4、显式锁和AQS
显式锁
Lock接口和核心方法
package com.xiangxue.ch4; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * @author Administrator * *使用显示锁的范式:一定要在finally中释放锁 */ public class LockDemo { private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private int count; public void increament() { lock.lock(); try { count++; }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public synchronized void incr2() {//可重入 count++; incr2(); } public synchronized void test3() {//可重入 incr2(); } }
1.Lock接口和synchronized的比较
synchronized 代码简洁,Lock:获取锁可以被中断,超时获取锁,尝试获取锁,读多写少用读写锁
2.可重入锁ReentrantLock、所谓锁的公平和非公平
如果在时间上,先对锁进行获取的请求,一定先被满足,这个锁就是公平的,不满足,就是非公平的
非公平的效率一般来讲更高
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
构造方法可以指定公平锁还是非公平锁,默认非公平。
3.ReadWriteLock接口和读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock
ReentrantLock和Syn关键字,都是排他锁,同一时刻,只允许同一个线程访问。
读写锁:同一时刻允许多个读线程同时访问,但是写线程访问的时候,所有的读和写都被阻塞,最适宜于读多写少的情况
package com.xiangxue.ch4.rw; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:对商品进行业务的应用 */ public class BusiApp { static final int readWriteRatio = 10;//读写线程的比例 static final int minthreadCount = 3;//最少线程数 //static CountDownLatch latch= new CountDownLatch(1); //读操作 private static class GetThread implements Runnable{ private GoodsService goodsService; public GetThread(GoodsService goodsService) { this.goodsService = goodsService; } @Override public void run() { // try { // latch.await();//让读写线程同时运行 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // } long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for(int i=0;i<100;i++){//操作100次 goodsService.getNum(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读取商品数据耗时:" +(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms"); } } //写操做 private static class SetThread implements Runnable{ private GoodsService goodsService; public SetThread(GoodsService goodsService) { this.goodsService = goodsService; } @Override public void run() { // try { // latch.await();//让读写线程同时运行 // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // } long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); Random r = new Random(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){//操作10次 SleepTools.ms(50); goodsService.setNum(r.nextInt(10)); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +"写商品数据耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms---------"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { GoodsInfo goodsInfo = new GoodsInfo("Cup",100000,10000); GoodsService goodsService = new UseRwLock(goodsInfo);/*new UseSyn(goodsInfo);*/ for(int i = 0;i<minthreadCount;i++){ Thread setT = new Thread(new SetThread(goodsService)); for(int j=0;j<readWriteRatio;j++) { Thread getT = new Thread(new GetThread(goodsService)); getT.start(); } SleepTools.ms(100); setT.start(); } //latch.countDown(); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.rw; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:用内置锁来实现商品服务接口 */ public class UseSyn implements GoodsService { private GoodsInfo goodsInfo; public UseSyn(GoodsInfo goodsInfo) { this.goodsInfo = goodsInfo; } @Override public synchronized GoodsInfo getNum() { SleepTools.ms(5); return this.goodsInfo; } @Override public synchronized void setNum(int number) { SleepTools.ms(5); goodsInfo.changeNumber(number); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.rw; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明: */ public class UseRwLock implements GoodsService { private GoodsInfo goodsInfo; private final ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); private final Lock getLock = lock.readLock();//读锁 private final Lock setLock = lock.writeLock();//写锁 public UseRwLock(GoodsInfo goodsInfo) { this.goodsInfo = goodsInfo; } @Override public GoodsInfo getNum() { getLock.lock(); try { SleepTools.ms(5); return this.goodsInfo; }finally { getLock.unlock(); } } @Override public void setNum(int number) { setLock.lock(); try { SleepTools.ms(5); goodsInfo.changeNumber(number); }finally { setLock.unlock(); } } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.rw; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:商品的实体类 */ public class GoodsInfo { private final String name; private double totalMoney;//总销售额 private int storeNumber;//库存数 public GoodsInfo(String name, int totalMoney, int storeNumber) { this.name = name; this.totalMoney = totalMoney; this.storeNumber = storeNumber; } public double getTotalMoney() { return totalMoney; } public int getStoreNumber() { return storeNumber; } public void changeNumber(int sellNumber){ this.totalMoney += sellNumber*25; this.storeNumber -= sellNumber; } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.rw; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:商品的服务的接口 */ public interface GoodsService { public GoodsInfo getNum();//获得商品的信息 public void setNum(int number);//设置商品的数量 }
4.Condition接口
5.用Lock和Condition实现等待通知
和之前的wait(),notify()不同,只需要signal,不用signalAll
package com.xiangxue.ch4.condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; /** * *@author Mark老师 * *类说明: */ public class ExpressCond { public final static String CITY = "ShangHai"; private int km;/*快递运输里程数*/ private String site;/*快递到达地点*/ private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition keCond = lock.newCondition(); private Condition siteCond = lock.newCondition(); public ExpressCond() { } public ExpressCond(int km, String site) { this.km = km; this.site = site; } /* 变化公里数,然后通知处于wait状态并需要处理公里数的线程进行业务处理*/ public void changeKm(){ lock.lock(); try { this.km = 101; keCond.signalAll(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } /* 变化地点,然后通知处于wait状态并需要处理地点的线程进行业务处理*/ public void changeSite(){ lock.lock(); try { this.site = "BeiJing"; siteCond.signal(); }finally { lock.unlock(); } } /*当快递的里程数大于100时更新数据库*/ public void waitKm(){ lock.lock(); try { while(this.km<=100) { try { keCond.await(); System.out.println("check km thread["+Thread.currentThread().getId() +"] is be notifed."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }finally { lock.unlock(); } System.out.println("the Km is "+this.km+",I will change db"); } /*当快递到达目的地时通知用户*/ public void waitSite(){ lock.lock(); try { while(CITY.equals(this.site)) { try { siteCond.await(); System.out.println("check site thread["+Thread.currentThread().getId() +"] is be notifed."); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }finally { lock.unlock(); } System.out.println("the site is "+this.site+",I will call user"); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.condition; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:测试Lock和Condition实现等待通知 */ public class TestCond { private static ExpressCond express = new ExpressCond(0,ExpressCond.CITY); /*检查里程数变化的线程,不满足条件,线程一直等待*/ private static class CheckKm extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { express.waitKm(); } } /*检查地点变化的线程,不满足条件,线程一直等待*/ private static class CheckSite extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { express.waitSite(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ new CheckSite().start(); } for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ new CheckKm().start(); } Thread.sleep(1000); express.changeKm();//快递里程变化 } }
了解LockSupport工具
park开头的方法
负责阻塞线程
unpark(Thread thread)方法
负责唤醒线程
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer深入分析
1.什么是AQS?学习它的必要性
Jdk中显示锁,读写锁,CountDownLatch,是基于AQS。
而内置锁是在语言层面上
2.AQS使用方式和其中的设计模式
继承,模板方法设计模式
package com.xiangxue.ch4.template; import java.util.Date; /** * @author mark *模板方法的父类 */ public abstract class SendCustom { public abstract void to(); public abstract void from(); public abstract void content(); public void date() { System.out.println(new Date()); } public abstract void send(); //框架方法-模板方法 public void sendMessage() { to(); from(); content(); date(); send(); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.template; /** * @author Mark *模板方法的派生类 */ public class SendSms extends SendCustom { @Override public void to() { System.out.println("Mark"); } @Override public void from() { System.out.println("Bill"); } @Override public void content() { System.out.println("Hello world"); } @Override public void send() { System.out.println("Send sms"); } public static void main(String[] args) { SendCustom sendC = new SendSms(); sendC.sendMessage(); } }
3.了解其中的方法
模板方法:
a.独占式获取
accquire 获取同步状态
acquireInterruptibly
tryAcquireNanos
b.共享式获取
acquireShared
acquireSharedInterruptibly
tryAcquireSharedNanos
c.独占式释放锁
release
d.共享式释放锁
releaseShared
4.需要子类覆盖的流程方法
独占式获取 tryAcquire
独占式释放 tryRelease
共享式获取 tryAcquireShared
共享式释放 tryReleaseShared
这个同步器是否处于独占模式 isHeldExclusively
同步状态state:
getState:获取当前的同步状态
setState:设置当前同步状态
compareAndSetState 使用CAS设置状态,保证状态设置的原子性
实现一个类似于ReentrantLock的锁
package com.xiangxue.ch4.aqs; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; /** *@author Mark * *类说明:实现一个自己的类ReentrantLock */ public class SelfLock implements Lock{ //state 表示获取到锁 state=1 获取到了锁,state=0,表示这个锁当前没有线程拿到 private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer{ //是否占用 protected boolean isHeldExclusively() { return getState()==1; } protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) { if(compareAndSetState(0,1)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); return true; } return false; } protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) { if(getState()==0) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); setState(0);//只有拿到锁的线程才能释放,只有一个,所以这里没有进行原子操作 return true; } Condition newCondition() { return new ConditionObject(); } } private final Sync sycn = new Sync(); @Override public void lock() { sycn.acquire(1); } @Override public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException { sycn.acquireInterruptibly(1); } @Override public boolean tryLock() { return sycn.tryAcquire(1); } @Override public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return sycn.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time)); } @Override public void unlock() { sycn.release(1); } @Override public Condition newCondition() { return sycn.newCondition(); } }
package com.xiangxue.ch4.aqs; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; import com.xiangxue.tools.SleepTools; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明: */ public class TestMyLock { public void test() { final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); class Worker extends Thread { public void run() { while (true) { lock.lock(); try { SleepTools.second(1); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); SleepTools.second(1); } finally { lock.unlock(); } SleepTools.second(2); } } } // 启动10个子线程 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Worker w = new Worker(); w.setDaemon(true); w.start(); } // 主线程每隔1秒换行 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { SleepTools.second(1); System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { TestMyLock testMyLock = new TestMyLock(); testMyLock.test(); } }
分析:
@Override public void lock() { sycn.acquire(1); }
acquire是模板方法。
接着:
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer中
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
接着:
private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer{
//是否占用
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState()==1;
}
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
if(compareAndSetState(0,1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
接着分析;acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)):就是将当前线程封装成一个节点然后添加到队列中
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
分析: enq(node);
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
分析:
节点的自旋
节点进入同步队列之后,就进入了一个自旋的过程,每个节点(或者说是线程)都在自省地观察,当条件满足,获取到了同步状态,就可以从这个自旋过程中退出,否则依旧留在这个自旋过程中。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal control in all acquire loops.*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;//获取前驱节点的等待状态
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
//SIGNAL状态:前驱节点释放同步状态或者被取消,将会通知后继节点。因此,可以放心的阻塞当前线程,返回true。
/* This node has already set status asking a release to signal it, so it can safely park.*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {//前驱节点被取消了,跳过前驱节点并重试
/* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and indicate retry. */
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {//独占模式下,一般情况下这里指前驱节点等待状态为SIGNAL
/* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking. */
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);//设置当前节点等待状态为SIGNAL
}
return false;
}
/** Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted 。return {@code true} if interrupted */
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);//阻塞当前线程
return Thread.interrupted();
}
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「nogos」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/sunxianghuang/article/details/52287968
============================================================================================================================
@Override
public void unlock() {
sycn.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {//重写的方法
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
if(getState()==0) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);//唤醒
}
5.AQS中的数据结构-节点和同步队列
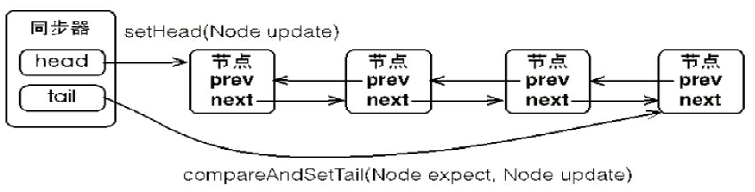
a.同步队列:先进先出,双向链表,上一个节点指向下一个节点,同时下一个节点有一个上一个节点的引用。
同时在同步器中有两个指示器, 一个头指示器,一个尾指示器,分别指向队列的头节点和为节点。
b.竞争失败的线程会打包成Node放到同步队列,Node可能的状态有:
CANCELLED:线程等待超时或者被中断了,需要从队列中移走
SIGNAL:后续的节点等待状态,当前节点,通知后面的节点去运行
CONDITION :当前节点处于等待队列
PROPAGATE:共享,表示状态要往后面的节点传播
0, 表示初始状态
c.节点就是用来把争夺锁失败的线程打包成一个节点放到同步队列中。同步队列就维持了拿锁失败的线程的列表。
6.节点在同步队列中的增加和移出
a.节点加入到同步队列
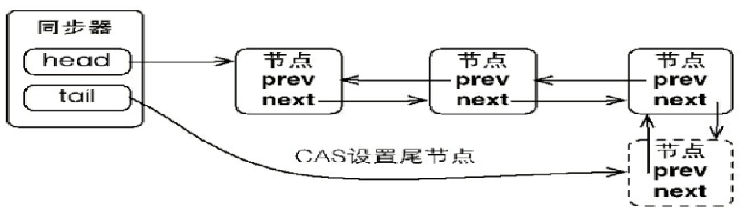
b.首节点的变化
7.独占式同步状态获取与释放

其他同步状态获取与释放
8.Condition分析
一个Condition包含一个等待队列
同步队列与等待队列
节点在队列之间的移动
await方法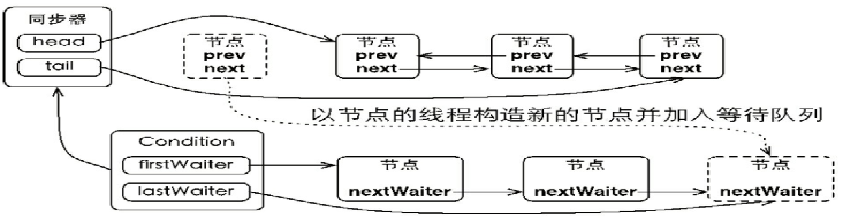
signal方法
9.了解ReentrantLock的实现
a.锁的可重入
b.公平和非公平锁
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); }
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
10.实现三元共享锁
package com.xiangxue.ch4.aqs; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject; /** *@author Mark老师 * *类说明:奇葩点的三元共享同步工具类 */ public class TrinityLock { //为3表示允许两个线程同时获得锁 private final Sync sync = new Sync(3); private static final class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { //private static final long serialVersionUID = -7889272986162341211L; Sync(int count) { if (count <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("count must large than zero."); } setState(count); } public int tryAcquireShared(int reduceCount) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int newCount = current - reduceCount; if (newCount < 0 || compareAndSetState(current, newCount)) { return newCount; } } } public boolean tryReleaseShared(int returnCount) { for (;;) { int current = getState(); int newCount = current + returnCount; if (compareAndSetState(current, newCount)) { return true; } } } final ConditionObject newCondition() { return new ConditionObject(); } } public void lock() { sync.acquireShared(1); } public void unlock() { sync.releaseShared(1); } public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException { sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1); } public boolean tryLock() { return sync.tryAcquireShared(1) >= 0; } public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time)); } public Condition newCondition() { return sync.newCondition(); } }