Bogdan has a birthday today and mom gave him a tree consisting of n vertecies. For every edge of the tree i, some number xi was written on it. In case you forget, a tree is a connected non-directed graph without cycles. After the present was granted, m guests consecutively come to Bogdan's party. When the i-th guest comes, he performs exactly one of the two possible operations:
- Chooses some number yi, and two vertecies ai and bi. After that, he moves along the edges of the tree from vertex ai to vertex biusing the shortest path (of course, such a path is unique in the tree). Every time he moves along some edge j, he replaces his current number yi by
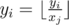 , that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj.
, that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj. - Chooses some edge pi and replaces the value written in it xpi by some positive integer ci < xpi.
As Bogdan cares about his guests, he decided to ease the process. Write a program that performs all the operations requested by guests and outputs the resulting value yi for each i of the first type.
The first line of the input contains integers, n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertecies in the tree granted to Bogdan by his mom and the number of guests that came to the party respectively.
Next n - 1 lines contain the description of the edges. The i-th of these lines contains three integers ui, vi and xi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi,1 ≤ xi ≤ 1018), denoting an edge that connects vertecies ui and vi, with the number xi initially written on it.
The following m lines describe operations, requested by Bogdan's guests. Each description contains three or four integers and has one of the two possible forms:
- 1 ai bi yi corresponds to a guest, who chooses the operation of the first type.
- 2 pi ci corresponds to a guests, who chooses the operation of the second type.
For each guest who chooses the operation of the first type, print the result of processing the value yi through the path from ai to bi.
6 6
1 2 1
1 3 7
1 4 4
2 5 5
2 6 2
1 4 6 17
2 3 2
1 4 6 17
1 5 5 20
2 4 1
1 5 1 3
2
4
20
3
2 x y,把第x条边的边权改为y
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") #define ls i<<1 #define rs ls | 1 #define mid ((ll+rr)>>1) #define pii pair<int,int> #define MP make_pair typedef long long LL; const long long INF = 1e18; const double Pi = acos(-1.0); const int N = 2e5+10, M = 5e5+11, inf = 2e9, mod = 998244353; LL c[N]; int head[N],t = 1, fv[N], f[N], deep[N], n, m, pa[N]; struct edge{int to,next,id;}e[N * 2]; struct Line { int x,y; LL z; Line(int x = 0, int y = 0, int z = 0) : x (x), y (y), z (z) {} }L[N]; void add(int u,int v,int id) {e[t].next = head[u];e[t].to = v;e[t].id = id; head[u] = t++; } int finds(int x) {return x == pa[x]? pa[x]:pa[x] = finds(pa[x]);} void update(int u,int to) { fv[to] = fv[u]; f[to] = f[u]; } void dfs(int u,int fa) { deep[u] = deep[fa] + 1; for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) { int to = e[i].to; if(to == fa) continue; fv[to] = e[i].id; f[to] = u; if(c[e[i].id] == 1) { pa[to] = finds(u); update(u,to); } dfs(to,u); } } LL Lca(int u,int v,LL res) { u = finds(u); v = finds(v); while(u != v) { if(deep[u] < deep[v]) swap(u,v); // cout<<deep[u]<<" "<<deep[v]<<" "<<fv[u]<<" "<<c[fv[u]]<<endl; res /= c[fv[u]]; if(res == 0) return res; u = finds(f[u]); } return res; } int main() { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) pa[i] = i; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { int a,b; scanf("%d%d%I64d",&a,&b,&c[i]); add(a,b,i);add(b,a,i); L[i] = Line(a,b,c[i]); } c[0] = 1; fv[1] = 0; f[1] = 1; dfs(1,0); while(m --) { int op, x; LL z,y; scanf("%d%d%I64d",&op,&x,&y); if(op == 1) { scanf("%I64d",&z); LL res = Lca(x,y,z); printf("%I64d ",res); } else { c[x] = y; int u = L[x].x; int v = L[x].y; if(deep[u] < deep[v]) swap(u,v); if(c[x] == 1) { pa[u] = finds(v); update(v,u); } } } }
树链剖分
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<cmath> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") #define ls i<<1 #define rs ls | 1 #define mid ((ll+rr)>>1) #define root 1,2,n #define lson ls , ll , mid #define rson rs , mid + 1 , rr #define pii pair<int,int> #define MP make_pair typedef long long LL; const long long INF = 1e18+200LL; const double Pi = acos(-1.0); const int N = 2e5+10, M = 5e5+11, inf = 2e9, mod = 998244353; LL sum[N << 2],val[N << 2]; int head[N], t = 1, tot, deep[N], top[N], f[N], siz[N], son[N], pos[N << 2]; int n,m; struct edge{int to,next;LL value;}e[N * 2]; struct Line{ int x,y;LL z; Line(int x = 0, int y = 0, LL z = 0) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {} }L[N]; void add(int u,int v) {e[t].next=head[u];e[t].to=v;head[u]=t++;} void dfs1(int u,int fa) { siz[u] = 1;son[u] = 0; deep[u] = deep[fa] + 1; f[u] = fa; for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) { int to = e[i].to; if(to == fa) continue; dfs1(to,u); siz[u] += siz[to]; if(siz[to] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = to; } } void dfs2(int u,int chan) { top[u] = son[chan] == u? top[chan] : u; pos[u] = ++tot; if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],u); for(int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) { int to = e[i].to; if(to == son[u] || to == chan) continue; dfs2(to,u); } } void push_up(int i) { if(log(sum[ls]*1.0) + log(sum[rs] * 1.0) > log(INF * 1.0)) sum[i] = INF; else sum[i] = sum[ls] * sum[rs]; } void build(int i,int ll,int rr) { if(ll == rr) { sum[i] = val[ll]; return ; } build(lson), build(rson); push_up(i); } void update(int i,int ll,int rr,int x,LL c) { if(ll == x && rr == x) { sum[i] = c; return ; } if(x <= mid) update(lson,x,c); else update(rson,x,c); push_up(i); } LL query(int i,int ll,int rr,int x,int y) { if(ll == x && rr == y) return sum[i]; if(y <= mid) return query(lson,x,y); else if(x > mid) return query(rson,x,y); else { LL fi = query(lson,x,mid); LL se = query(rson,mid+1,y); if(log(fi*1.0) + log(se * 1.0) > log(INF * 1.0)) { return INF; } else return fi*se; } } LL sub_query(int x,int y,LL res) { while(top[x] != top[y]) { if(deep[top[x]] < deep[top[y]]) swap(x,y); // cout<<pos[top[x]]<<" "<<pos[x]<<endl; res /= query(root,pos[top[x]],pos[x]); if(res == 0) return 0; x = f[top[x]]; } if(x == y) return res; if(deep[x] < deep[y]) swap(x,y); // cout<<query(root,pos[y]+1,pos[x])<<endl; return res / query(root,pos[y]+1,pos[x]); } int main () { scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i = 1; i <= n-1; ++i) { int a,b; LL c; scanf("%d%d%I64d",&a,&b,&c); add(a,b); add(b,a); L[i] = Line(a,b,c); } dfs1(1,0); dfs2(1,0); for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { if(deep[L[i].x] < deep[L[i].y]) swap(L[i].x,L[i].y); val[pos[L[i].x]] = L[i].z; } build(root); while(m--) { int op,x; LL y,z; scanf("%d%d%I64d",&op,&x,&y); if(op == 1) { scanf("%I64d",&z); printf("%I64d ",sub_query(x,y,z)); }else { update(root,pos[L[x].x],y); } } }