Given the root of a binary tree, turn the tree upside down and return the new root.
You can turn a binary tree upside down with the following steps:
- The original left child becomes the new root.
- The original root becomes the new right child.
- The original right child becomes the new left child.
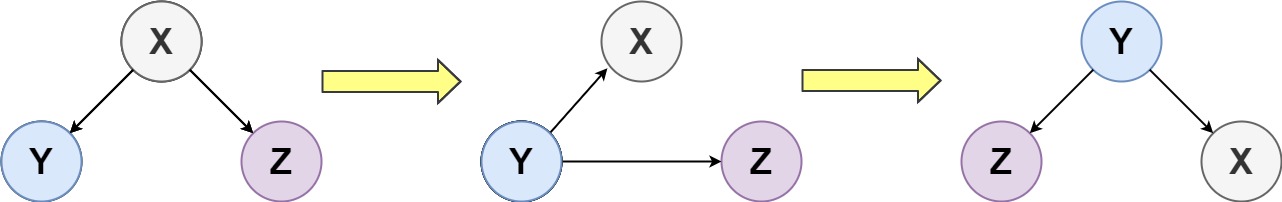
The mentioned steps are done level by level, it is guaranteed that every node in the given tree has either 0 or 2 children.
Example 1:
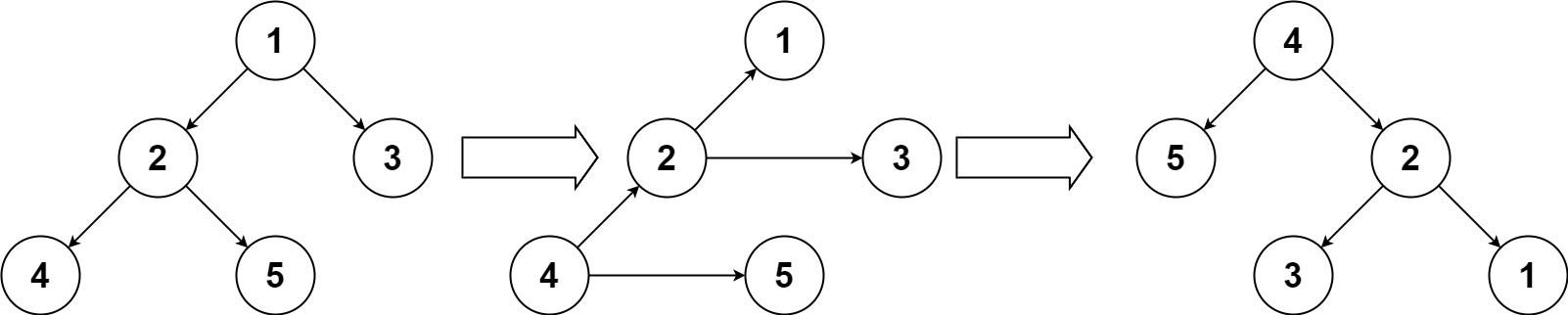
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: [4,5,2,null,null,3,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[0, 10]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10Every node has either 0 or 2 children.
上下翻转二叉树。题意是给一个二叉树,请你翻转一下。我的理解是基本是把这个二叉树顺时针旋转120度的感觉。
如上图,最小的左孩子成了根节点,而原来的根节点成了最小的右孩子。我这里给出递归和迭代两种做法。首先递归的思路是不断往左子树走,找到新的根节点,然后将新的根节点跟他的左右孩子分别连好,然后再断开原来的根节点及其左右孩子的联系。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { 18 // corner case 19 if (root == null || root.left == null && root.right == null) { 20 return root; 21 } 22 23 // normal case 24 TreeNode newRoot = upsideDownBinaryTree(root.left); 25 root.left.left = root.right; 26 root.left.right = root; 27 root.left = null; 28 root.right = null; 29 return newRoot; 30 } 31 }
迭代的做法需要用到stack,有点类似中序遍历的感觉。一开始也是需要不断往左子树走,边走边把遇到的节点入栈。当走到最左子树的时候会停下,此时pop出来的栈顶元素就是新的根节点newRoot。再pop一个元素出来,这个元素是新的根节点的右孩子,因为他也是原来的某个父级节点,所以我们暂时把他命名为oriParent。同时oriParent的右孩子(如果有的话),是newRoot的左孩子。最后记得把oriParent原来的左右链接断开。
时间O(n)
空间O(n)
Java实现
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode left; 6 * TreeNode right; 7 * TreeNode() {} 8 * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } 9 * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { 10 * this.val = val; 11 * this.left = left; 12 * this.right = right; 13 * } 14 * } 15 */ 16 class Solution { 17 public TreeNode upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { 18 // corner case 19 if (root == null) { 20 return null; 21 } 22 // normal case 23 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 24 while (root != null) { 25 stack.push(root); 26 root = root.left; 27 } 28 TreeNode newRoot = stack.pop(); 29 TreeNode cur = newRoot; 30 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { 31 TreeNode oriParent = stack.pop(); 32 cur.right = oriParent; 33 if (oriParent.right != null) { 34 cur.left = oriParent.right; 35 } 36 cur = oriParent; 37 oriParent.left = null; 38 oriParent.right = null; 39 } 40 return newRoot; 41 } 42 }