You are given an array a consisting of n integers, and additionally an integer m. You have to choose some sequence of indices b1, b2, ..., bk (1 ≤ b1 < b2 < ... < bk ≤ n) in such a way that the value of 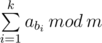 is maximized. Chosen sequence can be empty.
is maximized. Chosen sequence can be empty.
Print the maximum possible value of 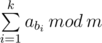 .
.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 35, 1 ≤ m ≤ 109).
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Print the maximum possible value of 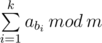 .
.
4 4
5 2 4 1
3
3 20
199 41 299
19
In the first example you can choose a sequence b = {1, 2}, so the sum 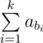 is equal to 7 (and that's 3 after taking it modulo 4).
is equal to 7 (and that's 3 after taking it modulo 4).
In the second example you can choose a sequence b = {3}.
分析:看到n≤35的条件时确实应该想到什么——假如n≤25,那么直接穷举2n情况即可,那么这个想法能否应用到35的情况中呢?答案时肯定的:使用Meet-in-the-Middle算法,即将原数组拆成两半,每一半都枚举2n/2个和(当然要mod m了),然后分别排序,枚举左半边取的和,再在右半边二分查找能拼出来的最大的和(假如左半边为x,则对右半边数组lower_bound(c,c+(1<<nr),m-x)-c-1,最后减1的原因是恰好求出小于m-x的最大值,即为答案)。这个算法能够成立的原因是:左右两边是加的关系,因此不存在加起来大于m,并且mod m后比不大于m的情况大——即(x+y)mod m<=max(x,y) mod m (0≤x,y<m)。
实现起来还是很简单的。