Spark Streaming
1. 目标
1.1. 掌握Spark Streaming的原理
1.2. 熟练使用Spark Streaming完成流式计算任务
2. Spark Streaming介绍
2.1. Spark Streaming概述
2.1.1. 什么是Spark Streaming
Spark Streaming类似于Apache Storm,用于流式数据的处理。根据其官方文档介绍,Spark Streaming有高吞吐量和容错能力强等特点。Spark Streaming支持的数据输入源很多,例如:Kafka、Flume、Twitter、ZeroMQ和简单的TCP套接字等等。数据输入后可以用Spark的高度抽象原语如:map、reduce、join、window等进行运算。而结果也能保存在很多地方,如HDFS,数据库等。另外Spark Streaming也能和MLlib(机器学习)以及Graphx完美融合。

2.1.2. Spark Streaming优点
1.易用
2.容错
3.易整合到Spark体系

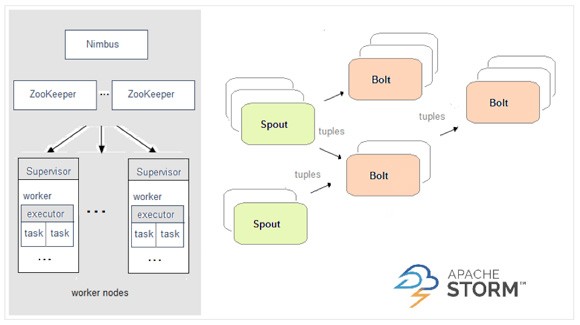
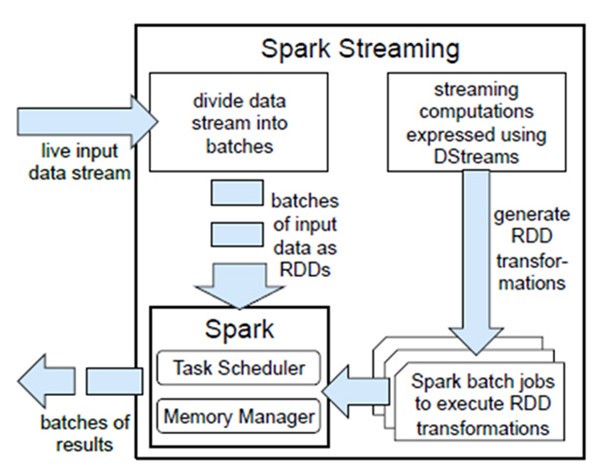
2.1.3. Spark与Storm的对比
|
Spark |
Storm |
 |
 |
|
开发语言:Scala |
开发语言:Clojure |
|
编程模型:DStream |
编程模型:Spout/Bolt |
 |
 |
3. DStream
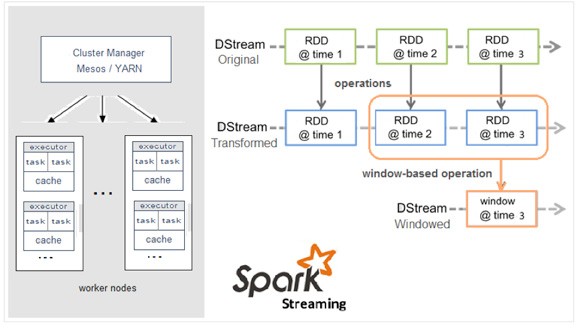
3.1. 什么是DStream
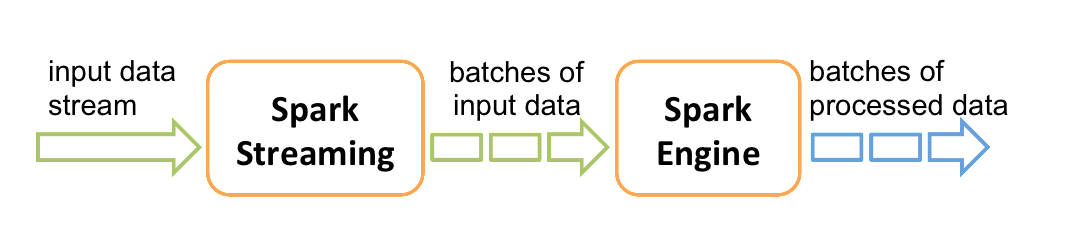
Discretized Stream是Spark Streaming的基础抽象,代表持续性的数据流和经过各种Spark原语操作后的结果数据流。在内部实现上,DStream是一系列连续的RDD来表示。每个RDD含有一段时间间隔内的数据,如下图:
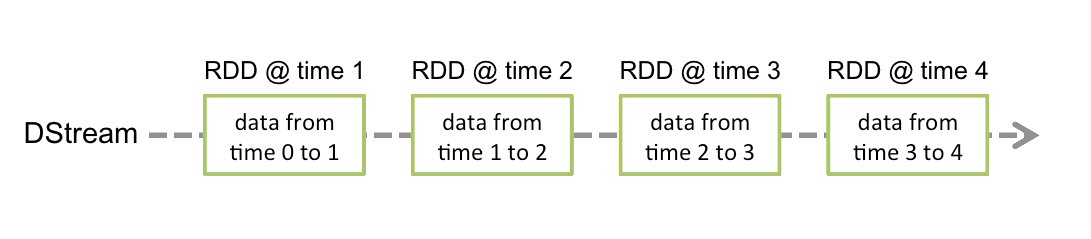
对数据的操作也是按照RDD为单位来进行的

