Berland has n cities connected by m bidirectional roads. No road connects a city to itself, and each pair of cities is connected by no more than one road. It is not guaranteed that you can get from any city to any other one, using only the existing roads.
The President of Berland decided to make changes to the road system and instructed the Ministry of Transport to make this reform. Now, each road should be unidirectional (only lead from one city to another).
In order not to cause great resentment among residents, the reform needs to be conducted so that there can be as few separate cities as possible. A city is considered separate, if no road leads into it, while it is allowed to have roads leading from this city.
Help the Ministry of Transport to find the minimum possible number of separate cities after the reform.
The first line of the input contains two positive integers, n and m — the number of the cities and the number of roads in Berland (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000).
Next m lines contain the descriptions of the roads: the i-th road is determined by two distinct integers xi, yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n, xi ≠ yi), where xi and yi are the numbers of the cities connected by the i-th road.
It is guaranteed that there is no more than one road between each pair of cities, but it is not guaranteed that from any city you can get to any other one, using only roads.
Print a single integer — the minimum number of separated cities after the reform.
4 3
2 1
1 3
4 3
1
5 5
2 1
1 3
2 3
2 5
4 3
0
6 5
1 2
2 3
4 5
4 6
5 6
1
In the first sample the following road orientation is allowed: 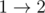 ,
,  ,
,  .
.
The second sample: 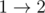 ,
, 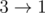 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  .
.
The third sample: 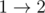 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  .
.
解题报告:
1、我的解决图形问题的数据结构,a、矩阵邻接图,b、STL,(vector)
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,m; int ans=0; int ans1; bool vis[100005];///是否访问过,若访问过,则构成回路,则没有孤立的点 vector<int>vec[100005];///记录各点的路径 void dfs(int pos,int pre) { if(vis[pos]) ///如果构成回路,ans1=0; { ans1=0; return ; } vis[pos]=1; ///广搜下面的点 for(int i=0;i<vec[pos].size();i++) { if(vec[pos][i]!=pre)///单向路径 dfs(vec[pos][i],pos); } } int main() { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); ///存各个点的路径 for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int a,b; scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); vec[a].push_back(b); vec[b].push_back(a); } ///搜索各个点 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { ///搜索过就不用搜了 if(vis[i]) continue; else { ans1=1; ///可能不能构成回路,先置为1,准备多一个孤立点 dfs(i,0); ///开始搜索这条路 ans=ans+ans1; } } printf("%d ",ans); return 0; }