新增一行:
insert into stu(stuName,stuAge,stuSex) values('张三',‘20’,‘男’)
增加列和删除列:
alter table new_table add column name varchar(30);## 增加一列 alter table new_table drop column name;## 删除一列 select *from new_table;
new_table的表结构: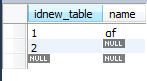
select Count(*) 和 select count(1)的结果一样,返回记录总行数,都包括对null的统计。
select count(1) from new_table;##结果是2
count(column)是不包括null的统计
select count(name) from new_table;##结果是1
exists:使用exist查询语句查询符合条件的记录,就返回一个真值(true),否则,将返回一个假值(false);当返回值为true时,外层查询语句进行查询。当返回值为false时,外层查询语句将不进行查询或者查询不出任何记录。
select *from employee where exists(select d_name from department where d_id=1003)
distinct:
去重语法:SELECT DISTINCT [COLUMN_NAME] FROM [TABLE_NAME].
先来看看去重之前的数据返回结果:
使用DISTINCT关键字后的数据返回结果:
having:
AVING语句通常与GROUP BY语句联合使用,用来过滤由GROUP BY语句返回的记录集。
HAVING语句的存在弥补了WHERE关键字不能与聚合函数联合使用的不足。
avg:
SELECT id, COUNT(course) as numcourse, AVG(score) as avgscore FROM student GROUP BY id HAVING AVG(score)>=80;
desc/asc
## 以逆字母顺序显示公司名称:(默认是asc) SELECT Company, OrderNumber FROM Orders ORDER BY Company DESC
创建索引:
在执行CREATE TABLE语句时可以创建索引,也可以单独用CREATE INDEX或ALTER TABLE来为表增加索引。
2.CREATE INDEX
CREATE INDEX可对表增加普通索引或UNIQUE索引。
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name (column_list)
如果有两个索引where A=? and B=?##区分度大的放在前面效果更好
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX index_name (column_list)
3.数据库分页查询
是用limit函数
取前5条数据
select * from table_name limit 0,5
或者
select * from table_name limit 5
查询第11到第15条数据
select * from table_name limit 10,5
limit关键字的用法:
LIMIT [offset,] rows
offset指定要返回的第一行的偏移量,rows第二个指定返回行的最大数目。初始行的偏移量是0(不是1)。