计算过程由Spark engine来完成
3.2. DStream相关操作
DStream上的原语与RDD的类似,分为Transformations(转换)和Output Operations(输出)两种,此外转换操作中还有一些比较特殊的原语,如:updateStateByKey()、transform()以及各种Window相关的原语。
3.2.1. Transformations on DStreams
|
Transformation |
Meaning |
|
map(func) |
Return a new DStream by passing each element of the source DStream through a function func. 通过函数func传递源DStream的每个元素,返回一个新的DStream |
|
flatMap(func) |
Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items. 类似于map,但是每个输入项都可以映射到0或多个输出项 |
|
filter(func) |
Return a new DStream by selecting only the records of the source DStream on which func returns true. 通过只选择func返回true的源DStream的记录,返回一个新的DStream |
|
repartition(numPartitions) |
Changes the level of parallelism in this DStream by creating more or fewer partitions. 通过创建更多或更少的分区来更改此DStream中的并行度级别 |
|
union(otherStream) |
Return a new DStream that contains the union of the elements in the source DStream and otherDStream. |
|
count() |
Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by counting the number of elements in each RDD of the source DStream. |
|
reduce(func) |
Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by aggregating the elements in each RDD of the source DStream using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be associative so that it can be computed in parallel. |
|
countByValue() |
When called on a DStream of elements of type K, return a new DStream of (K, Long) pairs where the value of each key is its frequency in each RDD of the source DStream. |
|
reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) |
When called on a DStream of (K, V) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function. Note: By default, this uses Spark's default number of parallel tasks (2 for local mode, and in cluster mode the number is determined by the config property spark.default.parallelism) to do the grouping. You can pass an optional numTasks argument to set a different number of tasks. |
|
join(otherStream, [numTasks]) |
When called on two DStreams of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. |
|
cogroup(otherStream, [numTasks]) |
When called on a DStream of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, Seq[V], Seq[W]) tuples. |
|
transform(func) |
Return a new DStream by applying a RDD-to-RDD function to every RDD of the source DStream. This can be used to do arbitrary RDD operations on the DStream. |
|
updateStateByKey(func) |
Return a new "state" DStream where the state for each key is updated by applying the given function on the previous state of the key and the new values for the key. This can be used to maintain arbitrary state data for each key. |
特殊的Transformations
1.UpdateStateByKey Operation
UpdateStateByKey原语用于记录历史记录,上文中Word Count示例中就用到了该特性。若不用UpdateStateByKey来更新状态,那么每次数据进来后分析完成后,结果输出后将不在保存
2.Transform Operation
Transform原语允许DStream上执行任意的RDD-to-RDD函数。通过该函数可以方便的扩展Spark API。此外,MLlib(机器学习)以及Graphx也是通过本函数来进行结合的。
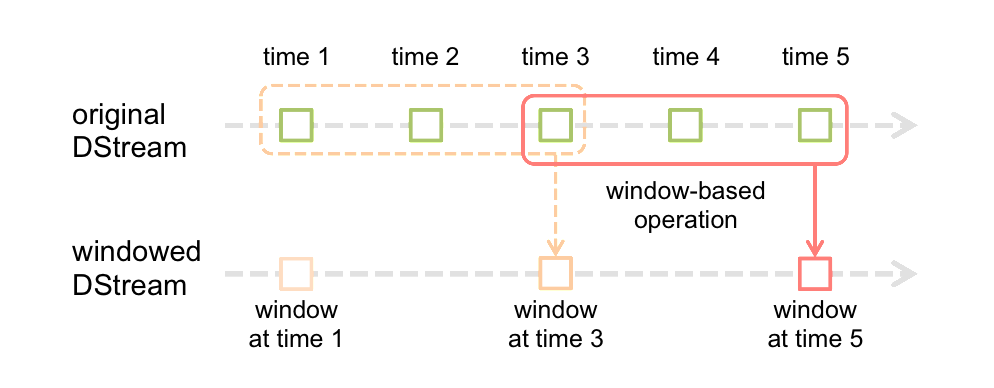
3.Window Operations
Window Operations有点类似于Storm中的State,可以设置窗口的大小和滑动窗口的间隔来动态的获取当前Steaming的允许状态
3.2.2. Output Operations on DStreams
Output Operations可以将DStream的数据输出到外部的数据库或文件系统,当某个Output Operations原语被调用时(与RDD的Action相同),streaming程序才会开始真正的计算过程。
|
Output Operation |
Meaning |
|
print() |
Prints the first ten elements of every batch of data in a DStream on the driver node running the streaming application. This is useful for development and debugging. |
|
saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as text files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as SequenceFiles of serialized Java objects. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]) |
Save this DStream's contents as Hadoop files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
|
foreachRDD(func) |
The most generic output operator that applies a function, func, to each RDD generated from the stream. This function should push the data in each RDD to an external system, such as saving the RDD to files, or writing it over the network to a database. Note that the function func is executed in the driver process running the streaming application, and will usually have RDD actions in it that will force the computation of the streaming RDDs. |
4. 实战
4.1. 用Spark Streaming实现实时WordCount
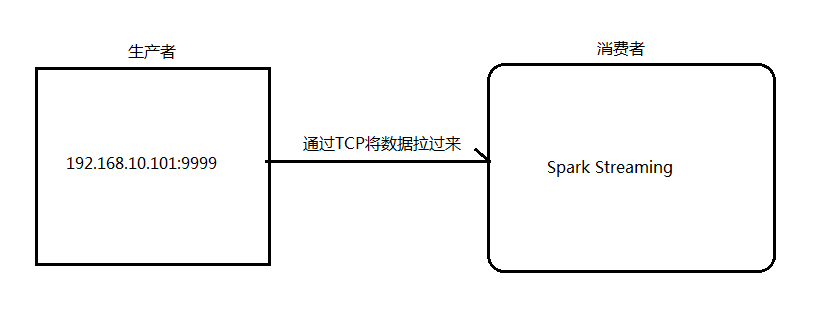
架构图:
1.安装并启动生成者
首先在一台Linux(ip:192.168.10.101)上用YUM安装nc工具
yum install -y nc
启动一个服务端并监听9999端口
nc -lk 9999
2.编写Spark Streaming程序
package cn.itcast.spark.streaming |
3.启动Spark Streaming程序:由于使用的是本地模式"local[2]"所以可以直接在本地运行该程序
注意:要指定并行度,如在本地运行设置setMaster("local[2]"),相当于启动两个线程,一个给receiver,一个给computer。如果是在集群中运行,必须要求集群中可用core数大于1
4.在Linux端命令行中输入单词

5.在IDEA控制台中查看结果

问题:结果每次在Linux段输入的单词次数都被正确的统计出来,但是结果不能累加!如果需要累加需要使用updateStateByKey(func)来更新状态,下面给出一个例子:
package cn.itcast.spark.streaming |
4.2. Spark Streaming整合Kafka完成网站点击流实时统计
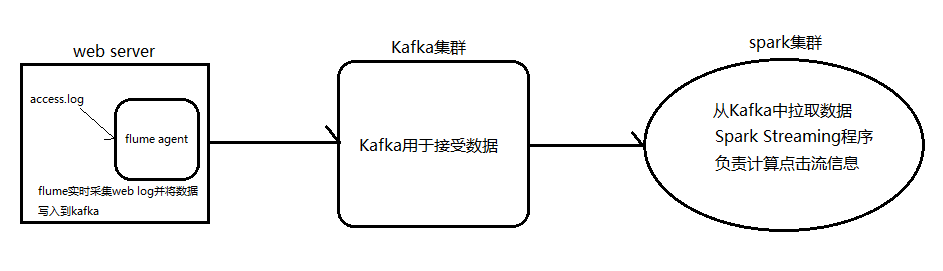
1.安装并配置zk
2.安装并配置Kafka
3.启动zk
4.启动Kafka
5.创建topic
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper node1.itcast.cn:2181,node2.itcast.cn:2181
--replication-factor 3 --partitions 3 --topic urlcount
6.编写Spark Streaming应用程序
package cn.itcast.spark.streaming // zkQuorum :zookeeper所在机器 groupId :topic所属群组 |