本章主要介绍了标准库顺序容器,包括
顺序容器的公共接口,如构造函数,添加/删除操作等
利用迭代器访问容器
不同顺序容器的差异
string的特殊操作
容器适配器,如栈,队列等
9.1
“按字典序插入到容器中”需要对数据进行排序,因此需要再容器中进行频繁的插入操作,vector和deque都是寻秩操作,vector在尾部以外的位置插入都很慢,deque在头尾以外位置插入很慢,而list在任意位置插入/删除都较快,所以(a)应使用list更合适。
(b)需要头尾插入/删除操作,list和dque都可以,但是需要频繁随机访问,deque更合适
(c)因为随机访问,也不需要头部进行插入/删除操作,vector更合适
9.2
list<deque<int>>idl;
9.3
它们指向同一个容器中的元素,或者是容器最后一个元素之后的位置,并且可以通过递增begin来达到end,即end不会出现在begin之前,但是编译器不会强制要求这些,程序员应确保这些约定。
9.4
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <iterator> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 bool find(vector<int>::iterator beg, vector<int>::iterator end, int ival) 8 { 9 for (; beg != end; beg++) 10 { 11 if (*beg == ival) 12 return true; 13 else 14 return false; 15 } 16 } 17 18 int main() 19 { 20 vector<int>ivec={1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 21 cout << find(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), 9) << endl; 22 cout << find(ivec.begin(), ivec.end(), 12) << endl; 23 system("pause"); 24 return 0; 25 }
非常简单的一个查找功能,但是执行时返回的都是0,调试过程中第一个是true,第二个是false,没问题
9.5
只需将上题的函数返回类型修改
1 vector<int>::iterator find(vector<int>::iterator beg, vector<int>::iterator end, int ival) 2 { 3 for (; beg != end; beg++) 4 { 5 if (*beg == ival) 6 return beg; 7 else 8 return end; 9 } 10 }
9.6
list迭代器不支持<运算,只支持递增、递减、==以及!=运算。因为从数据结构的角度,deque和vector中的元素在内存中是连续的,因此可以实现迭代器大小,而list则是将元素以链表方式存储,两个指针的大小关系与它们指向的元素前后关系并一定吻合,实现<运算。
9.7
vector<int>::iterator
9.8
每个容器都定义了多个类型,如:size_type、iterator、const iterator通过类型别名,可以在不了解容器中元素的情况下使用它。如果需要元素类型,可以使用容器的value_type,如果需要元素类型的一个引用,可以使用reference或const reference。9.8答案如下
读取string的list中的元素: list<string>::value_type
写入list 使用list<string>::reference 元素的左值类型,与value_type&相同
9.9
以c开头的版本是C++新标准引入的,用以支持auto与begin和end函数结合使用的,,cbegin返回指向容器第一个元素的const迭代器,可以用来访问只读方式访问容器元素,不能对容器元素做修改。当不需要写访问时应用cbegin,begin与auto结合使用时获得的迭代器依赖于容器类型。有两个版本,一个const的一个非const的。
9.11
1 vector<int> iv1;//执行默认初始化,vector为空,即size为0,容器中没有元素,capacity为0,未分配存储空间 2 vector<int>iv2(iv1);//拷贝初始化,iv2为iv1的拷贝,要求iv2的类型与和元素数量必须与iv1相同 3 vector<int> iv3 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//列表初始化,iv3初始化为列表中元素的拷贝 4 vector<int>iv4(iv3.begin() + 1, iv3.end());//iv4初始化为两个迭代器制定范围的元素的拷贝,元素类型必须相同,容器 5 //类型可以不同 6 vector<int>iv5(5);//默认初始化,iv5包含5个元素,每个元素的初始值执行默认值初始化 7 vector<int>iv6(6, 6);//iv6初始化为6个6
9.12
上题注释部分有解释
list<int>与vector<double>容器类型不同,但int和double可以转换,可以使用迭代器范围实现拷贝。vector<int>可以直接用来拷贝初始化vector<double>。
9.14
将char* 转换为string,使用迭代器范围赋值拷贝
1 list<char*>cl = { "Hello","C++","primer" }; 2 vector<string>svec; 3 svec.assign(cl.begin(), cl.end()); 4 for (auto it : svec) 5 cout << it << " "; 6 cout << endl;
9.15
标准库容器支持关系运算
1 vector<int>ivec1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 }; 2 vector<int>ivec2 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 }; 3 vector<int>ivec3 = { 1,2,3,5,4,6 }; 4 vector<int>ivec4 = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; 5 cout << (ivec1 == ivec2) << endl; 6 cout << (ivec1 == ivec3) << endl; 7 cout << (ivec1 == ivec4) << endl; 8 ivec1.push_back(7); 9 for (auto it : ivec1) 10 cout << it << " "; 11 cout << endl; 12 ivec1.pop_back(); 13 for (auto it : ivec1) 14 cout << it << " "; 15 cout << endl; 16 cout << (ivec1 == ivec2) << endl;
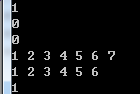
由执行结果看,两个vector的capacity不会影响相等性判断,我vec1的添加/删除操作导致vector扩容后仍与我vec2相等
9.16
比较一个list<int>中元素是否与一个vector<int>中的元素是否相等,首先应比较个数是否相等,若个数不等,则直接给出不等退出。若个数相等,再比较对应元素是否相等,需要遍历两个容器
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <list> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 bool equal(list<int>&il, vector<int>&iv) 8 { 9 if (il.size() != iv.size()) 10 return false; 11 auto lbeg = il.cbegin(); 12 auto vbeg = iv.cbegin(); 13 auto lend = il.cend(); 14 for (; lbeg != lend;lbeg++, vbeg++) 15 { 16 if (*lbeg != *vbeg) 17 return false; 18 else 19 return true; 20 } 21 22 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 list<int> il1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; 28 list<int>il2 = { 1,2,3,4,6 }; 29 vector<int>iv1 = { 1,2,3,4 }; 30 vector<int>iv2 = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; 31 cout << equal(il1, iv1) << endl; 32 cout << equal(il1, iv2) << endl; 33 cout << equal(il2, iv2) << endl; 34 35 system("pause"); 36 return 0; 37 }
9.18
1 string word; 2 deque<string>sd; 3 cout << "please enter the strings:" << endl; 4 while (cin >> word) 5 //sd.push_back(word); 6 sd.push_front(word); 7 for (auto it:sd) 8 cout << it << " "; 9 cout << endl;
容器是deque,使用push_front,首尾添加元素的性能比较好,但是,push_front添加元素的顺序与输出顺序是相反的,若想保持顺序相同,可以使用push_back。
9.19
与上一题并无太大差别,
9.20
可以延伸到按整除某个数的得到的余数,插入到deque中
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <list> 3 #include <deque> 4 #include <vector> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main() 9 { 10 int num; 11 list<int>il; 12 deque<int>odd_deque; 13 deque<int>even_deque; 14 cout << "please input numbers:" << endl; 15 while (cin >> num) 16 il.push_back(num); 17 //9.20 18 /*for (auto it = il.begin(); it != il.end(); ++it) 19 { 20 if (*it % 2) 21 odd_deque.push_back(*it); 22 else 23 even_deque.push_back(*it); 24 } 25 cout << "奇数有:" << endl; 26 for (auto i : odd_deque) 27 cout << i << " "; 28 cout << endl; 29 cout << "偶数有:" << endl; 30 for (auto i : even_deque) 31 cout << i << " "; 32 cout << endl;*/ 33 34 //9.20延伸,实现使用vector将被4整除的和余数分别为1,2,3数放在四个vector中 35 vector<int> iv0,iv1,iv2,iv3; 36 for (auto it = il.begin(); it != il.end(); ++it) 37 { 38 switch (*it%4) 39 { 40 case 0: 41 iv0.push_back(*it); 42 break; 43 case 1: 44 iv1.push_back(*it); 45 break; 46 case 2: 47 iv2.push_back(*it); 48 break; 49 case 3: 50 iv3.push_back(*it); 51 break; 52 53 54 } 55 } 56 cout << "被4整除的是:" << endl; 57 for (auto i : iv0) 58 cout << i << " "; 59 cout << endl; 60 cout << "余数为1的是;" << endl; 61 for (auto i : iv1) 62 cout << i << " "; 63 cout << endl; 64 cout << "余数为2的是;" << endl; 65 for (auto i : iv2) 66 cout << i << " "; 67 cout << endl; 68 cout << "余数为3的是;" << endl; 69 for (auto i : iv3) 70 cout << i << " "; 71 cout << endl; 72 system("pause"); 73 return 0; 74 75 }
9.21
循环工作的过程和结果是一样的,只是list的首元素之前插入新元素的性能优于vector的,因为vector需要移动后面所有元素。
9.22
箱一个vector、string或deque插入元素会是现有指向容器的迭代器、引用和指针失效。
循环中没有对iter进行递增操作,iter不能向mid推进,其次,即使加入了iter++,由于使用了insert插入新元素,insert返回的是指向新元素的迭代器,原iter已失效,iter++也不能起到将迭代器向前推进一个位置的作用,修改如下:
应将insert返回的迭代器赋给iter,这样,iter始终指向新插入的元素,而insert是将新元素插入到原iter指向的元素的前一个元素,因此iter++应执行两次才是原来的iter指向的元素下一个元素。另外,insert会使mid失效,所以循环无法在正确位置结束,所以mid=iv.begin()+org_size/2+new_ele,其中,org_size=iv.size,iv未插入任何新元素之前,new_ele初始值为0,每插入一个元素,递增1。修改完整的如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 vector<int>iv = { 1,2,2,1 }; 9 int some_value = 2; 10 vector<int>::iterator iter = iv.begin(); 11 int org_size = iv.size(); 12 int new_ele = 0; 13 while (iter != (iv.begin() + org_size + new_ele)) 14 { 15 if (*iter == some_value) 16 { 17 iter = iv.insert(iter, 2 * some_value); 18 new_ele++; 19 iter++; 20 iter++; 21 } 22 else 23 iter++; 24 } 25 26 for (auto it : iv) 27 cout << it << " "; 28 cout << endl; 29 system("pause"); 30 return 0; 31 }
上面只是简单实现原程序想要实现的功能,vector中的元素可以从指定文件中读取,比较的元素可以由用户输入
9.23
四个值一样,都是vector中的唯一的元素
9.24
at和下标操作只适用于string、vector、deque和array
在容器中访问元素的成员函数(即,front、back、下标和at)返回的都是引用,如果容器是一个const对象,返回是是一个const引用。
9.24
使用前应先检查vector是否为空,若为空,使用at访问时会抛出一个out_of_range异常,程序不能捕获异常就会直接退出,后面三种不会抛出异常,而是直接退出。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 vector<int> iv = { 1,2,3 }; 9 if (iv.size() != 0) 10 { 11 cout << iv.at(0) << endl; 12 cout << iv[0] << endl; 13 cout << iv.front() << endl; 14 cout << *(iv.begin()) << endl; 15 } 16 system("pause"); 17 return 0; 18 }
9.25
如果ele1和ele2相等,则容器保持不变,即使两个两个迭代器都指向尾后迭代器也是如此
9.26
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <list> 4 #include <iterator> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 int ia[] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; 10 vector<int>iv; 11 list<int>il; 12 //iv.assign(ia,ia.end()); 13 iv.assign(ia, ia + 10); 14 il.assign(ia, ia+10); 15 for (auto it : iv) 16 cout << it << " "; 17 cout << endl; 18 for (auto it : il) 19 cout << it << " "; 20 cout << endl; 21 22 //vector<int>::iterator it1 =iv.begin(); 23 /*for (auto it1 : iv) 24 { 25 if() 26 }*/ 27 vector<int>::iterator it1 = iv.begin(); 28 while (it1 != iv.end()) 29 { 30 if (!(*it1%2)) 31 it1 = iv.erase(it1); 32 else 33 it1++; 34 } 35 list<int>::iterator it2 = il.begin(); 36 while (it2 != il.end()) 37 { 38 if (*it2 % 2) 39 it2 = il.erase(it2); 40 else 41 it2++; 42 43 } 44 for (auto it : iv) 45 cout << it << " "; 46 cout << endl; 47 for (auto it : il) 48 cout << it << " "; 49 cout << endl; 50 51 system("pause"); 52 return 0; 53 }
9.27
forward_list 是单向链表数据结构,只有前驱节点指向后继节点的指针,没有反向的指针,所以当删除一个元素后,应该调整前驱指针指向后继指针,从而删除当前元素。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <forward_list> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 int num; 9 forward_list<int> iflst; 10 cout << "please enter numbers:" << endl; 11 while (cin >> num) 12 iflst.push_front(num);//array ,forward_list不支持push_back 13 14 //for (auto i : iflst)//由于每次进list都是在头部,所以输出与输入顺序相反 15 // cout << i << " "; 16 auto pre = iflst.before_begin(); 17 auto curr = iflst.begin(); 18 //for (auto it = curr; it != iflst.end(); ++it) 19 while(curr!=iflst.end()) 20 { 21 if (*curr % 2) 22 { 23 curr=iflst.erase_after(pre); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 //curr = pre; 28 pre =curr; 29 curr++; 30 } 31 32 } 33 34 for (auto i : iflst) 35 cout << i << " "; 36 cout << endl; 37 system("pause"); 38 return 0; 39 }
另外,输出的顺序与输入进list的元素顺序相反。
9.28
还是联系forward_list 的操作
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <forward_list> 3 #include <string> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 void find_insert(forward_list<string>&sflst, const string& str1, const string& str2) 8 { 9 auto pre = sflst.before_begin(); 10 auto curr = sflst.begin(); 11 bool inserted = false; 12 while (curr != sflst.end()) 13 { 14 if (*curr == str1) 15 { 16 curr = sflst.insert_after(curr, str2);//insert_after 返回的指向插入后元素的迭代器,也就是指向str2 17 inserted = true; 18 } 19 else 20 pre = curr; 21 curr++; 22 } 23 if (!inserted) 24 sflst.insert_after(pre, str2);//如果没有找到,此时pre指向sflst的最后一个元素,使用insert_after 插入到尾后 25 } 26 27 int main() 28 { 29 forward_list<string> sflst = { "Hello","C++" }; 30 find_insert(sflst, "C++", "primer"); 31 for (auto it : sflst) 32 cout << it << " "; 33 cout << endl; 34 forward_list<string>sflst1 = { "Hello","Primer" }; 35 find_insert(sflst1, "Hello", "C++"); 36 for (auto it : sflst1) 37 cout << it << " "; 38 cout << endl; 39 40 system("pause"); 41 return 0; 42 }
9.3.5 改变容器的大小
resizelai:增大或缩小容器,array不支持resize。c.resize(n):调整c的大小为n.
9.29
1 vec.resize(100);//会想vec末尾添加75个元素,并进行值初始化 2 vec.resize(10);//将vec末尾90个元素
9.30
因为调用单参数的resize,若是添加元素,会对新元素进行初始化,若元素是类类型,该类必须提供默认构造函数
9.3.6 容器操作可能使迭代器失效
由于想迭代器添加元素和从迭代器删除元素的代码可能会使迭代器失效,因此必须保证每次改变容器的操作之后懂正确的重新定位迭代器,尤其是vector、string和deque。
改变容器的循环程序:
1 //删除偶数元素,复制奇数元素 2 vector<int> iv = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 }; 3 auto iter = iv.begin(); 4 while (iter != iv.end()) 5 { 6 if (*iter % 2) 7 { 8 iter = iv.insert(iter, *iter);//复制当前元素,该语句在iter指向的元素之前添加一个*iterd 元素, 9 //返回指向该元素的迭代器,所以iter加2才能指向原来iter的下一个迭代器 10 iter += 2; 11 } 12 else 13 iter = iv.erase(iter);//删除偶数元素,erase返回删除元素之后的元素的迭代器,不用再移动迭代器 14 15 16 }
不要保存end返回的迭代器
当向vector或string添加元素或从其删除元素,或在deque中首元素之外的任何位置添加/删除元素,原来end返回的迭代器总是失效。因此添加或删除的循环过程必须反复调用end,不能在循环之前保存end返回的迭代器9.31
9.31
list和forward_list与其他容器不同的是,迭代器不支持加减运算,因为链表中元素在内存中可能不是连续的,无法通过地址间加减偏移量实现,所以应该多次调用递增运算符实现加法操作
所以将上题第10行改为
1 iter++; 2 iter++;
就是list实现相同功能的代码,但是forward_list是单链表结构,删除元素时需要将当前的前驱指向当前节点的后继,需要维护“前驱”和“后继”两个迭代器
while循环如下
1 auto pre = iflst.before_begin(); 2 auto curr = iflst.begin(); 3 while (curr != iflst.end()) 4 { 5 if (*curr % 2) 6 { 7 curr = iflst.insert_after(curr, *curr); 8 pre = curr; 9 curr++; 10 } 11 else 12 curr = iflst.erase_after(pre); 13 }
9.32
