本篇主要讲述以下几点:
1、AuthenticationManager、ProviderManager和AuthenticationProvider三者之间的关系
2、以UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter为例,如何使用AuthenticationProvider的子类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider、
DaoAuthenticationProvider来验证用户名密码
3、Authentication、UserDetails的内部结构
先来看一张时序图:
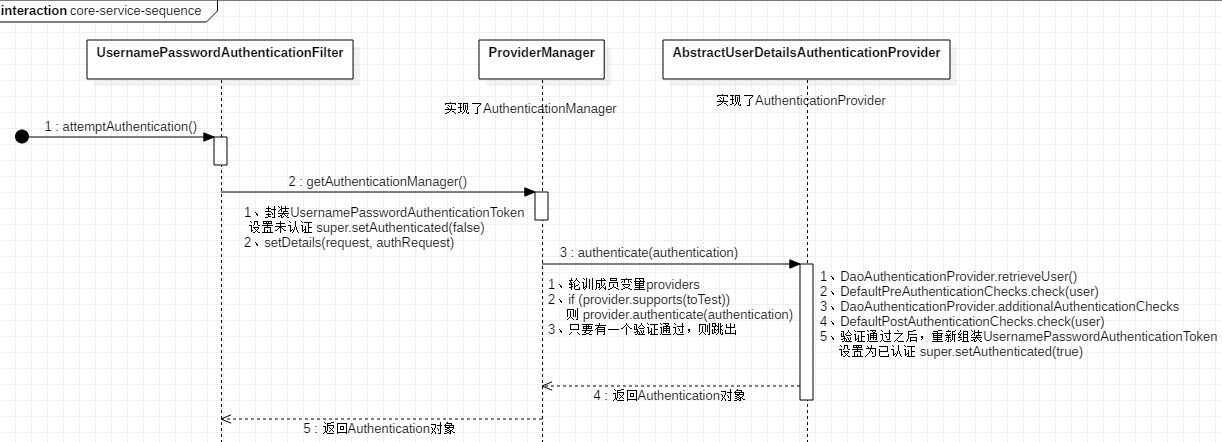
从上图可以看出验证逻辑为:
1、在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter的attemptAuthentication()方法中,调用AuthenticationManager进行认证
2、AuthenticationManager接收Authentication对象作为参数,并通过authenticate方法对其进行验证(实际由其实现类ProviderManager完成)
3、在ProviderManager的authenticate方法中,轮训成员变量List<AuthenticationProvider> providers。该providers中如果有一个
AuthenticationProvider的supports函数返回true,那么就会调用该AuthenticationProvider的authenticate函数认证,如果认证成功则整个
认证过程结束。如果不成功,则继续使用下一个合适的AuthenticationProvider进行认证,只要有一个认证成功则为认证成功。
4、UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken实现了Authentication,主要是将用户输入的用户名密码进行封装,并提供给
AuthenticationManager进行验证,验证成功后,返回一个认证成功的UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken对象
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager是一个接口,是认证方法的入口,接收一个Authentication对象作为参数
public interface AuthenticationManager { Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; }
ProviderManager
它是AuthenticationManager的一个实现类,实现了authenticate(Authentication authentication)方法,还有一个成员变量
List<AuthenticationProvider> providers
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean { ...... private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList(); public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { ...... } }
AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider也是一个接口,包含两个函数authenticate和supports。当Spring Security默认提供的Provider不能满足需求的时候,可以通过实现AuthenticationProvider接口来扩展出不同的认证提供者
public interface AuthenticationProvider { //通过参数Authentication对象,进行认证 Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException; //是否支持该认证类型 boolean supports(Class<?> authentication); }
Authentication
Authentication是一个接口,通过该接口可以获得用户相关信息、安全实体的标识以及认证请求的上下文信息等
在Spring Security中,有很多Authentication的实现类。如UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken、AnonymousAuthenticationToken和
RememberMeAuthenticationToken等等
通常不会被扩展,除非是为了支持某种特定类型的认证
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable { //权限结合,可使用AuthorityUtils.commaSeparatedStringToAuthorityList("admin, ROLE_ADMIN")返回字符串权限集合 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); //用户名密码认证时可以理解为密码 Object getCredentials(); //认证时包含的一些信息。如remoteAddress、sessionId Object getDetails(); //用户名密码认证时可理解时用户名 Object getPrincipal(); //是否被认证,认证为true boolean isAuthenticated(); //设置是否被认证 void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException; }
UserDetails
UserDetails也是一个接口,主要封装用户名密码是否过期、是否可用等信息
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable { //权限集合 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); //密码 String getPassword(); //用户名 String getUsername(); //用户名是否没有过期 boolean isAccountNonExpired(); //用户名是否没有锁定 boolean isAccountNonLocked(); //用户密码是否没有过期 boolean isCredentialsNonExpired(); //账号是否可用(可理解为是否删除) boolean isEnabled(); }
接下来看具体的实现方法:
ProviderManager
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { //获取当前的Authentication的认证类型 Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass(); AuthenticationException lastException = null; Authentication result = null; boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); //遍历所有的providers for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) { //判断该provider是否支持当前的认证类型。不支持,遍历下一个 if (!provider.supports(toTest)) { continue; } if (debug) { logger.debug("Authentication attempt using " + provider.getClass().getName()); } try { //调用provider的authenticat方法认证 result = provider.authenticate(authentication); if (result != null) { //认证通过的话,将认证结果的details赋值到当前认证对象authentication。然后跳出循环 copyDetails(authentication, result); break; } } catch (AccountStatusException e) { prepareException(e, authentication); // SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to // invalid account status throw e; } catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) { prepareException(e, authentication); throw e; } catch (AuthenticationException e) { lastException = e; } } ...... }
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider是 AuthenticationProvider 的核心实现类
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { //如果authentication不是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken类型,则抛出异常 Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication, messages.getMessage( "AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports", "Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported")); // 获取用户名 String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED" : authentication.getName(); //从缓存中获取UserDetails boolean cacheWasUsed = true; UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username); //缓存中没有,则从子类DaoAuthenticationProvider中获取 if (user == null) { cacheWasUsed = false; try { //获取用户信息。由子类DaoAuthenticationProvider实现 user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); } ...... } try { //前检查。由DefaultPreAuthenticationChecks实现(主要判断当前用户是否锁定,过期,冻结User) preAuthenticationChecks.check(user); //附加检查。由子类DaoAuthenticationProvider实现 additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); } catch (AuthenticationException exception) { ...... } //后检查。由DefaultPostAuthenticationChecks实现(检测密码是否过期) postAuthenticationChecks.check(user); if (!cacheWasUsed) { this.userCache.putUserInCache(user); } Object principalToReturn = user; if (forcePrincipalAsString) { principalToReturn = user.getUsername(); } //将已通过验证的用户信息封装成 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象并返回 return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user); }
1、前检查和后检查的参数为UserDetails,正好对应UserDetails中的4个isXXX方法
2、retrieveUser()和additionalAuthenticationChecks()由子类DaoAuthenticationProvider实现
3、createSuccessAuthentication如下:
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal, Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) { //重新封装成UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken。包含用户名、密码,以及对应的权限 //该构造方法会给父类Authentication赋值: super.setAuthenticated(true) UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken( principal, authentication.getCredentials(), authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities())); result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails()); return result; }
DaoAuthenticationProvider
DaoAuthenticationProvider实现了父类的retrieveUser()和additionalAuthenticationChecks()方法
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { UserDetails loadedUser; try { //调用UserDetailsService接口的loadUserByUsername获取用户信息 //通过实现UserDetailsService接口来扩展对用户密码的校验 loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username); } ...... //如果找不到该用户,则抛出异常 if (loadedUser == null) { throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException( "UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation"); } return loadedUser; }
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation") protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { Object salt = null; if (this.saltSource != null) { salt = this.saltSource.getSalt(userDetails); } //密码为空,则直接抛出异常 if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) { logger.debug("Authentication failed: no credentials provided"); throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage( "AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials")); } //获取用户输入的密码 String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString(); //将缓存中的密码(也可能是自定义查询的密码)与用户输入密码匹配 //如果匹配不上,则抛出异常 if (!passwordEncoder.isPasswordValid(userDetails.getPassword(), presentedPassword, salt)) { logger.debug("Authentication failed: password does not match stored value"); throw new BadCredentialsException(messages.getMessage( "AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials")); } }
关于UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername方法,可参考Spring Security认证配置(一)