12.22 71. 两地调度
公司计划面试 2N 人。第 i 人飞往 A 市的费用为costs[i][0],飞往 B 市的费用为 costs[i][1]。
返回将每个人都飞到某座城市的最低费用,要求每个城市都有 N 人抵达。
输入:[[10,20],[30,200],[400,50],[30,20]]
输出:110
解释:
第一个人去 A 市,费用为 10。
第二个人去 A 市,费用为 30。
第三个人去 B 市,费用为 50。
第四个人去 B 市,费用为 20。
最低总费用为 10 + 30 + 50 + 20 = 110,每个城市都有一半的人在面试。
最优解思路
公司首先将这 2N 个人全都安排飞往 BB 市,再选出 N 个人改变它们的行程,让他们飞往 A 市。如果选择改变一个人的行程,那么公司将会额外付出 price_A - price_B 的费用,这个费用可正可负。因此最优的方案是,选出 price_A - price_B 最小的 NN 个人,让他们飞往 A 市,其余人飞往 B 市。
最优解
class Solution:
def twoCitySchedCost(self, costs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
# Sort by a gain which company has
# by sending a person to city A and not to city B
costs.sort(key = lambda x : x[0] - x[1])
total = 0
n = len(costs) // 2
# To optimize the company expenses,
# send the first n persons to the city A
# and the others to the city B
for i in range(n):
total += costs[i][0] + costs[i + n][1]
return total
12.23 72. 最长单词
给定一组单词words,编写一个程序,找出其中的最长单词,且该单词由这组单词中的其他单词组合而成。若有多个长度相同的结果,返回其中字典序最小的一项,若没有符合要求的单词则返回空字符串。
输入: ["cat","banana","dog","nana","walk","walker","dogwalker"]
输出: "dogwalker"
解释: "dogwalker"可由"dog"和"walker"组成。
最优解思路
先把字符串数组排序,字符串长的在前面,相同长度的字典序小的在前面,排好序后加入到set里判断是否包含,从第一个字符串开始判断,看是否由其它字符串组成,这里可以用递归
递归出口: 如果字符串长的长度为0,说明遍历完了,之前的都满足条件,返回true
递归操作: 遍历字符串的第0个位置开始,判断set里是否有,如果0到i的字符串正好包含在set里,下次从i+1的位置开始判断,直到遍历完了,字符串长度为0,没找到则返回false
最优解
class Solution {
public String longestWord(String[] words) {
Arrays.sort(words,(o1,o2)->{
if(o1.length() == o2.length())
return o1.compareTo(o2);
else{
return Integer.compare(o2.length(),o1.length());
}
});
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(words));
for(String word : words){
set.remove(word);
if(find(set,word))
return word;
}
return "";
}
public boolean find(Set<String> set, String word){
if(word.length() == 0)
return true;
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++){
if(set.contains(word.substring(0,i+1)) && find(set,word.substring(i+1)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
12.26 73. 二叉搜索树迭代器
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器。
调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数。
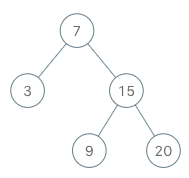
BSTIterator iterator = new BSTIterator(root);
iterator.next(); // 返回 3
iterator.next(); // 返回 7
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 9
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 15
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 true
iterator.next(); // 返回 20
iterator.hasNext(); // 返回 false
思路
中序遍历树,各节点的值加入列表,pop。
最优解
class BSTIterator:
def __init__(self, root: TreeNode):
# Array containing all the nodes in the sorted order
self.nodes_sorted = []
# Pointer to the next smallest element in the BST
self.index = -1
# Call to flatten the input binary search tree
self._inorder(root)
def _inorder(self, root):
if not root:
return
self._inorder(root.left)
self.nodes_sorted.append(root.val)
self._inorder(root.right)
def next(self) -> int:
"""
@return the next smallest number
"""
self.index += 1
return self.nodes_sorted[self.index]
def hasNext(self) -> bool:
"""
@return whether we have a next smallest number
"""
return self.index + 1 < len(self.nodes_sorted)
12.26 74. 买卖股票的最佳时机
给定一个整数数组 prices,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 ;非负整数 fee 代表了交易股票的手续费用。
你可以无限次地完成交易,但是你每笔交易都需要付手续费。如果你已经购买了一个股票,在卖出它之前你就不能再继续购买股票了。
返回获得利润的最大值。
注意:这里的一笔交易指买入持有并卖出股票的整个过程,每笔交易你只需要为支付一次手续费。
输入: prices = [1, 3, 2, 8, 4, 9], fee = 2
输出: 8
解释: 能够达到的最大利润:
在此处买入 prices[0] = 1
在此处卖出 prices[3] = 8
在此处买入 prices[4] = 4
在此处卖出 prices[5] = 9
总利润: ((8 - 1) - 2) + ((9 - 4) - 2) = 8.
最优解思路
解一:动态规划
考虑 dp[i][0]的转移方程,如果这一天交易完后手里没有股票,那么可能的转移状态为前一天已经没有股票,即 dp[i-1][0],或者前一天结束的时候手里持有一支股票,即 dp[i-1][1],这时候我们要将其卖出,并获得prices[i] 的收益,但需要支付 fee 的手续费。因此为了收益最大化,我们列出如下的转移方程:
dp[i][0]=max{dp[i−1][0],dp[i−1][1]+prices[i]−fee}
再来按照同样的方式考虑 dp[i][1] 按状态转移,那么可能的转移状态为前一天已经持有一支股票,即 dp[i-1]][1],或者前一天结束时还没有股票,即dp[i-1]][0] ,这时候我们要将其买入,并减少prices[i] 的收益。可以列出如下的转移方程:
dp[i][1]=max{dp[i−1][1],dp[i−1][0]−prices[i]}
对于初始状态,根据状态定义我们可以知道第 0 天交易结束的时候有dp[0][0]=0 以及dp[0][1]=-price[0].
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int:
n = len(prices)
dp = [[0, -prices[0]]] + [[0, 0] for _ in range(n - 1)]
for i in range(1, n):
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i] - fee)
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] - prices[i])
return dp[n - 1][0]
解二:贪心算法
即当我们卖出一支股票时,我们就立即获得了以相同价格并且免除手续费买入一支股票的权利。
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int], fee: int) -> int:
n = len(prices)
buy = prices[0] + fee
profit = 0
for i in range(1, n):
if prices[i] + fee < buy:
buy = prices[i] + fee
elif prices[i] > buy:
profit += prices[i] - buy
buy = prices[i]
return profit
12.28 75. LRU缓存机制
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity) 以正整数作为容量 capacity 初始化 LRU 缓存
int get(int key) 如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回 -1 。
void put(int key, int value) 如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
思路
LRU缓存机制是通过hash表辅以双向链表实现的。
- 双向链表按照被使用的顺序存储了这些键值对,靠近头部的键值对是最近使用的,而靠近尾部的键值对是最久未使用的。
- 哈希表即为普通的哈希映射(HashMap),通过缓存数据的键映射到其在双向链表中的位置。
最优解
class DLinkedNode:
def __init__(self, key=0, value=0):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.prev = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache:
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
self.cache = dict()
# 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
self.head = DLinkedNode()
self.tail = DLinkedNode()
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.prev = self.head
self.capacity = capacity
self.size = 0
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key not in self.cache:
return -1
# 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
node = self.cache[key]
self.moveToHead(node)
return node.value
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key not in self.cache:
# 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
node = DLinkedNode(key, value)
# 添加进哈希表
self.cache[key] = node
# 添加至双向链表的头部
self.addToHead(node)
self.size += 1
if self.size > self.capacity:
# 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
removed = self.removeTail()
# 删除哈希表中对应的项
self.cache.pop(removed.key)
self.size -= 1
else:
# 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node = self.cache[key]
node.value = value
self.moveToHead(node)
def addToHead(self, node):
node.prev = self.head
node.next = self.head.next
self.head.next.prev = node
self.head.next = node
def removeNode(self, node):
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
def moveToHead(self, node):
self.removeNode(node)
self.addToHead(node)
def removeTail(self):
node = self.tail.prev
self.removeNode(node)
return node
最优解总结
hash表key是存出键,value是链表的索引,链表的值时value。这样查询,插入复杂度都是o1
get操作,判断是否存在,不存在返回-1,存在把对应的链表索引换到头部。
put操作,若存在和get操作类似,不存在则创建一个新的链表节点,放到头部再判断长度,超过规定长度就会从尾部去除。