上一篇讲了hash数据类型的相关实现方法,没有茅塞顿开也至少知道redis如何搞事情的了吧。
本篇咱们继续来看redis中的数据类型的实现: list 相关操作实现。
同样,我们以使用者的角度,开始理解list提供的功能,相应的数据结构承载,再到具体实现,以这样一个思路来理解redis之list。
零、redis list相关操作方法
从官方的手册中可以查到相关的使用方法。
1> BLPOP key1 [key2] timeout
功能: 移出并获取列表的第一个元素, 如果列表没有元素会阻塞列表直到等待超时或发现可弹出元素为止。(LPOP的阻塞版本)
返回值: 获取到元素的key和被弹出的元素值2> BRPOP key1 [key2 ] timeout
功能: 移出并获取列表的最后一个元素, 如果列表没有元素会阻塞列表直到等待超时或发现可弹出元素为止。(RPOP 的阻塞版本)
返回值: 获取到元素的key和被弹出的元素值3> BRPOPLPUSH source destination timeout
功能: 从列表中弹出一个值,将弹出的元素插入到另外一个列表中并返回它; 如果列表没有元素会阻塞列表直到等待超时或发现可弹出元素为止。(RPOPLPUSH 的阻塞版本)
返回值: 被转移的元素值或者为nil4> LINDEX key index
功能: 通过索引获取列表中的元素
返回值: 查找到的元素值,超出范围时返回nil5> LINSERT key BEFORE|AFTER pivot value
功能: 在列表的元素前或者后插入元素
返回值: 插入后的list长度6> LLEN key
功能: 获取列表长度
返回值: 列表长度7> LPOP key
功能: 移出并获取列表的第一个元素
返回值: 第一个元素或者nil8> LPUSH key value1 [value2]
功能: 将一个或多个值插入到列表头部
返回值: 插入后的list长度9> LPUSHX key value
将一个值插入到已存在的列表头部,如果key不存在则不做任何操作
返回值: 插入后的list长度10> LRANGE key start stop
功能: 获取列表指定范围内的元素 (包含起止边界)
返回值: 值列表11> LREM key count value
功能: 移除列表元素, count>0:移除正向匹配的count个元素,count<0:移除逆向匹配的count个元素, count=0,只移除匹配的元素
返回值: 移除的元素个数12> LSET key index value
功能: 通过索引设置列表元素的值
返回值: OK or err13> LTRIM key start stop
功能: 对一个列表进行修剪(trim),就是说,让列表只保留指定区间内的元素,不在指定区间之内的元素都将被删除。
返回值: OK14> RPOP key
功能: 移除列表的最后一个元素,返回值为移除的元素。
返回值: 最后一个元素值或者nil15> RPOPLPUSH source destination
功能: 移除列表的最后一个元素,并将该元素添加到另一个列表并返回
返回值: 被转移的元素16> RPUSH key value1 [value2]
功能: 在列表中添加一个或多个值
返回值: 插入后的list长度17> RPUSHX key value
功能: 为已存在的列表添加值
返回值: 插入后的list长度
redis中的实现方法定义如下:
{"rpush",rpushCommand,-3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lpush",lpushCommand,-3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"rpushx",rpushxCommand,3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lpushx",lpushxCommand,3,"wmF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"linsert",linsertCommand,5,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"rpop",rpopCommand,2,"wF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lpop",lpopCommand,2,"wF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"brpop",brpopCommand,-3,"ws",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"brpoplpush",brpoplpushCommand,4,"wms",0,NULL,1,2,1,0,0},
{"blpop",blpopCommand,-3,"ws",0,NULL,1,-2,1,0,0},
{"llen",llenCommand,2,"rF",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lindex",lindexCommand,3,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lset",lsetCommand,4,"wm",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lrange",lrangeCommand,4,"r",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"ltrim",ltrimCommand,4,"w",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"lrem",lremCommand,4,"w",0,NULL,1,1,1,0,0},
{"rpoplpush",rpoplpushCommand,3,"wm",0,NULL,1,2,1,0,0},
一、list相关数据结构
说到list或者说链表,我们能想到什么数据结构呢?单向链表、双向链表、循环链表... 好像都挺简单的,还有啥?? 我们来看下redis 的实现:
// quicklist 是其实数据容器,由head,tail 进行迭代,所以算是一个双向链表 /* quicklist is a 32 byte struct (on 64-bit systems) describing a quicklist. * 'count' is the number of total entries. * 'len' is the number of quicklist nodes. * 'compress' is: -1 if compression disabled, otherwise it's the number * of quicklistNodes to leave uncompressed at ends of quicklist. * 'fill' is the user-requested (or default) fill factor. */ typedef struct quicklist { // 头节点 quicklistNode *head; // 尾节点 quicklistNode *tail; // 现有元素个数 unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists */ // 现有的 quicklistNode 个数,一个 node 可能包含n个元素 unsigned int len; /* number of quicklistNodes */ // 填充因子 int fill : 16; /* fill factor for individual nodes */ // 多深的链表无需压缩 unsigned int compress : 16; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */ } quicklist; // 链表中的每个节点 typedef struct quicklistEntry { const quicklist *quicklist; quicklistNode *node; // 当前迭代元素的ziplist的偏移位置指针 unsigned char *zi; // 纯粹的 value, 值来源 zi unsigned char *value; // 占用空间大小 unsigned int sz; long long longval; // 当前节点偏移 int offset; } quicklistEntry; // 链表元素节点使用 quicklistNode /* quicklistNode is a 32 byte struct describing a ziplist for a quicklist. * We use bit fields keep the quicklistNode at 32 bytes. * count: 16 bits, max 65536 (max zl bytes is 65k, so max count actually < 32k). * encoding: 2 bits, RAW=1, LZF=2. * container: 2 bits, NONE=1, ZIPLIST=2. * recompress: 1 bit, bool, true if node is temporarry decompressed for usage. * attempted_compress: 1 bit, boolean, used for verifying during testing. * extra: 12 bits, free for future use; pads out the remainder of 32 bits */ typedef struct quicklistNode { struct quicklistNode *prev; struct quicklistNode *next; // zl 为ziplist链表,保存count个元素值 unsigned char *zl; unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */ unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist */ unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */ unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */ unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */ unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */ unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */ } quicklistNode; // list迭代器 typedef struct quicklistIter { const quicklist *quicklist; quicklistNode *current; unsigned char *zi; long offset; /* offset in current ziplist */ int direction; } quicklistIter; // ziplist 数据结构 typedef struct zlentry { unsigned int prevrawlensize, prevrawlen; unsigned int lensize, len; unsigned int headersize; unsigned char encoding; unsigned char *p; } zlentry;
二、rpush/lpush 新增元素操作实现
rpush是所尾部添加元素,lpush是从头部添加元素,本质上都是一样的,redis实际上也是完全复用一套代码。
