Spring可以帮助我们管理软件开发过程中的对象,以及如何创建和维护对象之间的关系。 Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)的容器框架,可以将组建的耦合度降至最低,即实现解耦,便于系统以后的维护和升级。
1.spring 开发
eclipse开发工具
maven搭建项目-添加spring-context依赖包
引入applicationContext.xml配置文件
2.IOC (Inversion of Control) :控制反转,通过容器来控制对象的创建及维护,对象中成员变量的创建及维护。反转就是将对象的控制权转移给容器处理,目的是获得更好的扩展性和可维护性。
3.Spring Core Container(即Spring核心容器)——Spring框架的核心
4.Spring管理Bean的原理
Spring的核心容器可以管理任何java类,容器可以初始化该类,并返回该类的实例。
xml配置方式:

<!-- spring中进行控制反转的标记 通过配置bean 可以指定某个class由spring来管理 spring在读取主配置文件的时候会将当前标记读取,并且根据当前标记的class 的值,通过反射来创建该bean的对象 id是用来给某个创建的对象设置一个唯一 标识 lazy-init:懒加载设置 默认为立即加载,即值为false 设置成true,会在用到该bean的时候才创建该bean的对象 -->
测试:
添加Junit依赖包
新建Javabean类(完整的),添加init、destroy方法(略。。。)
配置xml文件:
<bean id="animal" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" lazy-init="false" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
方法测试:
1 public class MyTest { 2 //ApplicationContext context=null; 3 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context=null; 4 @Before 5 public void before(){ 6 context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); 7 } 8 //测试destroy需要关闭容器,关闭容器的时候会自动销毁容器中的对象 9 @Test 10 public void test1(){ 11 Animal animal = context.getBean("animal", Animal.class); 12 System.out.println(animal); 13 context.close();//容器关闭,对象销毁 destroy调用只在单例模式下有效 (默认单例) 14 } 15 }
单例与多例

<!-- bean的作用域 scope:默认是单例singleton pototype 表示多实例 每次getBean都会创建一个新的对象 --> <bean name="animal1" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" scope="prototype"></bean>
1 @Test 2 public void test2(){ 3 //修改了作用域后,每次getBean都会创建一个对象 4 Animal animal1 = context.getBean("animal1", Animal.class); 5 Animal animal2 = context.getBean("animal1", Animal.class); 6 }
5.Bean对象的实例化
A.用构造器来实例化
如果不指定调用哪个构造器,spring默认会调用无参构造方法。
例:<bean name="animal1" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" scope="prototype"></bean>
1 <!-- 2 constructor-arg:设置构造方法注入,通过该标签来设置构造方法中 的 index的位置上的参数, 3 赋于value属性的值 4 index:构造方法中的参数的索引位置,从0开始计算 5 value:设置属性值,只有String和基本数据类型可以直接用value指定值 6 ref:如果需要引用其他的bean作为属性值,用ref(用其他bean的id或name) 7 type:设置当前参数的类型,可以省略 8 -->
<bean id="animal" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" lazy-init="false" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <constructor-arg index="0" type="java.lang.String" value="小花"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="18"></constructor-arg> </bean>
B.使用静态工厂实例化
类中声明静态工厂方法
public Animal() { super(); System.out.println("无参Animal"); } public static Animal getInstance(){ System.out.println("静态工厂创建实例"); return new Animal(); }
<!-- factory-method:使用对象静态工厂的方式创建对象 --> <bean id="animal2" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" factory-method="getInstance"></bean>
C.使用实例工厂实例化
<!-- 通过对象工厂创建对象 1.创建工厂对象 2.设置bean使用工厂对象的方法来创建 -->
1 public class AnimalFactory { 2 public Animal getInstance(){ 3 System.out.println("工厂方法调用"); 4 return new Animal(); 5 } 6 }
<bean id="animalFactory" class="com.rong.entity.AnimalFactory"></bean> <bean id="animal3" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" factory-bean="animalFactory" factory-method="getInstance"></bean>
1 @Test 2 public void test4(){ 3 Animal animal = context.getBean("animal3", Animal.class); 4 System.out.println(animal); 5 }
D.延时实例化——lazy-init
6.依赖注入(DI全称是Dependency Injection)
<!-- DI 依赖注入配置 即通过spring去做 构造方法或set方法给属性赋值工作 -->
A.构造方法注入(示例如上)
B.set方法注入
1)类中提供set方法
2)在spring主配置文件中通过property属性来设置(value和ref属性不能同时使用)
<!-- setter注入 property :调用setter方法设置属性值 name:设置哪个属性赋值 value:给该属性赋予什么值 ref : 给引用类型属性赋值 -->
1 <bean id="animal3" class="com.rong.entity.Animal" factory-bean="animalFactory" factory-method="getInstance"> 2 <property name="age" value="60"></property> 3 <property name="type" value="www"></property> 4 </bean>
C.自动装配的方式
<!-- 自动装配 ,一般结合依赖注入使用 -->
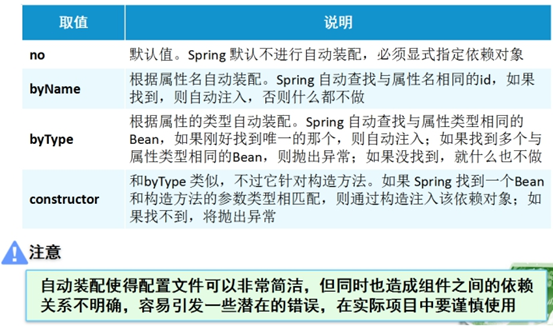
1 <!-- 2 autowire:使用自动装配的方式,给当前bean的属性赋值 3 byType:spring自动检索容器中有哪些bean,并且找到符合当前bean的属性的类型的bean出来,如果找到了 4 则自动给该属性赋值 5 byName:spring自动根据当前bean的属性的名称,从容器中查找与该属性名一致的bean,注入到该属性上 6 --> 7 8 <!-- <bean id="favourite" class="com.web.entity.Favourite"> 9 <property name="sport" value="游泳"></property> 10 </bean> --> 11 <bean id="favourite2" class="com.web.entity.Favourite"> 12 <property name="sport" value="打篮球"></property> 13 </bean> 14 <!-- <bean id="myAnimal" class="com.web.entity.Animal" autowire="byName"></bean> --> 15 <bean id="myAnimal2" class="com.web.entity.Animal" autowire="byType"></bean>
list、set、map、property的注入方式
1 package com.web.entity; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.Map; 6 import java.util.Map.Entry; 7 import java.util.Properties; 8 import java.util.Set; 9 10 public class MyBean { 11 private List<String> cities; 12 private Set<String> names; 13 private Map<String,Integer> map; 14 private Properties props; 15 public List<String> getCities() { 16 return cities; 17 } 18 public void setCities(List<String> cities) { 19 this.cities = cities; 20 } 21 public Set<String> getNames() { 22 return names; 23 } 24 public void setNames(Set<String> names) { 25 this.names = names; 26 } 27 public Map<String, Integer> getMap() { 28 return map; 29 } 30 public void setMap(Map<String, Integer> map) { 31 this.map = map; 32 } 33 public Properties getProps() { 34 return props; 35 } 36 public void setProps(Properties props) { 37 this.props = props; 38 } 39 40 public void show(){ 41 System.out.println("list=========="); 42 for (String string : cities) { 43 System.out.println(string); 44 } 45 System.out.println("set=========="); 46 for (String name : names) { 47 System.out.println(name); 48 } 49 System.out.println("map=========="); 50 Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); 51 Iterator<Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = entrySet.iterator(); 52 while(iterator.hasNext()){ 53 Entry<String, Integer> entry = iterator.next(); 54 String key = entry.getKey(); 55 Integer value = entry.getValue(); 56 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 57 } 58 System.out.println("property=========="); 59 Set<Object> Set = props.keySet(); 60 for (Object object : Set) { 61 String key=(String)object; 62 String value = props.getProperty(key); 63 System.out.println(key+":"+value); 64 } 65 66 67 } 68 69 }
<bean id="myBean" class="com.web.entity.MyBean"> <property name="cities"> <list> <value>北京</value> <value>上海</value> <value>广州</value> <value>深圳</value> </list> </property> <property name="names"> <set> <value>胡歌</value> <value>杨幂</value> <value>霍建华</value> <value>叶剑英</value> </set> </property> <property name="map"> <map> <entry> <key> <value>Java</value> </key> <value>100</value> </entry> <entry> <key> <value>C++</value> </key> <value>98</value> </entry> <entry> <key> <value>Android</value> </key> <value>96</value> </entry> </map> </property> <!-- ref引用方式 --> <!-- <property name="props" ref="dbProps"> </property> --> <!-- 直接赋值方式 --> <property name="props"> <props> <prop key="username">#{dbProps.username}</prop> <prop key="password">#{dbProps.password}</prop> <prop key="driver">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- 读取配置文件转成Properties对象 id:唯一标识 location:从哪里读取文件 classpath: 通过类路径开始读取 --> <util:properties id="dbProps" location="classpath:db.properties"></util:properties>
1 url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/utf8?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 2 username=root 3 password=123123 4 driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver