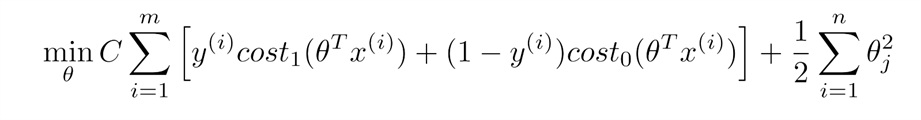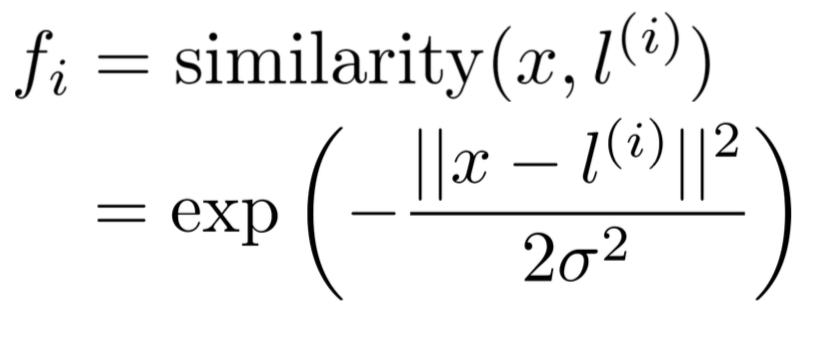吴恩达 MachineLearning Week7
知识点小结
- 支持向量机svm( support vector machine),将 cost function 的公式改造一下,得到如下公式
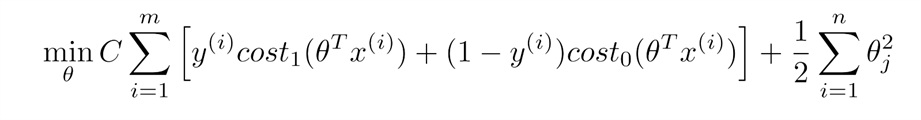
。其中 C 在这里等同于 1 / lambda。
- Gaussian kernel,对于输入数据做处理,用来计算数据集和选定的轴之间的相似程度,轴也是从数据集中选取。公式如下:
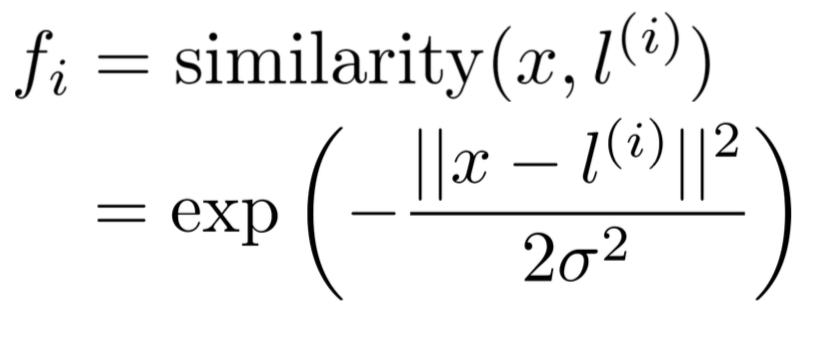
于是 fi 就用来代替 svm 方程中的 xi。
- 当 C 越大时,模型误差越小,但过拟合现象会越严重,越小时则相反。而当 Kernel 中的 sigma 值越大时。
模型误差会变大,但过拟合现象会越轻。
- Gaussian kernel 适用于数据参数的维度较少,而数据量适中的情况下。
课后作业代码
gaussianKernel.m
function sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma)
%RBFKERNEL returns a radial basis function kernel between x1 and x2
% sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2) returns a gaussian kernel between x1 and x2
% and returns the value in sim
% Ensure that x1 and x2 are column vectors
x1 = x1(:); x2 = x2(:);
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
sim = 0;
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return the similarity between x1
% and x2 computed using a Gaussian kernel with bandwidth
% sigma
%
%
sim = exp( -sum((x1 - x2) .^ 2) / (2 * sigma .^ 2));
% =============================================================
end
dataset3Params.m
function [C, sigma] = dataset3Params(X, y, Xval, yval)
%DATASET3PARAMS returns your choice of C and sigma for Part 3 of the exercise
%where you select the optimal (C, sigma) learning parameters to use for SVM
%with RBF kernel
% [C, sigma] = DATASET3PARAMS(X, y, Xval, yval) returns your choice of C and
% sigma. You should complete this function to return the optimal C and
% sigma based on a cross-validation set.
%
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
C = 1;
sigma = 0.3;
C_vec = [0.01 , 0.03 , 0.1 , 0.3 , 1 , 3 , 10 , 30]'
sigma_vec = [0.01 , 0.03 , 0.1 , 0.3 , 1 , 3 , 10 , 30]'
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return the optimal C and sigma
% learning parameters found using the cross validation set.
% You can use svmPredict to predict the labels on the cross
% validation set. For example,
% predictions = svmPredict(model, Xval);
% will return the predictions on the cross validation set.