// t_list.c, lpush void lpushCommand(client *c) { // 使用 LIST_HEAD|LIST_TAIL 作为插入位置标识 pushGenericCommand(c,LIST_HEAD); } void rpushCommand(client *c) { pushGenericCommand(c,LIST_TAIL); } // t_list.c, 实际的push操作 void pushGenericCommand(client *c, int where) { int j, waiting = 0, pushed = 0; // 在db中查找对应的key实例,查到或者查不到 robj *lobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]); // 查到的情况下,需要验证数据类型 if (lobj && lobj->type != OBJ_LIST) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return; } for (j = 2; j < c->argc; j++) { c->argv[j] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[j]); if (!lobj) { // 1. 在没有key实例的情况下,先创建key实例到db中 lobj = createQuicklistObject(); // 2. 设置 fill和depth 参数 // fill 默认: -2 // depth 默认: 0 quicklistSetOptions(lobj->ptr, server.list_max_ziplist_size, server.list_compress_depth); dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],lobj); } // 3. 一个个元素添加进去 listTypePush(lobj,c->argv[j],where); pushed++; } // 返回list长度 addReplyLongLong(c, waiting + (lobj ? listTypeLength(lobj) : 0)); if (pushed) { // 命令传播 char *event = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? "lpush" : "rpush"; signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_LIST,event,c->argv[1],c->db->id); } server.dirty += pushed; } // 1. 创建初始list // object.c, 创建初始list robj *createQuicklistObject(void) { quicklist *l = quicklistCreate(); robj *o = createObject(OBJ_LIST,l); o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST; return o; } // quicklist.c, 创建一个新的list容器,初始化默认值 /* Create a new quicklist. * Free with quicklistRelease(). */ quicklist *quicklistCreate(void) { struct quicklist *quicklist; quicklist = zmalloc(sizeof(*quicklist)); quicklist->head = quicklist->tail = NULL; quicklist->len = 0; quicklist->count = 0; quicklist->compress = 0; quicklist->fill = -2; return quicklist; } // 2. 设置quicklist 的fill和depth 值 // quicklist.c void quicklistSetOptions(quicklist *quicklist, int fill, int depth) { quicklistSetFill(quicklist, fill); quicklistSetCompressDepth(quicklist, depth); } // quicklist.c, 设置 fill 参数 void quicklistSetFill(quicklist *quicklist, int fill) { if (fill > FILL_MAX) { fill = FILL_MAX; } else if (fill < -5) { fill = -5; } quicklist->fill = fill; } // quicklist.c, 设置 depth 参数 void quicklistSetCompressDepth(quicklist *quicklist, int compress) { if (compress > COMPRESS_MAX) { compress = COMPRESS_MAX; } else if (compress < 0) { compress = 0; } quicklist->compress = compress; } // 3. 将元素添加进list中 // t_list.c, /* The function pushes an element to the specified list object 'subject', * at head or tail position as specified by 'where'. * * There is no need for the caller to increment the refcount of 'value' as * the function takes care of it if needed. */ void listTypePush(robj *subject, robj *value, int where) { if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { int pos = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? QUICKLIST_HEAD : QUICKLIST_TAIL; // 解码value value = getDecodedObject(value); size_t len = sdslen(value->ptr); // 将value添加到链表中 quicklistPush(subject->ptr, value->ptr, len, pos); // 减小value的引用,如果是被解编码后的对象,此时会将内存释放 decrRefCount(value); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } // object.c /* Get a decoded version of an encoded object (returned as a new object). * If the object is already raw-encoded just increment the ref count. */ robj *getDecodedObject(robj *o) { robj *dec; // OBJ_ENCODING_RAW,OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR 编码直接返回,引用计数+1(原因是: 原始robj一个引用,转换后的robj一个引用) if (sdsEncodedObject(o)) { incrRefCount(o); return o; } if (o->type == OBJ_STRING && o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) { char buf[32]; // 整型转换为字符型,返回string型的robj ll2string(buf,32,(long)o->ptr); dec = createStringObject(buf,strlen(buf)); return dec; } else { serverPanic("Unknown encoding type"); } } // quicklist.c, 添加value到链表中 /* Wrapper to allow argument-based switching between HEAD/TAIL pop */ void quicklistPush(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, const size_t sz, int where) { // 根据where决定添加到表头还表尾 if (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD) { quicklistPushHead(quicklist, value, sz); } else if (where == QUICKLIST_TAIL) { quicklistPushTail(quicklist, value, sz); } } // quicklist.c, 添加表头数据 /* Add new entry to head node of quicklist. * * Returns 0 if used existing head. * Returns 1 if new head created. */ int quicklistPushHead(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) { quicklistNode *orig_head = quicklist->head; // likely 对不同平台处理 __builtin_expect(!!(x), 1), // 判断是否允许插入元素,实际上是判断 head 的ziplist空间是否已占满, 没有则直接往里面插入即可 // fill 默认: -2 // depth 默认: 0 if (likely( _quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->head, quicklist->fill, sz))) { // 3.1. 添加head节点的zl链表中, zl 为ziplist 链表节点 quicklist->head->zl = ziplistPush(quicklist->head->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD); // 3.2. 更新头节点size大小 quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->head); } else { // 如果head已占满,则创建一个新的 quicklistNode 节点进行插入 quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode(); node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD); quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node); // 3.3. 插入新节点到head之前 _quicklistInsertNodeBefore(quicklist, quicklist->head, node); } // 将链表计数+1, 避免获取总数时迭代计算 quicklist->count++; quicklist->head->count++; return (orig_head != quicklist->head); } // quicklist.c, 判断是否允许插入元素 REDIS_STATIC int _quicklistNodeAllowInsert(const quicklistNode *node, const int fill, const size_t sz) { if (unlikely(!node)) return 0; int ziplist_overhead; /* size of previous offset */ if (sz < 254) ziplist_overhead = 1; else ziplist_overhead = 5; /* size of forward offset */ if (sz < 64) ziplist_overhead += 1; else if (likely(sz < 16384)) ziplist_overhead += 2; else ziplist_overhead += 5; /* new_sz overestimates if 'sz' encodes to an integer type */ // 加上需要添加的新元素的长度后,进行阀值判定,如果在阀值内,则返回1,否则返回0 unsigned int new_sz = node->sz + sz + ziplist_overhead; // 使用fill参数判定 if (likely(_quicklistNodeSizeMeetsOptimizationRequirement(new_sz, fill))) return 1; else if (!sizeMeetsSafetyLimit(new_sz)) return 0; else if ((int)node->count < fill) return 1; else return 0; } // quicklist.c REDIS_STATIC int _quicklistNodeSizeMeetsOptimizationRequirement(const size_t sz, const int fill) { if (fill >= 0) return 0; size_t offset = (-fill) - 1; // /* Optimization levels for size-based filling */ // static const size_t optimization_level[] = {4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536}; // offset < 5, offset 默认将等于 1, sz <= 8292 if (offset < (sizeof(optimization_level) / sizeof(*optimization_level))) { if (sz <= optimization_level[offset]) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } else { return 0; } } // SIZE_SAFETY_LIMIT 8192 #define sizeMeetsSafetyLimit(sz) ((sz) <= SIZE_SAFETY_LIMIT) // 3.1. 