不合法。因为很多编译器对于实参求值、向形参传递的处理顺序是从右至左的。这样的hau话,insert语句就是先求值,再插入,那么插入的是当前奇数的下一个元素,insert的第一个参数的迭代器指向的位置是错误的,造成程序混乱,最终导致程序崩溃。
9.33
向vector添加元素后,原有迭代器会失效。所以,若不将insert的返回结果赋给begin,原有的又已失效,会造成程序混乱崩溃,对于此程序,保存end和不将insert的返回值赋给begin都会使程序崩溃
9.34
while循环没有花括号,那么++iter就是循环体外的语句了,不再是循环体内的最后一句,所以,容器只要不为空,程序就会进入死循环。
1.若第一个元素是奇数,if条件满足,复制当前奇数元素,并返回指向当前元素的迭代器,还是奇数,继续执行,一直循环下去
2.若第一个元素是偶数,if不会被执行,iter也不变,继续while,if仍然不被执行,iter任然不变,保持这种状态一直循环下去
9.35
容器的size是指容器中已保存的元素的数量,capacity是在容器没有重新分配内存时可以保存元素的数量。所以capacity>=size
9.37
list是链表,添加新元素时,会从内存分配一个新节点保存它,删除元素时,该节点占用的内存会被立即释放,所以,链表占用的内存空间与保存当前元素所需空间相等,array是大小固定的数组,定义时一次性分配内存,不可改变
9.38
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <vector> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 vector<int>iv; 9 /*vector<int>::size_type s; 10 vector<int>::size_type c*/; 11 12 //for ( s = iv.size, c = iv.capacity; s <= c; s++) 13 iv.push_back(3); 14 cout << "size: " << iv.size() << "," << "capacity: " << iv.capacity() << endl; 15 16 17 /*for (s = iv.size, c = iv.capacity; s <= c; s++)*/ 18 iv.push_back(3); 19 cout << "size: " << iv.size() << "," << "capacity: " << iv.capacity() << endl; 20 21 //for (s = iv.size, c = iv.capacity; s <= c; s++) 22 iv.push_back(3); 23 cout << "size: " << iv.size() << "," << "capacity: " << iv.capacity() << endl; 24 25 //for (s = iv.size, c = iv.capacity; s <= c; s++) 26 iv.push_back(3); 27 cout << "size: " << iv.size() << "," << "capacity: " << iv.capacity() << endl; 28 for (auto it : iv) 29 cout << it << " "; 30 cout << endl; 31 system("pause"); 32 return 0; 33 }
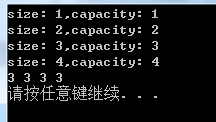
我的编译器capacity的增长是与size一样的,之前看到数据结构中有提到vector的capacity是成倍增长的
9.39
reserse为svec分配了可容纳1024个string的内存空间,接着向svec添加元素,如果string数量不大于1024,则capacity不变,否则按一定规则扩容,然后resize向svecd 末尾添加当前string数量一半的内存空间,并初始化为空字符串。如果capacity不足,则扩容。
9.40
跟编译器有关
9.41
vector提供了data函数,返回内存空间首地址。将此返回值作为string的构造函数的第一个参数,将vector的size返回值作为第二个参数,可以获取vector<char>中是数据。
1 vector<char> vc = { 'H','e','l','l','o' }; 2 string str(vc.data(), vc.size()); 3 cout << str << endl;
9.42
每次至少读取100个字符,可以使用reserve预先为string分配空间,然后逐个读取字符存入string
1 void read_string(string& str) 2 { 3 str.reserve(100); 4 char ch; 5 while (cin >> ch) 6 str.push_back(ch); 7 }
9.43
1.使用迭代器iter遍历s,如果s中剩余字符串长度小于oldVal的长度时,不需要再检查了,否则,继续检查
2.一旦出现相等的字符,需要利用循环检查后面的是否每一个字符与oldVal 中的相等。直到遍历完oldVal。否则便不是相等
3.一旦在s中找到oldVal,使用erase删除s中与oldVal相等的部分,然后使用循环和insert将newVal插入s中,并且由于insert是将要插入的元素插入到当前iter指向的位置之前,所以使用逆序插入。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 void replace(string &str, const string& str1, const string& str2) 9 { 10 auto len = str1.size(); 11 if (!len) 12 return; 13 auto iter = str.begin(); 14 while (iter<=str.end()-len) 15 16 { 17 auto iter1 = iter; 18 auto iter2 = str1.begin(); 19 while (iter2 != str1.end() && *iter1 == *iter2) 20 { 21 iter1++; 22 iter2++; 23 } 24 if (iter2 == str1.end()) 25 { 26 iter = str.erase(iter, iter1); 27 if (str2.size()) 28 { 29 iter2 = str2.end(); 30 while (iter2 > str2.begin()) 31 32 { 33 iter2--; 34 iter = str.insert(iter, *iter2); 35 36 } 37 } 38 else 39 iter += str2.size(); 40 } 41 else 42 iter++; 43 } 44 } 45 int main() 46 { 47 string s = "I have pass tho the line,have you pass tho it."; 48 string s1 = "tho"; 49 string s2 = "through"; 50 replace(s, s1, s2); 51 cout << s << endl; 52 system("pause"); 53 return 0; 54 }