%
% Note: You can compute the prediction error using
% mean(double(predictions ~= yval))
%
X2 = X;
X1 = X;
minError = 1000000000;
for i = 1 : length(C_vec)
for j = 1 : length(sigma_vec)
model = svmTrain(X, y, C_vec(i), @(X1, X2) gaussianKernel(X1, X2, sigma_vec(j)));
predictions = svmPredict(model, Xval);
error = mean(double(predictions ~= yval));
if error < minError
minError = error;
C = C_vec(i);
sigma = sigma_vec(j);
end
end
end
% =========================================================================
end
processEmail.m
function word_indices = processEmail(email_contents)
%PROCESSEMAIL preprocesses a the body of an email and
%returns a list of word_indices
% word_indices = PROCESSEMAIL(email_contents) preprocesses
% the body of an email and returns a list of indices of the
% words contained in the email.
%
% Load Vocabulary
vocabList = getVocabList();
% Init return value
word_indices = [];
% ========================== Preprocess Email ===========================
% Find the Headers (
and remove )
% Uncomment the following lines if you are working with raw emails with the
% full headers
% hdrstart = strfind(email_contents, ([char(10) char(10)]));
% email_contents = email_contents(hdrstart(1):end);
% Lower case
email_contents = lower(email_contents);
% Strip all HTML
% Looks for any expression that starts with < and ends with > and replace
% and does not have any < or > in the tag it with a space
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '<[^<>]+>', ' ');
% Handle Numbers
% Look for one or more characters between 0-9
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[0-9]+', 'number');
% Handle URLS
% Look for strings starting with http:// or https://
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, ...
'(http|https)://[^s]*', 'httpaddr');
% Handle Email Addresses
% Look for strings with @ in the middle
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[^s]+@[^s]+', 'emailaddr');
% Handle $ sign
email_contents = regexprep(email_contents, '[$]+', 'dollar');
% ========================== Tokenize Email ===========================
% Output the email to screen as well
fprintf('
==== Processed Email ====
');
% Process file
l = 0;
while ~isempty(email_contents)
% Tokenize and also get rid of any punctuation
[str, email_contents] = ...
strtok(email_contents, ...
[' @$/#.-:&*+=[]?!(){},''">_<;%' char(10) char(13)]);
% Remove any non alphanumeric characters
str = regexprep(str, '[^a-zA-Z0-9]', '');
% Stem the word
% (the porterStemmer sometimes has issues, so we use a try catch block)
try str = porterStemmer(strtrim(str));
catch str = ''; continue;
end;
% Skip the word if it is too short
if length(str) < 1
continue;
end
% Look up the word in the dictionary and add to word_indices if
% found
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to add the index of str to
% word_indices if it is in the vocabulary. At this point
% of the code, you have a stemmed word from the email in
% the variable str. You should look up str in the
% vocabulary list (vocabList). If a match exists, you
% should add the index of the word to the word_indices
% vector. Concretely, if str = 'action', then you should
% look up the vocabulary list to find where in vocabList
% 'action' appears. For example, if vocabList{18} =
% 'action', then, you should add 18 to the word_indices
% vector (e.g., word_indices = [word_indices ; 18]; ).
for i = 1 : length(vocabList)
if strcmp(str,vocabList{i}) == 1
word_indices = [word_indices ; i];
break
end
end
% =============================================================
% Print to screen, ensuring that the output lines are not too long
if (l + length(str) + 1) > 78
fprintf('
');
l = 0;
end
fprintf('%s ', str);
l = l + length(str) + 1;
end
% Print footer
fprintf('
=========================
');
end
emailFeatures.m
function x = emailFeatures(word_indices)
%EMAILFEATURES takes in a word_indices vector and produces a feature vector
%from the word indices
% x = EMAILFEATURES(word_indices) takes in a word_indices vector and
% produces a feature vector from the word indices.
% Total number of words in the dictionary
n = 1899;
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
x = zeros(n, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return a feature vector for the
% given email (word_indices). To help make it easier to
% process the emails, we have have already pre-processed each
% email and converted each word in the email into an index in
% a fixed dictionary (of 1899 words). The variable
% word_indices contains the list of indices of the words
% which occur in one email.
%
% Concretely, if an email has the text:
%
% The quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog.
%
% Then, the word_indices vector for this text might look
% like:
%
% 60 100 33 44 10 53 60 58 5
%
% where, we have mapped each word onto a number, for example:
%
% the -- 60
% quick -- 100
% ...
%
% (note: the above numbers are just an example and are not the
% actual mappings).
%
% Your task is take one such word_indices vector and construct
% a binary feature vector that indicates whether a particular
% word occurs in the email. That is, x(i) = 1 when word i
% is present in the email. Concretely, if the word 'the' (say,
% index 60) appears in the email, then x(60) = 1. The feature
% vector should look like:
%
% x = [ 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ... 0 0 0 0 1 ... 0 0 0 1 0 ..];
%
%
for i = 1 : length(word_indices)
x(word_indices(i)) = 1;
end
% =========================================================================
end