向每个链表节点中添加value, 实际是向 ziplist push 数据 // ziplist.c, push *s 数据到 zl 中 unsigned char *ziplistPush(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen, int where) { unsigned char *p; p = (where == ZIPLIST_HEAD) ? ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl) : ZIPLIST_ENTRY_END(zl); // 具体添加元素方法,有点复杂。简单点说就是 判断容量、扩容、按照ziplist协议添加元素 return __ziplistInsert(zl,p,s,slen); } // ziplist.c, 在hash的数据介绍时已详细介绍 /* Insert item at "p". */ static unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) { size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen; unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0; size_t offset; int nextdiff = 0; unsigned char encoding = 0; long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a value that is easy to see if for some reason we use it uninitialized. */ zlentry tail; /* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */ if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); } else { unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) { prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail); } } /* See if the entry can be encoded */ if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) { /* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */ reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding); } else { /* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipEncodeLength will use the * string length to figure out how to encode it. */ reqlen = slen; } /* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and * the length of the payload. */ reqlen += zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,prevlen); reqlen += zipEncodeLength(NULL,encoding,slen); /* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to * make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in * its prevlen field. */ nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0; /* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */ offset = p-zl; zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff); p = zl+offset; /* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */ if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { /* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */ memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff); /* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */ zipPrevEncodeLength(p+reqlen,reqlen); /* Update offset for tail */ ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen); /* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take * "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the * size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */ zipEntry(p+reqlen, &tail); if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) { ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff); } } else { /* This element will be the new tail. */ ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl); } /* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so * we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */ if (nextdiff != 0) { offset = p-zl; zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen); p = zl+offset; } /* Write the entry */ p += zipPrevEncodeLength(p,prevlen); p += zipEncodeLength(p,encoding,slen); if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) { memcpy(p,s,slen); } else { zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding); } ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1); return zl; } // 3.2. 更新node的size (实际占用内存空间大小) // quicklist.c, 更新node的size, 其实就是重新统计node的ziplist长度 #define quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node) do { (node)->sz = ziplistBlobLen((node)->zl); } while (0) // 3.3. 添加新链表节点到head之前 // quicklist.c, /* Wrappers for node inserting around existing node. */ REDIS_STATIC void _quicklistInsertNodeBefore(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistNode *old_node, quicklistNode *new_node) { __quicklistInsertNode(quicklist, old_node, new_node, 0); } /* Insert 'new_node' after 'old_node' if 'after' is 1. * Insert 'new_node' before 'old_node' if 'after' is 0. * Note: 'new_node' is *always* uncompressed, so if we assign it to * head or tail, we do not need to uncompress it. */ REDIS_STATIC void __quicklistInsertNode(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistNode *old_node, quicklistNode *new_node, int after) { if (after) { new_node->prev = old_node; if (old_node) { new_node->next = old_node->next; if (old_node->next) old_node->next->prev = new_node; old_node->next = new_node; } if (quicklist->tail == old_node) quicklist->tail = new_node; } else { // 插入new_node到old_node之前 new_node->next = old_node; if (old_node) { new_node->prev = old_node->prev; if (old_node->prev) old_node->prev->next = new_node; old_node->prev = new_node; } // 替换头节点位置 if (quicklist->head == old_node) quicklist->head = new_node; } /* If this insert creates the only element so far, initialize head/tail. */ // 第一个元素 if (quicklist->len == 0) { quicklist->head = quicklist->tail = new_node; } // 压缩list if (old_node) quicklistCompress(quicklist, old_node); quicklist->len++; } // quicklist.c, 压缩list #define quicklistCompress(_ql, _node) do { if ((_node)->recompress) // recompress quicklistCompressNode((_node)); else // __quicklistCompress((_ql), (_node)); } while (0) // recompress /* Compress only uncompressed nodes. */ #define quicklistCompressNode(_node) do { if ((_node) && (_node)->encoding == QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_RAW) { __quicklistCompressNode((_node)); } } while (0) /* Compress the ziplist in 'node' and update encoding details. * Returns 1 if ziplist compressed successfully. * Returns 0 if compression failed or if ziplist too small to compress. */ REDIS_STATIC int __quicklistCompressNode(quicklistNode *node) { #ifdef REDIS_TEST node->attempted_compress = 1; #endif /* Don't bother compressing small values */ if (node->sz < MIN_COMPRESS_BYTES) return 0; quicklistLZF *lzf = zmalloc(sizeof(*lzf) + node->sz); /* Cancel if compression fails or doesn't compress small enough */ // lzf 压缩算法,有点复杂咯 if (((lzf->sz = lzf_compress(node->zl, node->sz, lzf->compressed, node->sz)) == 0) || lzf->sz + MIN_COMPRESS_IMPROVE >= node->sz) { /* lzf_compress aborts/rejects compression if value not compressable. */ zfree(lzf); return 0; } lzf = zrealloc(lzf, sizeof(*lzf) + lzf->sz); zfree(node->zl); node->zl = (unsigned char *)lzf; node->encoding = QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_LZF; node->recompress = 0; return 1; } /* Force 'quicklist' to meet compression guidelines set by compress depth. * The only way to guarantee interior nodes get compressed is to iterate * to our "interior" compress depth then compress the next node we find. * If compress depth is larger than the entire list, we return immediately. */ REDIS_STATIC void __quicklistCompress(const quicklist *quicklist, quicklistNode *node) { /* If length is less than our compress depth (from both sides), * we can't compress anything. */ if (!quicklistAllowsCompression(quicklist) || quicklist->len < (unsigned int)(quicklist->compress * 2)) return; #if 0 /* Optimized cases for small depth counts */ if (quicklist->compress == 1) { quicklistNode *h = quicklist->head, *t = quicklist->tail; quicklistDecompressNode(h); quicklistDecompressNode(t); if (h != node && t != node) quicklistCompressNode(node); return; } else if (quicklist->compress == 2) { quicklistNode *h = quicklist->head, *hn = h->next, *hnn = hn->next; quicklistNode *t = quicklist->tail, *tp = t->prev, *tpp = tp->prev; quicklistDecompressNode(h); quicklistDecompressNode(hn); quicklistDecompressNode(t); quicklistDecompressNode(tp); if (h != node && hn != node && t != node && tp != node) { quicklistCompressNode(node); } if (hnn != t) { quicklistCompressNode(hnn); } if (tpp != h) { quicklistCompressNode(tpp); } return; } #endif /* Iterate until we reach compress depth for both sides of the list.a * Note: because we do length checks at the *top* of this function, * we can skip explicit null checks below. Everything exists. */ quicklistNode *forward = quicklist->head; quicklistNode *reverse = quicklist->tail; int depth = 0; int in_depth = 0; while (depth++ < quicklist->compress) { // 解压缩??? quicklistDecompressNode(forward); quicklistDecompressNode(reverse); if (forward == node || reverse == node) in_depth = 1; if (forward == reverse) return; forward = forward->next; reverse = reverse->prev; } if (!in_depth) quicklistCompressNode(node); if (depth > 2) { /* At this point, forward and reverse are one node beyond depth */ // 压缩 quicklistCompressNode(forward); quicklistCompressNode(reverse); } } /* Decompress only compressed nodes. */ #define quicklistDecompressNode(_node) do { if ((_node) && (_node)->encoding == QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_LZF) { __quicklistDecompressNode((_node)); } } while (0) /* Uncompress the ziplist in 'node' and update encoding details. * Returns 1 on successful decode, 0 on failure to decode. */ REDIS_STATIC int __quicklistDecompressNode(quicklistNode *node) { #ifdef REDIS_TEST node->attempted_compress = 0; #endif void *decompressed = zmalloc(node->sz); quicklistLZF *lzf = (quicklistLZF *)node->zl; if (lzf_decompress(lzf->compressed, lzf->sz, decompressed, node->sz) == 0) { /* Someone requested decompress, but we can't decompress. Not good. */ zfree(decompressed); return 0; } zfree(lzf); node->zl = decompressed; node->encoding = QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_RAW; return 1; }
总体来说,redis的list实现不是纯粹的单双向链表,而是 使用双向链表+ziplist 的方式实现链表功能,既节省了内存空间,对于查找来说时间复杂度也相对小。我们用一个时序图来重新审视下:

三、lindex/lrange/rrange 查找操作
读数据是数据库的一个另一个重要功能。一般来说,有单个查询,批量查询,范围查询之类的功能,咱们就分头说说。
// 1. 单个查询 lindex key index // t_list.c, 通过下标查找元素值 void lindexCommand(client *c) { robj *o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk); // 如果key本身就不存在,直接返回,空已响应 if (o == NULL || checkType(c,o,OBJ_LIST)) return; long index; robj *value = NULL; // 解析index字段,赋给 index 变量 if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &index, NULL) != C_OK)) return; if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { quicklistEntry entry; // 根据index查询list数据 if (quicklistIndex(o->ptr, index, &entry)) { // 使用两个字段来保存value if (entry.value) { value = createStringObject((char*)entry.value,entry.sz); } else { value = createStringObjectFromLongLong(entry.longval); } addReplyBulk(c,value); decrRefCount(value); } else { addReply(c,shared.nullbulk); } } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } // quicklist.c, 根据 index 查找元素 /* Populate 'entry' with the element at the specified zero-based index * where 0 is the head, 1 is the element next to head * and so on. Negative integers are used in order to count * from the tail, -1 is the last element, -2 the penultimate * and so on. If the index is out of range 0 is returned. * * Returns 1 if element found * Returns 0 if element not found */ int quicklistIndex(const quicklist *quicklist, const long long idx, quicklistEntry *entry) { quicklistNode *n; unsigned long long accum = 0; unsigned long long index; int forward = idx < 0 ? 0 : 1; /* < 0 -> reverse, 0+ -> forward */ // 初始化 quicklistEntry, 设置默认值 initEntry(entry); entry->quicklist = quicklist; // index为负数时,逆向搜索 if (!forward) { index = (-idx) - 1; n = quicklist->tail; } else { index = idx; n = quicklist->head; } if (index >= quicklist->count) return 0; while (likely(n)) { // n->count 代表每个list节点里的实际元素的个数(ziplist里可能包含n个元素) // 此处代表只会迭代到 index 所在的list节点就停止了 if ((accum + n->count) > index) { break; } else { D("Skipping over (%p) %u at accum %lld", (void *)n, n->count, accum); // 依次迭代 accum += n->count; n = forward ? n->next : n->prev; } } // 如果已经迭代完成,说明未找到index元素 if (!n) return 0; D("Found node: %p at accum %llu, idx %llu, sub+ %llu, sub- %llu", (void *)n, accum, index, index - accum, (-index) - 1 + accum); entry->node = n; if (forward) { /* forward = normal head-to-tail offset. */ // index-accum 代表index节点在 当前n节点中的偏移 entry->offset = index - accum; } else { /* reverse = need negative offset for tail-to-head, so undo * the result of the original if (index < 0) above. */ // 逆向搜索定位 如-1=1-1+0,-2=2-1+0 entry->offset = (-index) - 1 + accum; } // 解压缩node数据 quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(entry->node); // 根据offset,查找ziplist中的sds value entry->zi = ziplistIndex(entry->node->zl, entry->offset); // 从zi中获取value,sz,longval 返回 (ziplist 协议) ziplistGet(entry->zi, &entry->value, &entry->sz, &entry->longval); /* The caller will use our result, so we don't re-compress here. * The caller can recompress or delete the node as needed. */ return 1; } // quicklist.c /* Simple way to give quicklistEntry structs default values with one call. */ #define initEntry(e) do { (e)->zi = (e)->value = NULL; (e)->longval = -123456789; (e)->quicklist = NULL; (e)->node = NULL; (e)->offset = 123456789; (e)->sz = 0; } while (0) // 解压缩node数据 /* Force node to not be immediately re-compresable */ #define quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(_node) do { if ((_node) && (_node)->encoding == QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_LZF) { __quicklistDecompressNode((_node)); (_node)->recompress = 1; } } while (0) /* Uncompress the ziplist in 'node' and update encoding details. * Returns 1 on successful decode, 0 on failure to decode. */ REDIS_STATIC int __quicklistDecompressNode(quicklistNode *node) { #ifdef REDIS_TEST node->attempted_compress = 0; #endif void *decompressed = zmalloc(node->sz); quicklistLZF *lzf = (quicklistLZF *)node->zl; if (lzf_decompress(lzf->compressed, lzf->sz, decompressed, node->sz) == 0) { /* Someone requested decompress, but we can't decompress. Not good. */ zfree(decompressed); return 0; } zfree(lzf); node->zl = decompressed; node->encoding = QUICKLIST_NODE_ENCODING_RAW; return 1; } // ziplist.c /* Returns an offset to use for iterating with ziplistNext. When the given * index is negative, the list is traversed back to front. When the list * doesn't contain an element at the provided index, NULL is returned. */ unsigned char *ziplistIndex(unsigned char *zl, int index) { unsigned char *p; unsigned int prevlensize, prevlen = 0; if (index < 0) { index = (-index)-1; p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl); if (p[0] != ZIP_END) { ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); while (prevlen > 0 && index--) { p -= prevlen; ZIP_DECODE_PREVLEN(p, prevlensize, prevlen); } } } else { p = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_HEAD(zl); while (p[0] != ZIP_END && index--) { p += zipRawEntryLength(p); } } return (p[0] == ZIP_END || index > 0) ? NULL : p; }
对于范围查找来说,按照redis之前的套路,有可能是在单个查找的上面再进行循环查找就可以了,是否是这样呢?我们来看看:
// 2. lrange 范围查询 // t_list.c void lrangeCommand(client *c) { robj *o; long start, end, llen, rangelen; // 解析 start,end 参数 if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &start, NULL) != C_OK) || (getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[3], &end, NULL) != C_OK)) return; if ((o = lookupKeyReadOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.emptymultibulk)) == NULL || checkType(c,o,OBJ_LIST)) return; // list 长度获取, 有个计数器在 llen = listTypeLength(o); /* convert negative indexes */ if (start < 0) start = llen+start; if (end < 0) end = llen+end; // 将-xx的下标转换为正数查询,如果负数过大,则以0计算 if (start < 0) start = 0; /* Invariant: start >= 0, so this test will be true when end < 0. * The range is empty when start > end or start >= length. */ if (start > end || start >= llen) { addReply(c,shared.emptymultibulk); return; } // end 过大,则限制 // end 不可能小于0,因为上一个 start > end 已限制 if (end >= llen) end = llen-1; rangelen = (end-start)+1; /* Return the result in form of a multi-bulk reply */ addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,rangelen); if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { // 返回列表迭代器, start-TAIL, LIST_TAIL 代表正向迭代 listTypeIterator *iter = listTypeInitIterator(o, start, LIST_TAIL); // 迭代到 rangelen=0 为止,依次向输出缓冲输出 while(rangelen--) { listTypeEntry entry; // 获取下一个元素 listTypeNext(iter, &entry); quicklistEntry *qe = &entry.entry; if (qe->value) { addReplyBulkCBuffer(c,qe->value,qe->sz); } else { addReplyBulkLongLong(c,qe->longval); } } listTypeReleaseIterator(iter); } else { serverPanic("List encoding is not QUICKLIST!"); } } // t_list.c, 统计list长度 unsigned long listTypeLength(robj *subject) { if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { return quicklistCount(subject->ptr); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } /* Return cached quicklist count */ unsigned int quicklistCount(quicklist *ql) { return ql->count; } // 初始化 list 迭代器 /* Initialize an iterator at the specified index. */ listTypeIterator *listTypeInitIterator(robj *subject, long index, unsigned char direction) { listTypeIterator *li = zmalloc(sizeof(listTypeIterator)); li->subject = subject; li->encoding = subject->encoding; li->direction = direction; li->iter = NULL; /* LIST_HEAD means start at TAIL and move *towards* head. * LIST_TAIL means start at HEAD and move *towards tail. */ int iter_direction = direction == LIST_HEAD ? AL_START_TAIL : AL_START_HEAD; if (li->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { li->iter = quicklistGetIteratorAtIdx(li->subject->ptr, iter_direction, index); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } return li; } /* Initialize an iterator at a specific offset 'idx' and make the iterator * return nodes in 'direction' direction. */ quicklistIter *quicklistGetIteratorAtIdx(const quicklist *quicklist, const int direction, const long long idx) { quicklistEntry entry; // 查找idx 元素先 (前面已介绍, 为 ziplist+quicklist 迭代获得) if (quicklistIndex(quicklist, idx, &entry)) { // 获取获取的是整个list的迭代器, 通过current和offset进行迭代 quicklistIter *base = quicklistGetIterator(quicklist, direction); base->zi = NULL; base->current = entry.node; base->offset = entry.offset; return base; } else { return NULL; } } // quicklist, list迭代器初始化 /* Returns a quicklist iterator 'iter'. After the initialization every * call to quicklistNext() will return the next element of the quicklist. */ quicklistIter *quicklistGetIterator(const quicklist *quicklist, int direction) { quicklistIter *iter; // 迭代器只包含当前元素 iter = zmalloc(sizeof(*iter)); if (direction == AL_START_HEAD) { iter->current = quicklist->head; iter->offset = 0; } else if (direction == AL_START_TAIL) { iter->current = quicklist->tail; iter->offset = -1; } iter->direction = direction; iter->quicklist = quicklist; iter->zi = NULL; return iter; } // 迭代器携带整个list 引用,及当前节点,如何进行迭代,则是重点 // t_list.c, 迭代list元素, 并将 当前节点赋给 entry /* Stores pointer to current the entry in the provided entry structure * and advances the position of the iterator. Returns 1 when the current * entry is in fact an entry, 0 otherwise. */ int listTypeNext(listTypeIterator *li, listTypeEntry *entry) { /* Protect from converting when iterating */ serverAssert(li->subject->encoding == li->encoding); entry->li = li; if (li->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { // 迭代iter(改变iter指向), 赋值给 entry->entry return quicklistNext(li->iter, &entry->entry); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } return 0; } // quicklist.c /* Get next element in iterator. * * Note: You must NOT insert into the list while iterating over it. * You *may* delete from the list while iterating using the * quicklistDelEntry() function. * If you insert into the quicklist while iterating, you should * re-create the iterator after your addition. * * iter = quicklistGetIterator(quicklist,<direction>); * quicklistEntry entry; * while (quicklistNext(iter, &entry)) { * if (entry.value) * [[ use entry.value with entry.sz ]] * else * [[ use entry.longval ]] * } * * Populates 'entry' with values for this iteration. * Returns 0 when iteration is complete or if iteration not possible. * If return value is 0, the contents of 'entry' are not valid. */ int quicklistNext(quicklistIter *iter, quicklistEntry *entry) { initEntry(entry); if (!iter) { D("Returning because no iter!"); return 0; } // 保存当前node, 及quicklist引用 entry->quicklist = iter->quicklist; entry->node = iter->current; if (!iter->current) { D("Returning because current node is NULL") return 0; } unsigned char *(*nextFn)(unsigned char *, unsigned char *) = NULL; int offset_update = 0; if (!iter->zi) { /* If !zi, use current index. */ // 初始化时 zi 未赋值,所以直接使用当前元素,使用offset进行查找 quicklistDecompressNodeForUse(iter->current); iter->zi = ziplistIndex(iter->current->zl, iter->offset); } else { /* else, use existing iterator offset and get prev/next as necessary. */ if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD) { nextFn = ziplistNext; offset_update = 1; } else if (iter->direction == AL_START_TAIL) { nextFn = ziplistPrev; offset_update = -1; } // 向前或向后迭代元素 iter->zi = nextFn(iter->current->zl, iter->zi); iter->offset += offset_update; } entry->zi = iter->zi; entry->offset = iter->offset; if (iter->zi) { /* Populate value from existing ziplist position */ // 从 zi 中获取值返回 (按ziplist协议) ziplistGet(entry->zi, &entry->value, &entry->sz, &entry->longval); return 1; } else { /* We ran out of ziplist entries. * Pick next node, update offset, then re-run retrieval. */ // 当前ziplist没有下一个元素了,递归查找下一个ziplist quicklistCompress(iter->quicklist, iter->current); if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD) { /* Forward traversal */ D("Jumping to start of next node"); iter->current = iter->current->next; iter->offset = 0; } else if (iter->direction == AL_START_TAIL) { /* Reverse traversal */ D("Jumping to end of previous node"); iter->current = iter->current->prev; iter->offset = -1; } iter->zi = NULL; return quicklistNext(iter, entry); } } // ziplist.c /* Get entry pointed to by 'p' and store in either '*sstr' or 'sval' depending * on the encoding of the entry. '*sstr' is always set to NULL to be able * to find out whether the string pointer or the integer value was set. * Return 0 if 'p' points to the end of the ziplist, 1 otherwise. */ unsigned int ziplistGet(unsigned char *p, unsigned char **sstr, unsigned int *slen, long long *sval) { zlentry entry; if (p == NULL || p[0] == ZIP_END) return 0; if (sstr) *sstr = NULL; zipEntry(p, &entry); if (ZIP_IS_STR(entry.encoding)) { if (sstr) { *slen = entry.len; *sstr = p+entry.headersize; } } else { if (sval) { *sval = zipLoadInteger(p+entry.headersize,entry.encoding); } } return 1; }
看起来并没有利用单个查找的代码,而是使用迭代器进行操作。看起来不难,但是有点绕,我们就用一个时序图来重新表达下:
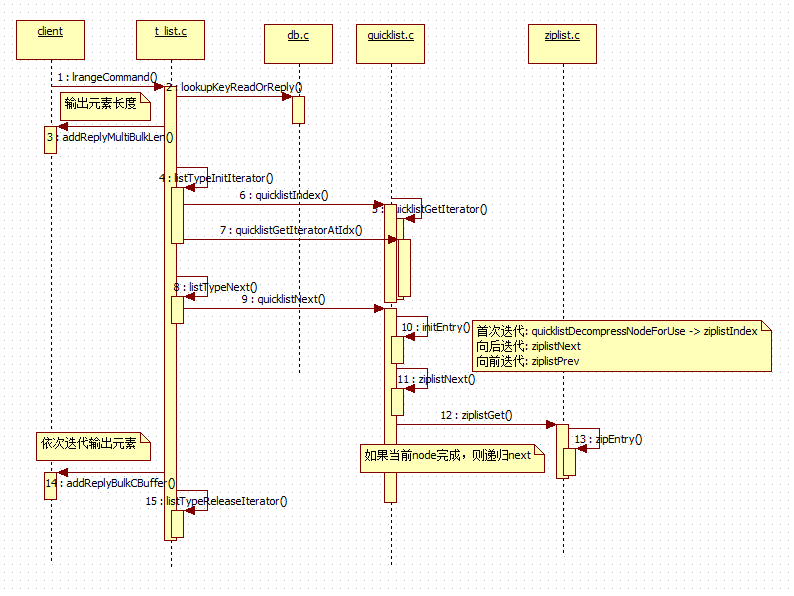
四、lrem 删除操作
增删改查,还是要凑够的。删除的操作,自然是要配置数据结构来做了,比如: 如何定位要删除的元素,删除后链表是否需要重排?
// LREM key count value, 只提供了范围删除的方式,单个数据删除可以通过此命令来完成 // t_list.c void lremCommand(client *c) { robj *subject, *obj; obj = c->argv[3]; long toremove; long removed = 0; if ((getLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[2], &toremove, NULL) != C_OK)) return; subject = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.czero); if (subject == NULL || checkType(c,subject,OBJ_LIST)) return; // 因是范围型删除,自然使用迭代删除是最好的选择了 listTypeIterator *li; if (toremove < 0) { toremove = -toremove; li = listTypeInitIterator(subject,-1,LIST_HEAD); } else { li = listTypeInitIterator(subject,0,LIST_TAIL); } listTypeEntry entry; // 迭代方式我们在查找操作已详细说明 while (listTypeNext(li,&entry)) { // 1. 比较元素是否是需要删除的对象,只有完全匹配才可以删除 if (listTypeEqual(&entry,obj)) { // 2. 实际的删除动作 listTypeDelete(li, &entry); server.dirty++; removed++; if (toremove && removed == toremove) break; } } listTypeReleaseIterator(li); // 如果没有任何元素后,将key从db中删除 if (listTypeLength(subject) == 0) { dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[1]); } addReplyLongLong(c,removed); if (removed) signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); } // 1. 是否与指定robj相等 // t_list.c, listTypeEntry 是否与指定robj相等 /* Compare the given object with the entry at the current position. */ int listTypeEqual(listTypeEntry *entry, robj *o) { if (entry->li->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,o,sdsEncodedObject(o)); return quicklistCompare(entry->entry.zi,o->ptr,sdslen(o->ptr)); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } // t_list.c int quicklistCompare(unsigned char *p1, unsigned char *p2, int p2_len) { // 元素本身是 ziplist 类型的,所以直接交由ziplist比对即可 return ziplistCompare(p1, p2, p2_len); } // ziplist.c /* Compare entry pointer to by 'p' with 'sstr' of length 'slen'. */ /* Return 1 if equal. */ unsigned int ziplistCompare(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *sstr, unsigned int slen) { zlentry entry; unsigned char sencoding; long long zval, sval; if (p[0] == ZIP_END) return 0; zipEntry(p, &entry); if (ZIP_IS_STR(entry.encoding)) { /* Raw compare */ if (entry.len == slen) { return memcmp(p+entry.headersize,sstr,slen) == 0; } else { return 0; } } else { /* Try to compare encoded values. Don't compare encoding because * different implementations may encoded integers differently. */ if (zipTryEncoding(sstr,slen,&sval,&sencoding)) { zval = zipLoadInteger(p+entry.headersize,entry.encoding); return zval == sval; } } return 0; } /* Delete the element pointed to. */ void listTypeDelete(listTypeIterator *iter, listTypeEntry *entry) { if (entry->li->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { quicklistDelEntry(iter->iter, &entry->entry); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } // 2. 执行删除操作 // t_list.c /* Delete the element pointed to. */ void listTypeDelete(listTypeIterator *iter, listTypeEntry *entry) { if (entry->li->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { quicklistDelEntry(iter->iter, &entry->entry); } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } } // quicklist.c /* Delete one element represented by 'entry' * * 'entry' stores enough metadata to delete the proper position in * the correct ziplist in the correct quicklist node. */ void quicklistDelEntry(quicklistIter *iter, quicklistEntry *entry) { quicklistNode *prev = entry->node->prev; quicklistNode *next = entry->node->next; int deleted_node = quicklistDelIndex((quicklist *)entry->quicklist, entry->node, &entry->zi); /* after delete, the zi is now invalid for any future usage. */ iter->zi = NULL; /* If current node is deleted, we must update iterator node and offset. */ if (deleted_node) { // 如果node被删除,则移动quicklist指针 if (iter->direction == AL_START_HEAD) { iter->current = next; iter->offset = 0; } else if (iter->direction == AL_START_TAIL) { iter->current = prev; iter->offset = -1; } } /* else if (!deleted_node), no changes needed. * we already reset iter->zi above, and the existing iter->offset * doesn't move again because: * - [1, 2, 3] => delete offset 1 => [1, 3]: next element still offset 1 * - [1, 2, 3] => delete offset 0 => [2, 3]: next element still offset 0 * if we deleted the last element at offet N and now * length of this ziplist is N-1, the next call into * quicklistNext() will jump to the next node. */ } // quicklist.c /* Delete one entry from list given the node for the entry and a pointer * to the entry in the node. * * Note: quicklistDelIndex() *requires* uncompressed nodes because you * already had to get *p from an uncompressed node somewhere. * * Returns 1 if the entire node was deleted, 0 if node still exists. * Also updates in/out param 'p' with the next offset in the ziplist. */ REDIS_STATIC int quicklistDelIndex(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistNode *node, unsigned char **p) { int gone = 0; // 同样,到最后一级,依旧是调用ziplist的方法进行删除 (按照 ziplist 协议操作即可) node->zl = ziplistDelete(node->zl, p); node->count--; // 如果node中没有元素了,就把当前node移除,否则更新 sz 大小 if (node->count == 0) { gone = 1; __quicklistDelNode(quicklist, node); } else { quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node); } quicklist->count--; /* If we deleted the node, the original node is no longer valid */ return gone ? 1 : 0; }
delete 操作总体来说就是一个迭代,比对,删除的操作,细节还是有点多的,只是都是些我们前面说过的技术,也就无所谓了。
五、lpop 弹出队列
这个功能大概和删除的意思差不多,就是删除最后一元素即可。事实上,我们也更喜欢使用redis这种功能。简单看看。
// 用法: LPOP key // t_list.c void lpopCommand(client *c) { popGenericCommand(c,LIST_HEAD); } void popGenericCommand(client *c, int where) { robj *o = lookupKeyWriteOrReply(c,c->argv[1],shared.nullbulk); if (o == NULL || checkType(c,o,OBJ_LIST)) return; // 弹出元素,重点看一下这个方法 robj *value = listTypePop(o,where); if (value == NULL) { addReply(c,shared.nullbulk); } else { char *event = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? "lpop" : "rpop"; addReplyBulk(c,value); decrRefCount(value); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_LIST,event,c->argv[1],c->db->id); if (listTypeLength(o) == 0) { notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del", c->argv[1],c->db->id); dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[1]); } signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[1]); server.dirty++; } } // t_list.c robj *listTypePop(robj *subject, int where) { long long vlong; robj *value = NULL; int ql_where = where == LIST_HEAD ? QUICKLIST_HEAD : QUICKLIST_TAIL; if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) { if (quicklistPopCustom(subject->ptr, ql_where, (unsigned char **)&value, NULL, &vlong, listPopSaver)) { if (!value) value = createStringObjectFromLongLong(vlong); } } else { serverPanic("Unknown list encoding"); } return value; } // quicklist.c /* pop from quicklist and return result in 'data' ptr. Value of 'data' * is the return value of 'saver' function pointer if the data is NOT a number. * * If the quicklist element is a long long, then the return value is returned in * 'sval'. * * Return value of 0 means no elements available. * Return value of 1 means check 'data' and 'sval' for values. * If 'data' is set, use 'data' and 'sz'. Otherwise, use 'sval'. */ int quicklistPopCustom(quicklist *quicklist, int where, unsigned char **data, unsigned int *sz, long long *sval, void *(*saver)(unsigned char *data, unsigned int sz)) { unsigned char *p; unsigned char *vstr; unsigned int vlen; long long vlong; int pos = (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD) ? 0 : -1; if (quicklist->count == 0) return 0; if (data) *data = NULL; if (sz) *sz = 0; if (sval) *sval = -123456789; quicklistNode *node; // 获取ziplist中的,第一个元素或者最后一个节点 if (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD && quicklist->head) { node = quicklist->head; } else if (where == QUICKLIST_TAIL && quicklist->tail) { node = quicklist->tail; } else { return 0; } // 获取ziplist中的,第一个元素或者最后一个元素 p = ziplistIndex(node->zl, pos); if (ziplistGet(p, &vstr, &vlen, &vlong)) { if (vstr) { if (data) // 创建string 对象返回 *data = saver(vstr, vlen); if (sz) *sz = vlen; } else { if (data) *data = NULL; if (sval) *sval = vlong; } // 删除获取数据后的元素 quicklistDelIndex(quicklist, node, &p); return 1; } return 0; }
弹出一个元素,大概分三步:
1. 获取头节点或尾节点;
2. 从ziplist中获取第一个元素或最后一个元素;
3. 删除头节点或尾节点;
六、blpop 阻塞式弹出元素
算是阻塞队列吧。我们只想看一下,像本地语言实现的阻塞,我们知道用锁+wait/notify机制。redis是如何进行阻塞的呢?
// 用法: BLPOP key1 [key2] timeout // t_list.c 同样 l/r 复用代码 void blpopCommand(client *c) { blockingPopGenericCommand(c,LIST_HEAD); } /* Blocking RPOP/LPOP */ void blockingPopGenericCommand(client *c, int where) { robj *o; mstime_t timeout; int j; if (getTimeoutFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[c->argc-1],&timeout,UNIT_SECONDS) != C_OK) return; // 循环查找多个key for (j = 1; j < c->argc-1; j++) { o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[j]); if (o != NULL) { if (o->type != OBJ_LIST) { addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr); return; } else { // 如果有值,则和非阻塞版本一样了,直接响应即可 if (listTypeLength(o) != 0) { /* Non empty list, this is like a non normal [LR]POP. */ char *event = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? "lpop" : "rpop"; robj *value = listTypePop(o,where); serverAssert(value != NULL); addReplyMultiBulkLen(c,2); addReplyBulk(c,c->argv[j]); addReplyBulk(c,value); decrRefCount(value); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_LIST,event, c->argv[j],c->db->id); if (listTypeLength(o) == 0) { dbDelete(c->db,c->argv[j]); notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_GENERIC,"del", c->argv[j],c->db->id); } signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[j]); server.dirty++; /* Replicate it as an [LR]POP instead of B[LR]POP. */ rewriteClientCommandVector(c,2, (where == LIST_HEAD) ? shared.lpop : shared.rpop, c->argv[j]); // 获取到值后直接结束流程 return; } } } } /* If we are inside a MULTI/EXEC and the list is empty the only thing * we can do is treating it as a timeout (even with timeout 0). */ if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI) { addReply(c,shared.nullmultibulk); return; } /* If the list is empty or the key does not exists we must block */ // 阻塞是在这里实现的 blockForKeys(c, c->argv + 1, c->argc - 2, timeout, NULL); } /* This is how the current blocking POP works, we use BLPOP as example: * - If the user calls BLPOP and the key exists and contains a non empty list * then LPOP is called instead. So BLPOP is semantically the same as LPOP * if blocking is not required. * - If instead BLPOP is called and the key does not exists or the list is * empty we need to block. In order to do so we remove the notification for * new data to read in the client socket (so that we'll not serve new * requests if the blocking request is not served). Also we put the client * in a dictionary (db->blocking_keys) mapping keys to a list of clients * blocking for this keys. * - If a PUSH operation against a key with blocked clients waiting is * performed, we mark this key as "ready", and after the current command, * MULTI/EXEC block, or script, is executed, we serve all the clients waiting * for this list, from the one that blocked first, to the last, accordingly * to the number of elements we have in the ready list. */ /* Set a client in blocking mode for the specified key, with the specified * timeout */ void blockForKeys(client *c, robj **keys, int numkeys, mstime_t timeout, robj *target) { dictEntry *de; list *l; int j; c->bpop.timeout = timeout; c->bpop.target = target; if (target != NULL) incrRefCount(target); // 阻塞入队判定 for (j = 0; j < numkeys; j++) { /* If the key already exists in the dict ignore it. */ if (dictAdd(c->bpop.keys,keys[j],NULL) != DICT_OK) continue; incrRefCount(keys[j]); /* And in the other "side", to map keys -> clients */ de = dictFind(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j]); if (de == NULL) { int retval; /* For every key we take a list of clients blocked for it */ l = listCreate(); // 将阻塞key放到 db 中,后台有线程去轮询 retval = dictAdd(c->db->blocking_keys,keys[j],l); incrRefCount(keys[j]); serverAssertWithInfo(c,keys[j],retval == DICT_OK); } else { l = dictGetVal(de); } // 将每个key 依次添加到 c->db->blocking_keys, 后续迭代将会重新检查取出 listAddNodeTail(l,c); } // 阻塞客户端,其实就是设置阻塞标识,然后等待key变更或超时,下一次扫描时将重新检测取出执行 blockClient(c,BLOCKED_LIST); } // block.c 设置阻塞标识 /* Block a client for the specific operation type. Once the CLIENT_BLOCKED * flag is set client query buffer is not longer processed, but accumulated, * and will be processed when the client is unblocked. */ void blockClient(client *c, int btype) { c->flags |= CLIENT_BLOCKED; c->btype = btype; server.bpop_blocked_clients++; }
redis阻塞功能的实现: 使用一个 db->blocking_keys 的列表来保存需要阻塞的请求,在下一次循环时,进行扫描这些队列的条件是否满足,从而决定是否继续阻塞或者取出。
思考: 从上面实现中,有个疑问:如何保证最多等待 timeout 时间或者最多循环多少次呢?你觉得应该如何处理呢?
OK, 至此,整个list数据结构的解析算是完整了。