ts.resample('5min').sum()
Out[75]:
2000-01-01 00:00:00 10
2000-01-01 00:05:00 35
2000-01-01 00:10:00 60
2000-01-01 00:15:00 85
2000-01-01 00:20:00 86
Freq: 5T, dtype: int64
In [76]: ts.resample('5min',closed='left').sum()
Out[76]:
2000-01-01 00:00:00 10
2000-01-01 00:05:00 35
2000-01-01 00:10:00 60
2000-01-01 00:15:00 85
2000-01-01 00:20:00 86
Freq: 5T, dtype: int64
In [77]:
In [77]: ts.resample('5min').max()
Out[77]:
2000-01-01 00:00:00 4
2000-01-01 00:05:00 9
2000-01-01 00:10:00 14
2000-01-01 00:15:00 19
2000-01-01 00:20:00 23
Freq: 5T, dtype: int64
In [78]:
In [78]: ts.resample('5min',closed='right').sum()
Out[78]:
1999-12-31 23:55:00 0
2000-01-01 00:00:00 15
2000-01-01 00:05:00 40
2000-01-01 00:10:00 65
2000-01-01 00:15:00 90
2000-01-01 00:20:00 66
Freq: 5T, dtype: int64
In [79]:
In [79]: ts.resample('5min',loffset='-1s').sum()
Out[79]:
1999-12-31 23:59:59 10
2000-01-01 00:04:59 35
2000-01-01 00:09:59 60
2000-01-01 00:14:59 85
2000-01-01 00:19:59 86
Freq: 5T, dtype: int64
In [80]:
# Open-High-Low-Close (OHLC) resampling
In [81]: ts.resample('5min').ohlc()
Out[81]:
open high low close
2000-01-01 00:00:00 0 4 0 4
2000-01-01 00:05:00 5 9 5 9
2000-01-01 00:10:00 10 14 10 14
2000-01-01 00:15:00 15 19 15 19
2000-01-01 00:20:00 20 23 20 23
In [82]:
Resampling with Periods
In [118]: frame = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(24, 4),
...: index=pd.period_range('1-2000', '12-2001', freq='M'),
...: columns=['Beijing', 'Luoyang', 'New York', 'Tokyo'])
In [119]: frame
Out[119]:
Beijing Luoyang New York Tokyo
2000-01 1.120268 -1.120345 -1.154800 0.443861
2000-02 0.611443 0.200576 -1.163600 -1.137567
2000-03 0.658112 2.332235 -1.718285 1.589246
2000-04 -0.863050 1.890877 2.046202 0.410414
2000-05 0.710052 -0.041623 0.122719 -1.141112
2000-06 0.299393 1.227689 0.718627 1.004851
2000-07 1.287335 -0.179045 -0.476422 0.949235
2000-08 -2.140590 0.433699 -0.783202 1.073706
2000-09 -0.149710 -0.580780 0.755274 0.514259
2000-10 0.190940 -0.187451 1.710803 -1.631272
2000-11 0.419288 0.565235 0.470381 0.599020
2000-12 0.951111 0.464671 -0.854858 -0.009189
2001-01 -1.383493 -0.147035 -0.379006 0.472686
2001-02 1.803475 -1.628368 -0.896757 -0.508827
2001-03 0.575910 -0.528299 1.182473 0.159452
2001-04 -1.056161 -0.475357 0.861852 1.168667
2001-05 -1.316565 0.354719 1.354205 -0.369083
2001-06 0.497406 -1.799904 -0.512882 -0.092718
2001-07 0.896944 -1.276022 0.137365 0.087199
2001-08 -0.046908 -0.650024 0.958182 -0.048369
2001-09 0.085401 1.067235 0.541318 0.853376
2001-10 1.165047 -0.794425 1.137002 0.064595
2001-11 -0.438006 0.706564 1.464403 0.278069
2001-12 -0.094644 0.666789 0.220349 -0.386617
In [120]: frame[:5]
Out[120]:
Beijing Luoyang New York Tokyo
2000-01 1.120268 -1.120345 -1.154800 0.443861
2000-02 0.611443 0.200576 -1.163600 -1.137567
2000-03 0.658112 2.332235 -1.718285 1.589246
2000-04 -0.863050 1.890877 2.046202 0.410414
2000-05 0.710052 -0.041623 0.122719 -1.141112
In [121]: annual_frame = frame.resample('A-DEC').mean()
In [122]: annual_frame
Out[122]:
Beijing Luoyang New York Tokyo
2000 0.257883 0.417145 -0.027263 0.222121
2001 0.057367 -0.375344 0.505709 0.139869
In [123]:
In [123]: annual_frame_max = frame.resample('A-DEC').max()
In [124]: annual_frame_max
Out[124]:
Beijing Luoyang New York Tokyo
2000 1.287335 2.332235 2.046202 1.589246
2001 1.803475 1.067235 1.464403 1.168667
In [125]:
DataFrame
# 第一种定义pandas.DataFrame方式:直接导入numpy的数据
In [186]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))) # 定义pandas.DataFrame
In [187]: print(df1)
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 2 3
1 4 5 6 7
2 8 9 10 11
In [188]:
In [178]: dates = pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6)
In [179]: print(dates)
DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01', '2016-01-02', '2016-01-03', '2016-01-04',
'2016-01-05', '2016-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
In [180]:
# 定义pandas.DataFrame,并指定列名和行名
In [184]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(6,4),index=dates,columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [185]: print(df)
a b c d
2016-01-01 1.193589 0.165348 1.598806 -0.478980
2016-01-02 1.188886 -1.232185 -0.633066 0.594805
2016-01-03 2.707996 -0.116420 1.622761 0.399708
2016-01-04 0.416469 1.593061 -0.044390 -0.031153
2016-01-05 -0.637080 1.680110 1.371026 0.821549
2016-01-06 -0.079359 1.421577 0.042537 1.058749
In [186]:
# 第二种定义pandas.DataFrame方式:把参数当做字典传入DataFrame
In [188]: df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A' : 1.,
...: 'B' : pd.Timestamp('20130102'),
...: 'C' : pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'),
...: 'D' : np.array([3] * 4,dtype='int32'),
...: 'E' : pd.Categorical(["test","train","test","train"]),
...: 'F' : 'foo'})
In [189]: print(df2)
A B C D E F
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
In [190]:
In [190]: print(df2.dtypes) # 查看DataFrame内容的类型
A float64
B datetime64[ns]
C float32
D int32
E category
F object
dtype: object
In [191]:
In [191]: print(df2.index) # 打印DataFrame列的名字
Int64Index([0, 1, 2, 3], dtype='int64')
In [192]:
In [192]: print(df2.columns) # 打印DataFrame行的名字
Index([u'A', u'B', u'C', u'D', u'E', u'F'], dtype='object')
In [193]:
In [194]: print(df2.values) # 打印DataFrame的内容
[[1.0 Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'test' 'foo']
[1.0 Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'train' 'foo']
[1.0 Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'test' 'foo']
[1.0 Timestamp('2013-01-02 00:00:00') 1.0 3 'train' 'foo']]
In [195]:
In [196]: print(df2)
A B C D E F
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
In [197]:
In [197]: print(df2.describe()) # 打印出DataFrame的数学运算的相关数据
A C D
count 4.0 4.0 4.0
mean 1.0 1.0 3.0
std 0.0 0.0 0.0
min 1.0 1.0 3.0
25% 1.0 1.0 3.0
50% 1.0 1.0 3.0
75% 1.0 1.0 3.0
max 1.0 1.0 3.0
In [198]:
In [200]: print(df2.T) # 把DataFrame进行transport,即转置
0 1 2 3
A 1 1 1 1
B 2013-01-02 00:00:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00 2013-01-02 00:00:00
C 1 1 1 1
D 3 3 3 3
E test train test train
F foo foo foo foo
In [201]:
# 对DataFrame排序
In [203]: print(df2)
A B C D E F
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
In [204]: df2.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False) # 按照index(列名)排序
Out[204]:
F E D C B A
0 foo test 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0
1 foo train 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0
2 foo test 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0
3 foo train 3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0
In [205]:
In [205]: df2.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=False) # 按照行名排序
Out[205]:
A B C D E F
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
In [206]:
In [207]: df2.sort_values(by='E') # 指定value进行排序
Out[207]:
A B C D E F
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
In [208]:
Pandas筛选数据
In [212]: dates = pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6)
In [213]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(24).reshape(6,4),index=dates,columns=['A','B','C','D'])
In [214]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [215]:
In [215]: print(df['A']) # 选取指定列
2016-01-01 0
