一、今日学习内容:
今天练习实验五的内容。
二、遇到的问题:
无
三、明日计划:
明天继续练习实验六的习题。
今日练习的具体内容如下:
1.人与学生
设计一个类people,有保护数据成员:age(年龄,整型),name(姓名,string),行为成员:两个构造函数(一个默认,另一个有参数);默认析构函数;void setValue(int m, string str)给age和name赋值;void display()输出age和name。
设计一个学生类student,公有继承类people,有私有成员:ID(学号,整型),行为成员:两个构造函数(一个默认,另一个有参数);默认析构函数;void setID(int m)给ID赋值;void displayID()输出ID。
在main函数定义学生对象,给对象初始化赋值或调用setValue()和setID()赋值,并输出学生的信息。
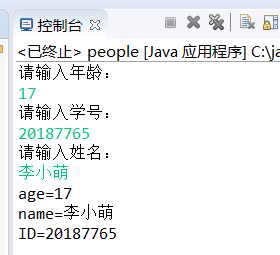
import java.util.Scanner; public class people { protected int age; protected String name; people(){ } people(int a,String s){ age=a; name=s; } public void setValue(int a,String s) { age=a; name=s; } public void display() { System.out.println("age="+age); System.out.println("name="+name); } public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); Scanner sc1=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入年龄:"); int n=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入学号:"); String i=sc1.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入姓名:"); String str=sc1.nextLine(); student1 stu=new student1(); stu.setValue(n, str); stu.setID(i); stu.display(); stu.displayID(); } } class student1 extends people{ private String ID; student1(){ } student1(String b){ ID=b; } public void displayID() { System.out.println("ID="+ID); } public void setID(String m) { ID=m; } }
测试截图:
2.多继承(用接口实现)
学生具有姓名,班级,学号等属性,有上课等行为;教师具有工号,工资等属性,有教课等行为;助教既是学生,又是老师,具有学生和老师的双重属性。请用类的多继承机制实现上述问题。
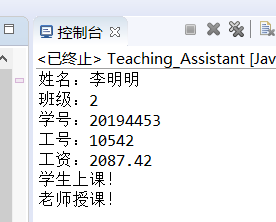
interface student2{ int ID=20194453; int class_s=2; String name="李明明"; void attend_class(); void display_student(); } interface teacher{ int ID_work=10542; double salary=2087.42; void teach_class(); void display_teacher(); } public class Teaching_Assistant implements student2,teacher { @Override public void attend_class() { System.out.println("学生上课!"); } public void teach_class() { System.out.println("老师授课!"); } public void display_student() { System.out.println("姓名:"+name); System.out.println("班级:"+class_s); System.out.println("学号:"+ID); } public void display_teacher() { System.out.println("工号:"+ID_work); System.out.println("工资:"+salary); } public static void main(String[] args) { student2 s=new Teaching_Assistant(); teacher t=new Teaching_Assistant(); s.display_student(); t.display_teacher(); s.attend_class(); t.teach_class(); } }
测试截图:
3.虚基类应用
编写动物类animal,受保护数据成员name(名称,string),age(年龄,int),公有函数成员void show(),输出“Animal, 名称, 年龄”;公有派生鱼类fish和兽类beast,鱼类增加受保护数据成员velocity(速度,int),公有函数成员void show(),输出“Fish, 名称, 年龄, 速度”;兽类增加受保护数据成员appetite(食量,int),公有函数成员void show(),输出“Beast, 名称, 年龄, 食量”;鱼类和兽类再公有派生两栖动物类amphibious,无添加数据成员,有公有函数成员void show(),输出 “Fish, 名称, 年龄, 速度”(第一行),“Beast, 名称, 年龄, 食量”(第二行)。每个类均有一个构造函数用于设置该类所有数据成员的属性值。
public abstract class animal { protected int age; protected String name; public abstract void show(); public abstract void setValue(int a,String s); public static void main(String[] args) { fish f=new fish(); f.setValue(2, "鲫鱼"); f.setvalue_fish(30); f.show(); f.show_fish(); System.out.println(); Beast b=new Beast(); b.setValue(3, "狮子"); b.setvalue_beast(39); b.show(); b.show_beast(); } } class fish extends animal{ protected int velocity; public void setvalue_fish(int v) { velocity=v; } public void show_fish() { System.out.println("Fish"); System.out.println("名称:"+name); System.out.println("年龄:"+age); System.out.println("速度:"+velocity); } @Override public void show() { System.out.println("年龄:"+age); System.out.println("姓名:"+name); } @Override public void setValue(int a,String s) { age=a; name=s; } } class Beast extends animal{ protected int appetite; void setvalue_beast(int x) { appetite=x; } public void show_beast() { System.out.println("Fish"); System.out.println("名称:"+name); System.out.println("年龄:"+age); System.out.println("食量:"+appetite); } @Override public void show() { System.out.println("年龄:"+age); System.out.println("姓名:"+name); } @Override public void setValue(int a, String s) { age=a; name=s; } }
测试截图:
