网上搜了一下,挺多打印table的方案,基本思路都是一层一层递归遍历table。(我就是参考这种思路做的^_^)
但大部分都不支持双向引用的打印。我所指的双向引用,就是a引用b, b又直接或间接引用a。例如下面的双向链表:
local node1 = {}
local node2 = {}
local node3 = {}
node1.value = 1
node1.pre = nil
node1.next = node2
node2.value = 2
node2.pre = node1
node2.next = node3
node3.value = 3
node3.pre = node2
node3.next = nil
像这样一个双链表,网上的很多方法,处理这种情况时,递归无法结束。因为,node1 表里有个 node2, 遍历node2时,又发现有个node1,如此反复
那要怎么处理呢?我的方案是:把每个table的父级table用一个链表保存起来,当判断到当前要处理的table存在于父级链表里,就停止处理。
完整代码如下:

1 ------ 把table转成string 2 -- sign 打印在最前面的一个标记 3 -- tab 待处理table 4 -- showAddress 是否显示table的地址 5 function TabToStr(sign, tab, showAddress) 6 7 -- 缓存table地址,防止递归死循环 8 local tabs = {}; 9 local check = function(cur_tab, key, parentKey, level) 10 local tempP = tabs[(level-1) .. parentKey] 11 while tempP do 12 if tempP.id == tostring(cur_tab) then 13 return false; 14 end 15 tempP = tempP.parent; 16 end 17 18 tabs[level .. key] = {}; 19 tabs[level .. key].id = tostring(cur_tab); 20 tabs[level .. key].parent = tabs[(level-1) .. parentKey]; 21 22 return true; 23 end 24 25 -- 处理直接传入table的情况 26 if tab == nil then 27 tab = sign; 28 sign = "table:"; 29 end 30 31 local targetType = type(tab); 32 if targetType == "table" then 33 local isHead = false; 34 local function dump(t, tKey, space, level) 35 local temp = {}; 36 if not isHead then 37 temp = {sign or "table:"}; 38 isHead = true; 39 end 40 41 if tKey ~= "_fields" then 42 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s{", string.rep(" ", level))); 43 end 44 for k, v in pairs(t) do 45 local key = tostring(k); 46 -- 协议返回内容 47 if key == "_fields" then 48 local fields = {}; 49 for fk, fv in pairs(v) do 50 fields[fk.name] = fv; 51 end 52 table.insert(temp, dump(fields, key, space, level)) 53 -- 如果是table模拟的类,忽略。 以下划线开头的字段, 忽略 54 elseif key == "class" or string.sub(key, 1, string.len("_")) == "_" then 55 -- 这里忽略 56 57 elseif type(v) == "table" then 58 if check(v, key, tKey, level) then 59 if showAddress then 60 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s %s", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, tostring(v), dump(v, key, space, level + 1))); 61 else 62 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, dump(v, key, space, level + 1))); 63 end 64 else 65 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s (loop)", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, tostring(v))); 66 end 67 else 68 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, tostring(v))); 69 end 70 end 71 if tKey ~= "_fields" then 72 table.insert(temp, string.format("%s}", string.rep(" ", level))); 73 end 74 75 return table.concat(temp, string.format("%s ", space)); 76 end 77 return dump(tab, "", "", 0); 78 else 79 return tostring(tab); 80 end 81 end
核心方法说明:
check 方法, 检测父级table链表中是否存在当前table
dump 方法, 递归遍历table
上面代码在实际项目中测试可用,一般情况可以直接使用。但有些是根据项目情况填充的内容。想要理解或改写的话,看下面的精简dump方法
local function dump(t, tKey, space, level) local temp = {}; table.insert(temp, string.format("%s{", string.rep(" ", level))); for k, v in pairs(t) do local key = tostring(k); if type(v) == "table" then if check(v, key, tKey, level) then table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, dump(v, key, space, level + 1))); else table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s (loop)", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, tostring(v))); end else table.insert(temp, string.format("%s%s: %s", string.rep(" ", level+1), key, tostring(v))); end end table.insert(temp, string.format("%s}", string.rep(" ", level))); return table.concat(temp, string.format("%s ", space)); end
测试:
tab = {1, 2, 3, 4, {5, 6, 7, 8}}
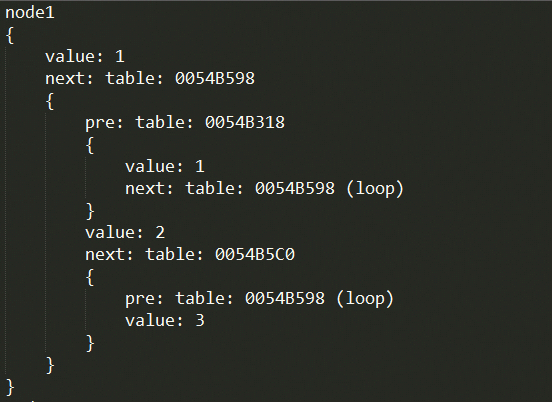
-- 这里的node1就是上面贴出的双向链表
print (TabToStr("node1", node1, true))
print (TabToStr("node1", node1))
print (TabToStr(tab))
结果: