一、转圈打印矩阵
【题目】
给定一个整型矩阵matrix,请按照转圈的方式打印它。例如:

打印结果为:1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11, 10
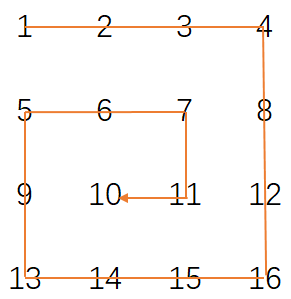
要求:额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
【分析】
用4个变量来标记左上角的点和右下角的点。
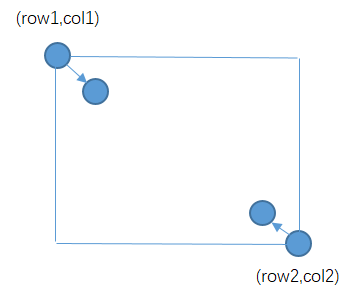
如果要打印这2个点形成矩阵的边界,可以写一个函数,具体是:col1++,加到col2的位置停止,然后row1++,加到row2的位置停止;然后row2--,减到row1停;col2--,减到col1停止

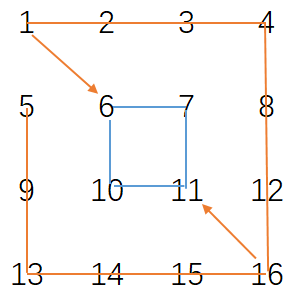
打印完最外层的1圈后,左上角的点往右下方移动,右下角的点往左上方移动;当row1>row2或col1>col2时流程结束
【代码实现】
public class PrintMatrixSpiralOrder { public static void spiralOrderPrint(int[][] matrix) { int row1 = 0; int col1 = 0; int row2 = matrix.length - 1; int col2 = matrix[0].length - 1; while (row1 <= row2 && col1 <= col2) { printEdge(matrix, row1++, col1++, row2--, col2--); } } public static void printEdge(int[][] m, int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) { //如果这个矩阵只有1行数 if (row1 == row2) { //打印这一行 for (int i = col1; i <= col2; i++) { System.out.print(m[i][col1] + " "); } //如果这个矩阵只有1列 } else if (col1 == col2) { //打印这一列 for (int i = row1; i <= row2; i++) { System.out.print(m[i][col1] + " "); } //如果是多乘多的矩阵 } else { int curC = col1; int curR = row1; while (curC != col2) { System.out.print(m[row1][curC] + " "); curC++; } while (curR != row2) { System.out.print(m[curR][col2] + " "); curR++; } while (curC != col1) { System.out.print(m[row2][curC] + " "); curC--; } while (curR != row1) { System.out.print(m[curR][col1] + " "); curR--; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}}; spiralOrderPrint(matrix); } }
二、旋转正方形矩阵
【题目】
给定一个整型正方形矩阵matrix,请把该矩阵调整成顺时针旋转90度的样子。
要求: 额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
【分析】
在给定的正方形中,先转最外圈,再转里面的。如果能保证最外层的数能转对,里面再依次转完即可。
举个例子:
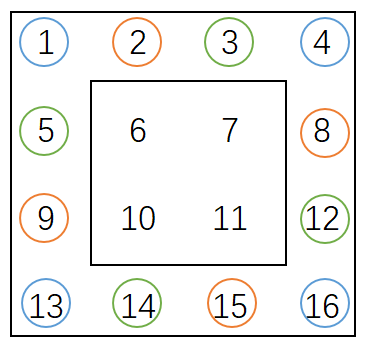
如果能把最外1圈的数转对,再转里面1圈(6,7,10,11),那么整体就旋转成功了。
先看最外1圈,从1开始,1、4、16、13之间相互交换位置,即1→4,4→16,16→13,13→1。
然后从2开始,2、8、15、9之间交换位置。再看第三组,3、12、14、5之间交换位置。
【代码实现】
public class RotateMatrix { public static void rotate(int[][] matrix) { int row1 = 0; int col1 = 0; int row2 = matrix.length - 1; int col2 = matrix[0].length - 1; while (row1 < row2) { rotateEdge(matrix, row1++, col1++, row2--, col2--); } } /** * 左上角的(row1,col1)和右下角的(row2,col2)一定要组成一个正方形,这是调用此函数的前提 * * @param m * @param row1 左上角的行号 * @param col1 左上角的列号 * @param row2 右下角的行 * @param col2 右下角的列 */ public static void rotateEdge(int[][] m, int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) { int times = col2 - col1; int tmp = 0; //从1出发,1、4、16、13之间相互交换位置,直至 for (int i = 0; i < times; i++) { tmp = m[row1][col1 + i]; m[row1][col1 + i] = m[row2 - i][col1]; m[row2 - i][col1] = m[row2][col2 - i]; m[row2][col2 - i] = m[row1 + i][col2]; m[row1 + i][col2] = tmp; } } public static void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) { for (int i = 0; i != matrix.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j != matrix[0].length; j++) { System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }, { 13, 14, 15, 16 } }; printMatrix(matrix); rotate(matrix); System.out.println("========="); printMatrix(matrix); } }
三、“之”字形打印矩阵
【题目】
给定一个矩阵matrix,按照“之”字形的方式打印这个矩阵,例如: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
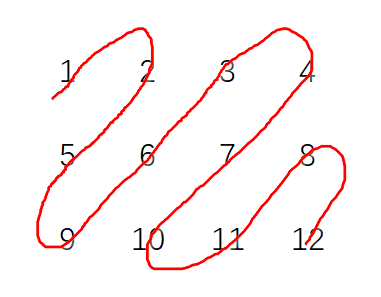
“之”字形打印的结果为:1,2,5,9,6,3,4,7,10,11,8,12
要求:额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
【分析】
如果把思路限制在1怎么变到2,2怎么变到5,5怎么变到9。。。这样是很愚蠢的!
我们应该这样想:
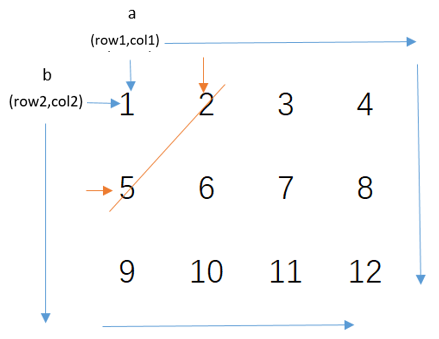
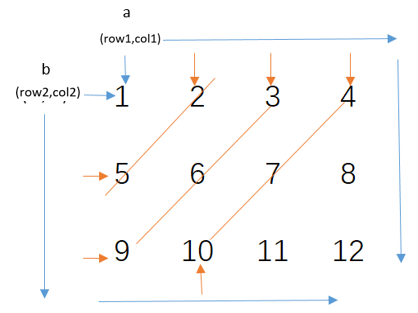
有一个(row1,col1),记为a点、(row2,col2),记为b点,一开始指向1的位置,并打印它。每次打印完后,a向右移动,移动到最右边后向下移动;b先向下移动,到最下方后再往右移动。
当a移动到2,b移动到5时,a、b两点可形成1条对角线;当a移动到3,b移动到9时,两点间也可以形成一条对角线;a移动到4,b移动到10时,又是1条对角线。。。

【代码实现】
public class ZigZagPrintMatrix { public static void printMatrixZigZag(int[][] matrix) { int row1 = 0; int col1 = 0; int row2 = 0; int col2 = 0; int endR = matrix.length - 1; int endC = matrix[0].length - 1; boolean fromUp = false; //当row1没走到结尾 while (row1 != endR + 1) { printLevel(matrix, row1, col1, row2, col2, fromUp); //到col1触到最后1列时,row1才开始增加 row1 = col1 == endC ? row1 + 1 : row1; //如果col1已经到最后,就不变,否则col1增加 col1 = col1 == endC ? col1 : col1 + 1; col2 = row2 == endR ? col2 + 1 : col2; row2 = row2 == endR ? row2 : row2 + 1; //对角线交替着打印 fromUp = !fromUp; } System.out.println(); } /** * (row1,col1)和(row2,col2)两个点连起来一定是一条对角线,这个函数就是打印对角线上的元素 * 并且这个函数可以实现从左下方到右上方打印,也可以实现从右上方到左下方的打印 * @param m * @param row1 * @param col1 * @param row2 * @param col2 * @param fromUp 控制对角线打印的方向。true:右上方到左下方 false:左下方到右上方 */ public static void printLevel(int[][] m, int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2, boolean fromUp) { //fromUp为true时,从右上方到左下方依次打印对角线上的元素 if (fromUp) { //row1 != row2 + 1等价于row1<=row2 while (row1 != row2 + 1) { System.out.print(m[row1++][col1--] + " "); } //fromUp为false时,从左下方到右上方依次打印对角线上的元素 } else { while (row2 != row1 - 1) { System.out.print(m[row2--][col2++] + " "); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}}; printMatrixZigZag(matrix); } }
四、在行列都排好序的矩阵中找数
【题目】
给定一个有N*M的整型矩阵matrix和一个整数K,matrix的每一行和每一 列都是排好序的。实现一个函数,判断K是否在matrix中。 例如:
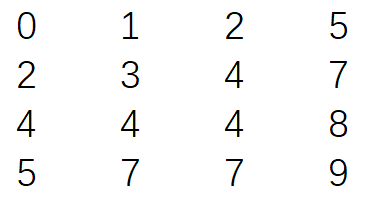
如果K为7,返回true;如果K为6,返回false。
要求:时间复杂度为O(N+M),额外空间复杂度为O(1)。
【分析】
如果通过遍历的方式,一共N*M个数,每个数都遍历,时间复杂度就是O(N*M),显然不符合要求。
通过例子来分析这个题目:

如果要判断6是否在上面的矩阵中,可以从右上角9开始查,9>6,因为每一列都是有序的,所以9这列底下的数一定没有6;
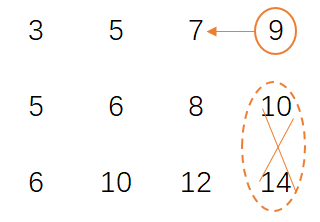
然后从9向左移动,来到7的位置,7>6,所以7底下的数一定没有6

继续从7往左移动,来到5的位置,5<6,所以5的左边一定比6小,于是从5往下走,来到6的位置,返回true
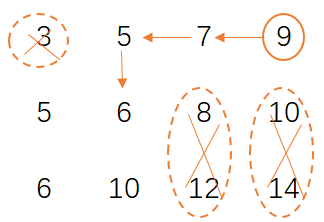
总结就是:从右上角开始,当前数大于要找的数,向左移动;当前数小于要找的数,向下移动;当前数如果等于要找的数,返回true;如果走到越界的位置还没找到,一定不存在,返回false。
注意:从左下角开始找也是可以的。但是不能从左上角或右下角开始找!
【代码实现】
public class FindNumInSortedMatrix { public static boolean isContains(int[][] matrix, int K) { int row = 0; int col = matrix[0].length - 1; while (row < matrix.length && col > -1) { if (matrix[row][col] == K) { return true; } else if (matrix[row][col] > K) { col--; } else { row++; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] matrix = new int[][]{{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6},// 0 {10, 12, 13, 15, 16, 17, 18},// 1 {23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29},// 2 {44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50},// 3 {65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71},// 4 {96, 97, 98, 99, 100, 111, 122},// 5 {166, 176, 186, 187, 190, 195, 200},// 6 {233, 243, 321, 341, 356, 370, 380} // 7 }; int K = 233; System.out.println(isContains(matrix, K)); } }