9.44
使用stirng 的find()函数和replace()函数
1 void replace_fun(string& s, const string& oldVal, const string& newVal) 2 { 3 string::size_type np = 0;//string 的find()函数,若查找成功,返回的是按查找规则找到的第一个字符的位置, 4 //若失败,返回的是npos,就是-1; 5 while ((np = s.find(oldVal, np)) != string::npos) 6 { 7 s.replace(np, oldVal.size(), newVal); 8 np += newVal.size(); 9 } 10 }
string类提供了6个不同的搜索函数,每个函数都有4个重载版本,每个搜索操作都返回一个string::size_type值,表示匹配发生位置下标,如果搜索失败,则返回一个名为string::npos 的static成员。标准库将npos定义为一个const string::size_type类型,并初始化为-1.
9.45
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void appellation(string &name, string& pre, string& succ) 7 { 8 //name.insert(name.begin(), 1, " ");//vs2015不支持这种操作 9 name.insert(0, " "); 10 //name.insert(name.begin(), pre.begin(), pre.end()); 11 //还可以使用长度管理操作实现 12 name.insert(0, pre); 13 //name.append(" "); 14 //长度管理实现 15 name.insert(name.size(), " "); 16 17 //name.append(succ.begin(), succ.end()); 18 //长度管理实现 19 name.insert(name.size(), succ); 20 21 22 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 string strName = "Willie Smith"; 28 string pre = "Mr"; 29 string succ = "II"; 30 //appellation(strName, "Mr", "II");//如果是这样,则appellation函数后两个参数应该是const型 31 //appellation(string& ,const string&,const string&); 32 appellation(strName, pre, succ); 33 cout << strName << endl; 34 system("pause"); 35 return 0; 36 }
string的搜索操作
1 str.find_first_of(args);//在str中查找 args中任何一个字符串第一次出现的位置 2 str.find_first_not_of(args);//在str中查找第一个不在args中的字符
9.47
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //void find_char(string& str1, string& str2) 7 void find_char(string& str1,const string& str2) 8 { 9 cout << "在" << str1 << "中查找" << str2 << "中的字符" << endl; 10 string::size_type pos = 0; 11 while ((pos = str1.find_first_of(str2, pos)) != string::npos) 12 { 13 cout << "pos: " << pos << " 的字符:" << str1[pos] << endl; 14 pos++; 15 } 16 } 17 //使用find_first_not_of实现 18 //main 函数中将find_char函数的调用调换位置 19 //查找数字时find_not_char(s1,"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz""ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"); 20 //查找字母时find_not_char(s1,"0123456789"); 21 22 int main() 23 { 24 string s1 = "a1b2c3d4e5f6"; 25 //string s2 = "236"; 26 cout << "查找s中的所有数字" << endl; 27 find_char(s1, "0123456789"); 28 cout << endl << endl;; 29 cout << "查找所有字母" << endl; 30 find_char(s1, "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz""ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"); 31 32 33 system("pause"); 34 return 0; 35 }
s.find(args) 查找s中args第一次出现的位置,即第一个与args匹配自妇产的位置。args是作为一个整体在s中出现,不是像s.find_first_of(),在s中查找args中任何一个字符串第一次出现的位置。所以对于该题返回npos
9.49
9.6 容器适配器