2016-01-02 4
2016-01-03 8
2016-01-04 12
2016-01-05 16
2016-01-06 20
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: int64
In [216]: print(df.A) # 等价于 df['A']
2016-01-01 0
2016-01-02 4
2016-01-03 8
2016-01-04 12
2016-01-05 16
2016-01-06 20
Freq: D, Name: A, dtype: int64
In [217]:
In [217]: print(df[0:3]) # 切片方式选取某些行
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
In [218]: print(df['2016-01-01':'2016-01-03']) # 等价于 df[0:3]
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
In [219]:
# select by label : loc
In [220]: print(df.loc['2016-01-02'])
A 4
B 5
C 6
D 7
Name: 2016-01-02 00:00:00, dtype: int64
In [221]:
In [221]: print(df.loc['2016-01-02']['B'])
5
In [222]:
In [227]: print(df.loc[:,['A','B']])
A B
2016-01-01 0 1
2016-01-02 4 5
2016-01-03 8 9
2016-01-04 12 13
2016-01-05 16 17
2016-01-06 20 21
In [228]:
In [228]: print(df.loc['2016-01-03',['A','B']])
A 8
B 9
Name: 2016-01-03 00:00:00, dtype: int64
In [229]:
In [232]: print(df.loc['2016-01-03':'2016-01-05',['A','B']])
A B
2016-01-03 8 9
2016-01-04 12 13
2016-01-05 16 17
In [233]:
# select by position : iloc
In [235]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [236]: print(df.iloc[3])
A 12
B 13
C 14
D 15
Name: 2016-01-04 00:00:00, dtype: int64
In [237]: print(df.iloc[3,1])
13
In [238]:
In [238]: print(df.iloc[3:5,1:3])
B C
2016-01-04 13 14
2016-01-05 17 18
In [239]:
In [240]: print(df.iloc[[1,3,5],1:3])
B C
2016-01-02 5 6
2016-01-04 13 14
2016-01-06 21 22
In [241]:
# mixed selection : ix
In [243]: print(df.ix[:3,['A','C']])
/usr/local/anaconda2/bin/ipython2:1: DeprecationWarning:
.ix is deprecated. Please use
.loc for label based indexing or
.iloc for positional indexing
See the documentation here:
http://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/indexing.html#ix-indexer-is-deprecated
#!/usr/local/anaconda2/bin/python
A C
2016-01-01 0 2
2016-01-02 4 6
2016-01-03 8 10
In [244]:
# Boolean indexing
In [9]: print(df[df.A>8])
A B C D
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [10]:
df.head(n) # 返回DataFrame前n行 df.tail(n) # 返回DateFrame后n行
Pandas设置值
# 给DataFrame设置值
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: import pandas as pd
In [3]: dates = pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6)
In [4]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(24).reshape(6,4),index=dates,columns=['A','B','C','D'])
In [5]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [6]:
In [7]: df.iloc[2,2] = 99
In [10]: df.loc['2016-01-02','B'] = 100
In [11]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 100 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 99 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [12]:
In [17]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [18]: df.A[df.A>4] = 0
In [19]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 0 9 10 11
2016-01-04 0 13 14 15
2016-01-05 0 17 18 19
2016-01-06 0 21 22 23
In [20]:
In [21]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [22]: df[df.A>4] = 0
In [23]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 0 0 0 0
2016-01-04 0 0 0 0
2016-01-05 0 0 0 0
2016-01-06 0 0 0 0
In [24]:
In [30]: df['F'] = np.nan # 增加一列,赋值为NaN
In [31]: print(df)
A B C D F
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3 NaN
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7 NaN
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11 NaN
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15 NaN
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19 NaN
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23 NaN
In [32]:
# 增加一列,需要制定行名
In [46]: df['F'] = pd.Series([1,2,3,4,5,6], index=pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6))
In [47]: print(df)
A B C D E F
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3 NaN 1
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7 NaN 2
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11 NaN 3
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15 NaN 4
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19 NaN 5
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23 NaN 6
In [48]:
Pandas删除DataFrame数据
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: import pandas as pd
In [3]: values = np.arange(12).reshape((3,4))
In [4]: print(values)
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
In [5]:
In [8]: df = pd.DataFrame(values,index=['row1','row2','row3'],columns=['A','B','C','D'])
In [9]: print(df)
A B C D
row1 0 1 2 3
row2 4 5 6 7
row3 8 9 10 11
In [10]:
In [10]: print(df.shape)
(3, 4)
In [11]:
In [11]: df.drop(columns='A',axis=1)
Out[11]:
B C D
row1 1 2 3
row2 5 6 7
row3 9 10 11
In [12]: df.drop(columns=['A','C'],axis=1)
Out[12]:
B D
row1 1 3
row2 5 7
row3 9 11
In [13]:
In [13]: df.drop(index='row2',axis=0)
Out[13]:
A B C D
row1 0 1 2 3
row3 8 9 10 11
In [14]: df.drop(index=['row2','row3'],axis=0)
Out[14]:
A B C D
row1 0 1 2 3
In [15]:
如果index用的是 “pd.date_range('20160101',periods=6)”
In [43]: print(df)
a b c d
2016-01-01 1.273748 0.949407 -0.446053 -0.126789
2016-01-02 -0.770801 1.641150 0.840216 -0.991219
2016-01-03 -0.164625 -1.459954 1.214388 0.281621
2016-01-04 1.863281 1.163653 0.319549 -1.545655
2016-01-05 0.452804 0.203472 -1.232536 0.681963
2016-01-06 0.171324 0.353359 1.674004 -2.026071
In [44]: print(df.index)
DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01', '2016-01-02', '2016-01-03', '2016-01-04',
'2016-01-05', '2016-01-06'],
dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq='D')
In [45]:
In [45]: df.drop(index=pd.datetime(2016,1,4),axis=0)
Out[45]:
a b c d
2016-01-01 1.273748 0.949407 -0.446053 -0.126789
2016-01-02 -0.770801 1.641150 0.840216 -0.991219
2016-01-03 -0.164625 -1.459954 1.214388 0.281621
2016-01-05 0.452804 0.203472 -1.232536 0.681963
2016-01-06 0.171324 0.353359 1.674004 -2.026071
In [46]: df.drop(index=[pd.datetime(2016,1,2),pd.datetime(2016,1,5)],axis=0)
Out[46]:
a b c d
2016-01-01 1.273748 0.949407 -0.446053 -0.126789
2016-01-03 -0.164625 -1.459954 1.214388 0.281621
2016-01-04 1.863281 1.163653 0.319549 -1.545655
2016-01-06 0.171324 0.353359 1.674004 -2.026071
In [47]:
Pandas处理丢失的数据
# 处理丢失数据
In [7]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 1 2 3
2016-01-02 4 5 6 7
2016-01-03 8 9 10 11
2016-01-04 12 13 14 15
2016-01-05 16 17 18 19
2016-01-06 20 21 22 23
In [8]: df.iloc[0,1] = np.nan
In [9]: df.iloc[1,2] = np.nan
In [10]: print(df)
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 NaN 2.0 3
2016-01-02 4 5.0 NaN 7
2016-01-03 8 9.0 10.0 11
2016-01-04 12 13.0 14.0 15
2016-01-05 16 17.0 18.0 19
2016-01-06 20 21.0 22.0 23
In [11]: print(df.dropna(axis=1,how='any')) # 删除NaN数据所在行,how = {'any','all'}
A D
2016-01-01 0 3
2016-01-02 4 7
2016-01-03 8 11
2016-01-04 12 15
2016-01-05 16 19
2016-01-06 20 23
In [12]: print(df.dropna(axis=0,how='any')) # 删除NaN数据所在行,how = {'any','all'}
A B C D
2016-01-03 8 9.0 10.0 11
2016-01-04 12 13.0 14.0 15
2016-01-05 16 17.0 18.0 19
2016-01-06 20 21.0 22.0 23
In [13]:
In [13]: print(df.dropna(axis=0,how='all'))
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 NaN 2.0 3
2016-01-02 4 5.0 NaN 7
2016-01-03 8 9.0 10.0 11
2016-01-04 12 13.0 14.0 15
2016-01-05 16 17.0 18.0 19
2016-01-06 20 21.0 22.0 23
In [14]:
In [14]: print(df.dropna(axis=1,how='all'))
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 NaN 2.0 3
2016-01-02 4 5.0 NaN 7
2016-01-03 8 9.0 10.0 11
2016-01-04 12 13.0 14.0 15
2016-01-05 16 17.0 18.0 19
2016-01-06 20 21.0 22.0 23
In [15]:
In [15]: df.fillna(value=0) # 把NaN填充为制定数值
Out[15]:
A B C D
2016-01-01 0 0.0 2.0 3
2016-01-02 4 5.0 0.0 7
2016-01-03 8 9.0 10.0 11
2016-01-04 12 13.0 14.0 15
2016-01-05 16 17.0 18.0 19
2016-01-06 20 21.0 22.0 23
In [16]:
In [19]: print(df.isnull()) # 把数值为NaN的位置标识出来
A B C D
2016-01-01 False True False False
2016-01-02 False False True False
2016-01-03 False False False False
2016-01-04 False False False False
2016-01-05 False False False False
2016-01-06 False False False False
In [20]:
In [22]: print(np.any(df.isnull()) == True) # 检查DataFrame是否含有NaN值
True
In [23]:
Pandas导入导出示例
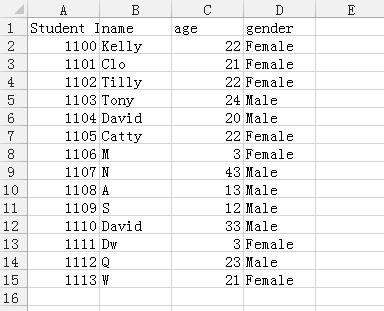
In [33]: import pandas as pd
In [34]: data = pd.read_csv('student.csv')
In [35]: print(data)
Student ID name age gender
0 1100 Kelly 22 Female
1 1101 Clo 21 Female
2 1102 Tilly 22 Female
3 1103 Tony 24 Male
4 1104 David 20 Male
5 1105 Catty 22 Female
6 1106 M 3 Female
7 1107 N 43 Male
8 1108 A 13 Male
9 1109 S 12 Male
10 1110 David 33 Male
11 1111 Dw 3 Female
12 1112 Q 23 Male
13 1113 W 21 Female
In [36]: print(type(data))
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
In [37]: data.to_pickle('student.pickle')
In [38]: data.to_json('student.json')
In [39]:
更多IO Tools参考:官方介绍
Pandas concat合并
# pandas 合并
# concatenating
In [40]: import numpy as np
In [41]: import pandas as pd
In [42]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*0, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [43]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*1, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [44]: df3 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*2, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [45]: print(df1)
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
In [46]: print(df2)
a b c d
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [47]: print(df3)
a b c d
0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
1 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
2 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
In [48]: result = pd.concat([df1,df2,df3],axis=0) # vertical 垂直合并
In [49]: print(result)
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
1 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
1 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
2 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
In [50]:
In [50]: result = pd.concat([df1,df2,df3],axis=0,ignore_index=True) # 序号重新排列
In [51]: print(result)
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
6 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
7 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
8 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0
In [52]:
# join合并 ['inner','outer']
In [63]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*0, columns=['a','b','c','d'],index=[1,2,3])
In [64]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*1, columns=['b','c','d','e'],index=[2,3,4])
In [65]: print(df1)
a b c d
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
In [66]: print(df2)
b c d e
2 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [67]:
In [67]: result = pd.concat([df1,df2]) # 即 pd.concat([df1,df2],join='outer') , 默认就是outer模式
/usr/local/anaconda2/bin/ipython2:1: FutureWarning: Sorting because non-concatenation axis is not aligned. A future version
of pandas will change to not sort by default.
To accept the future behavior, pass 'sort=True'.
To retain the current behavior and silence the warning, pass sort=False
#!/usr/local/anaconda2/bin/python
In [68]:
In [68]: print(result)
a b c d e
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN
2 NaN 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 NaN 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 NaN 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [69]:
In [70]: result = pd.concat([df1,df2],join='inner') # inner模式
In [71]: print(result)
b c d
1 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [72]:
In [72]: result = pd.concat([df1,df2],join='inner',ignore_index=True)
In [73]: print(result)
b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0
5 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [74]:
# join_axes合并
In [78]: res = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1)
In [79]: print(res)
a b c d b c d e
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 NaN NaN NaN NaN 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [80]:
In [74]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*0, columns=['a','b','c','d'],index=[1,2,3])
In [75]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*1, columns=['b','c','d','e'],index=[2,3,4])
In [76]: res = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1, join_axes=[df1.index])
In [77]: print(res)
a b c d b c d e
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [78]:
In [80]: res = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1, join_axes=[df2.index])
In [81]: print(res)
a b c d b c d e
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
3 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 NaN NaN NaN NaN 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [82]:
# append合并
In [87]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*0, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [88]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*1, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [89]: df1.append(df2,ignore_index=True)
Out[89]:
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [90]: df3 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*1, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [91]: df1.append([df2,df3],ignore_index=True)
Out[91]:
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
4 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
5 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
6 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
7 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
8 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
In [92]:
# 添加一行数据到DataFrame
In [92]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.ones((3,4))*0, columns=['a','b','c','d'])
In [93]: s1 = pd.Series([1,2,3,4], index=['a','b','c','d'])
In [94]: res = df1.append(s1,ignore_index=True)
In [95]: print(res)
a b c d
0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
3 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
In [96]:
Pandas merge合并
# merge合并
In [99]: import pandas as pd
In [100]: left = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3'],
...: 'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
...: 'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']})
In [101]: right = pd.DataFrame({'key': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2', 'K3'],
...: 'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
...: 'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']})
In [102]:
In [102]: print(left)
A B key
0 A0 B0 K0
1 A1 B1 K1
2 A2 B2 K2
3 A3 B3 K3
In [103]: print(right)
C D key
0 C0 D0 K0
1 C1 D1 K1
2 C2 D2 K2
3 C3 D3 K3
In [104]:
In [104]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on='key')
In [105]: print(res)
A B key C D
0 A0 B0 K0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 K1 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 K2 C2 D2
3 A3 B3 K3 C3 D3
In [106]:
# consider two keys
In [106]: left = pd.DataFrame({'key1': ['K0', 'K0', 'K1', 'K2'],
...: 'key2': ['K0', 'K1', 'K0', 'K1'],
...: 'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
...: 'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']})
In [107]: right = pd.DataFrame({'key1': ['K0', 'K1', 'K1', 'K2'],
...: 'key2': ['K0', 'K0', 'K0', 'K0'],
...: 'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
...: 'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']})
In [108]: print(left)
A B key1 key2
0 A0 B0 K0 K0
1 A1 B1 K0 K1
2 A2 B2 K1 K0
3 A3 B3 K2 K1
In [109]: print(right)
C D key1 key2
0 C0 D0 K0 K0
1 C1 D1 K1 K0
2 C2 D2 K1 K0
3 C3 D3 K2 K0
In [110]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on=['key1','key2'])
In [111]: print(res)
A B key1 key2 C D
0 A0 B0 K0 K0 C0 D0
1 A2 B2 K1 K0 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 K1 K0 C2 D2
# how={'left','right','inner','outer'}
In [112]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on=['key1','key2'],how='inner') # 默认就是inner模式
In [113]: print(res)
A B key1 key2 C D
0 A0 B0 K0 K0 C0 D0
1 A2 B2 K1 K0 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 K1 K0 C2 D2
In [114]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on=['key1','key2'],how='outer')
In [115]: print(res)
A B key1 key2 C D
0 A0 B0 K0 K0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 K0 K1 NaN NaN
2 A2 B2 K1 K0 C1 D1
3 A2 B2 K1 K0 C2 D2
4 A3 B3 K2 K1 NaN NaN
5 NaN NaN K2 K0 C3 D3
In [116]:
In [116]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on=['key1','key2'],how='left')
In [117]: print(res)
A B key1 key2 C D
0 A0 B0 K0 K0 C0 D0
1 A1 B1 K0 K1 NaN NaN
2 A2 B2 K1 K0 C1 D1
3 A2 B2 K1 K0 C2 D2
4 A3 B3 K2 K1 NaN NaN
In [118]: res = pd.merge(left,right,on=['key1','key2'],how='right')
In [119]: print(res)
A B key1 key2 C D
0 A0 B0 K0 K0 C0 D0
1 A2 B2 K1 K0 C1 D1
2 A2 B2 K1 K0 C2 D2
3 NaN NaN K2 K0 C3 D3
In [120]:
# indicator
In [121]: df1 = pd.DataFrame({'col1':[0,1], 'col_left':['a','b']})
In [122]: df2 = pd.DataFrame({'col1':[1,2,2],'col_right':[2,2,2]})
In [123]: print(df1)
col1 col_left
0 0 a
1 1 b
In [124]: print(df2)
col1 col_right
0 1 2
1 2 2
2 2 2
In [125]: res = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='col1', how='outer', indicator=True) # 给一个提示
In [126]: print(res)
col1 col_left col_right _merge
0 0 a NaN left_only
1 1 b 2.0 both
2 2 NaN 2.0 right_only
3 2 NaN 2.0 right_only
In [127]:
In [129]: res = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='col1', how='outer', indicator='indicator_column') # 指定提示的列名
In [130]: print(res)
col1 col_left col_right indicator_column
0 0 a NaN left_only
1 1 b 2.0 both
2 2 NaN 2.0 right_only
3 2 NaN 2.0 right_only
In [131]:
In [127]: res = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='col1', how='outer', indicator=False)
In [128]: print(res)
col1 col_left col_right
0 0 a NaN
1 1 b 2.0
2 2 NaN 2.0
3 2 NaN 2.0
In [129]:
In [131]: left = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2'],
...: 'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']},
...: index=['K0', 'K1', 'K2'])
In [132]: right = pd.DataFrame({'C': ['C0', 'C2', 'C3'],
...: 'D': ['D0', 'D2', 'D3']},
...: index=['K0', 'K2', 'K3'])
In [133]: print(left)
A B
K0 A0 B0
K1 A1 B1
K2 A2 B2
In [134]: print(right)
C D
K0 C0 D0
K2 C2 D2
K3 C3 D3
In [135]: res = pd.merge(left, right, left_index=True, right_index=True, how='outer')
In [136]: print(res)
A B C D
K0 A0 B0 C0 D0
K1 A1 B1 NaN NaN
K2 A2 B2 C2 D2
K3 NaN NaN C3 D3
In [137]: res = pd.merge(left, right, left_index=True, right_index=True, how='inner')
In [138]: print(res)
A B C D
K0 A0 B0 C0 D0
K2 A2 B2 C2 D2
In [139]:
# handle overlapping
In [139]: boys = pd.DataFrame({'k': ['K0', 'K1', 'K2'], 'age': [1, 2, 3]})
In [140]: girls = pd.DataFrame({'k': ['K0', 'K0', 'K3'], 'age': [4, 5, 6]})
In [141]: print(boys)
age k
0 1 K0
1 2 K1
2 3 K2
In [142]: print(girls)
age k
0 4 K0
1 5 K0
2 6 K3
In [143]: res = pd.merge(boys, girls, on='k', suffixes=['_boy', '_girl'], how='inner')
In [144]: print(res)
age_boy k age_girl
0 1 K0 4
1 1 K0 5
In [145]: res = pd.merge(boys, girls, on='k', suffixes=['_boy', '_girl'], how='outer')
In [146]: print(res)
age_boy k age_girl
0 1.0 K0 4.0
1 1.0 K0 5.0
2 2.0 K1 NaN
3 3.0 K2 NaN
4 NaN K3 6.0
In [147]:
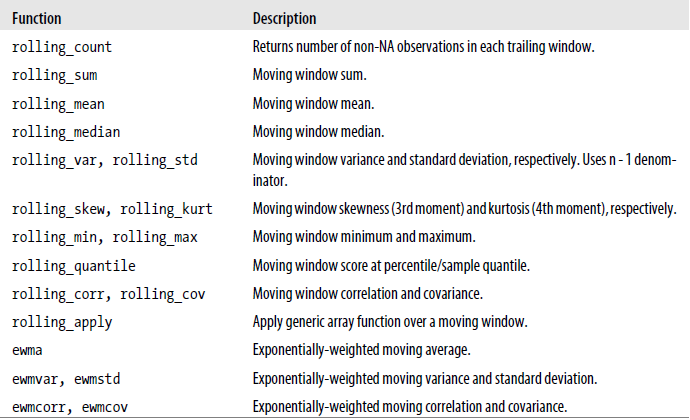
Pandas Moving Window Functions
Pandas plot可视化
#!/usr/bin/python2.7 import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Series data = pd.Series(np.random.randn(1000),index=np.arange(1000)) data = data.cumsum() data.plot() plt.show()
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# DataFrame
data = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000,4),
index=np.arange(1000),
columns=list("ABCD"))
data = data.cumsum()
# print(data.head(6))
data.plot()
plt.show()
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# DataFrame
data = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(1000,4),
index=np.arange(1000),
columns=list("ABCD"))
data = data.cumsum()
# print(data.head(6))
# plot method:
# 'bar','hist','box','kde','aera','scatter','pie','hexbin'...
ax = data.plot.scatter(x='A',y='B',color='DarkBlue',label='Class AB')
data.plot.scatter(x='A',y='C',color='DarkGreen',label='Class AC',ax=ax)
plt.show()
补充:Matplotlib 3D图像
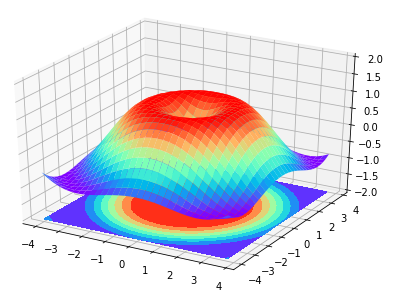
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
# X,Y value
X = np.arange(-4,4,0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4,4,0.25)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X,Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2+Y**2)
# height value
Z = np.sin(R)
ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow'))
plt.show()
#!/usr/bin/python2.7
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
# X,Y value
X = np.arange(-4,4,0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4,4,0.25)
X,Y = np.meshgrid(X,Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2+Y**2)
# height value
Z = np.sin(R)
ax.plot_surface(X,Y,Z,rstride=1,cstride=1,cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow'))
ax.contourf(X,Y,Z,zdir='z',offset=-2,cmap='rainbow') # 增加等高线
ax.set_zlim(-2,2)
plt.show()