1、TCP 粘包和拆包基本介绍
2、TCP 粘包和拆包 实例演示
3、netty 自定义协议解决 TCP 粘包和拆包
1、TCP 粘包和拆包基本介绍 <--返回目录
TCP 是面向连接的,面向流的,提供高可靠性服务,收发两端(客户端和服务器端)都要一 一成对的 socket。因此发送端为了将多个发给接收端的包更有效的发给对方,使用了优化方法(Nagle 算法),将多次间隔较小且数据量小的数据,合并成一个大的数据块,然后进行封包。这样虽然提高了效率,但是接收端就难于分辨出完整的数据包了,因为面向流的通信是无消息保护边界的。
由TCP 无消息保护边界,需要在接收端处理消息边界问题,也就是我们所说的粘包、拆包问题。
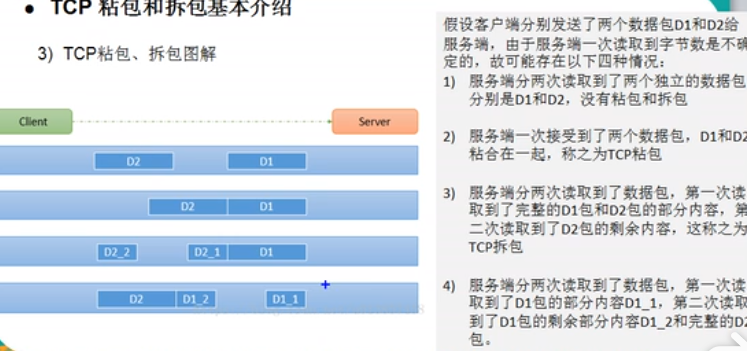
2、TCP 粘包和拆包 实例演示 <--返回目录
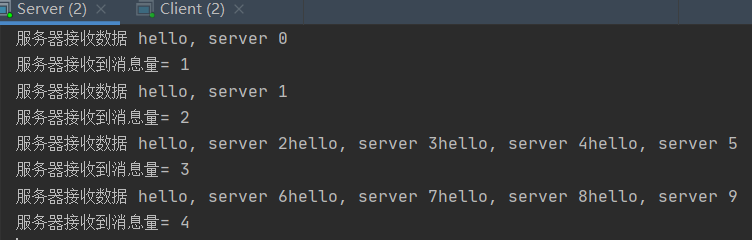
在编写 netty 程序时,如果没有做处理,就会发生粘包和拆包的问题。看一个具体的实例:
Server 端程序

package com.oy.tcp; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); NioEventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap .group(boss, work) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(8005).sync(); System.out.println("server started and listen " + 8005); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); work.shutdownGracefully(); } } } package com.oy.tcp; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; import java.util.UUID; public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { //System.out.println("服务器收到的数据:" + msg.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); byte[] buffer = new byte[msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(buffer); // 将 buffer 转成字符串 String message = new String(buffer, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); System.out.println("服务器接收数据 " + message); System.out.println("服务器接收到消息量= " + (++this.count)); // 服务器会送数据 ByteBuf response = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), CharsetUtil.UTF_8); ctx.writeAndFlush(response); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
Client 端程序

package com.oy.tcp; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap .group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8005).sync(); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } } package com.oy.tcp; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { byte[] buffer = new byte[msg.readableBytes()]; msg.readBytes(buffer); // 将 buffer 转成字符串 String message = new String(buffer, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); System.out.println("客户端接收数据 " + message); System.out.println("客户端接收到消息量= " + (++this.count)); } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { // 客户端发送 10 条数据 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, server " + i, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); ctx.writeAndFlush(buffer); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
3、netty 自定义协议解决 TCP 粘包和拆包 <--返回目录
使用 自定义协议 + 编解码器 来解决。关键是要解决服务器每次读取数据长度的问题,这个问题解决,就不会出现服务器多读或少读数据问题,从而避免 TCP 粘包和拆包。
案例:
- 要求客户端发送 5 个 Message 对象,客户端每次发送一个 Message 对象
- 服务器端每次接收一个 Message 对象,分 5 次进行解码,每次读取到一个 Message,会回复一个 Message 对象给客户端
封装传输数据类 MessageProtocol

package com.oy.prototcp; public class MessageProtocol { private int len; private byte[] content; public int getLen() { return len; } public void setLen(int len) { this.len = len; } public byte[] getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(byte[] content) { this.content = content; } }
编码器
package com.oy.prototcp; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToByteEncoder; public class MessageEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<MessageProtocol> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, MessageProtocol msg, ByteBuf out) throws Exception { System.out.println("MessageEncoder#encode() 被调用"); out.writeInt(msg.getLen()); out.writeBytes(msg.getContent()); } }
解码器
package com.oy.prototcp; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.ReplayingDecoder; import java.util.List; public class MessageDecoder extends ReplayingDecoder<Void> { @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { System.out.println("MessageDecoder#decode() 被调用"); // 将得到的二进制字节码 =》 MessageProtocol 对象 int len = in.readInt(); byte[] content = new byte[len]; in.readBytes(content); // 封装成 MessageProtoCol 对象,传递给下一个 handler MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol(); messageProtocol.setLen(len); messageProtocol.setContent(content); out.add(messageProtocol); } }
服务器端 Server
package com.oy.prototcp; import com.google.gson.internal.$Gson$Preconditions; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; public class Server { public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); NioEventLoopGroup work = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap .group(boss, work) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MessageDecoder()); // 解码器 pipeline.addLast(new MyServerHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(8005).sync(); System.out.println("server started and listen " + 8005); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { boss.shutdownGracefully(); work.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
MyServerHandler
package com.oy.prototcp; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class MyServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol> { private int count; @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception { int len = msg.getLen(); byte[] content = msg.getContent(); System.out.println("服务器接收到数据. 长度:" + len + ", 内容:" + new String(content, Charset.forName("utf-8"))); System.out.println("服务器接收到消息包数量" + (++this.count)); } }
客户端 Client
package com.oy.prototcp; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); bootstrap .group(group) .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new MessageEncoder()); // 编码器 pipeline.addLast(new MyClientHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8005).sync(); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
MyClientHandler
package com.oy.prototcp; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import java.nio.charset.Charset; public class MyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<MessageProtocol> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageProtocol msg) throws Exception { } @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { String messsage = "您好,吃了没"; byte[] content = messsage.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")); int len = messsage.getBytes(Charset.forName("utf-8")).length; // 创建协议包对象 MessageProtocol messageProtocol = new MessageProtocol(); messageProtocol.setContent(content); messageProtocol.setLen(len); ctx.writeAndFlush(messageProtocol); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
---
