描述
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
你是否可以不用额外空间解决此题?
解法一:哈希表
思路
最直接的解法就是利用一个集合保存每次遍历的节点的引用。之后,从链表头开始遍历,每遍历一个节点,就判断该节点的引用是否在集合中,如果不在集合中,则将该节点的引用放入集合中;如果在集合中,则返回该节点的引用(环的入口)。当然,如果能遍历到链表尾部,此时链表无环,返回 null。
Java 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode curr = head;
Set<ListNode> nodesSeen = new HashSet<>();
while (curr != null) {
if (nodesSeen.contains(curr)) {
return curr;
}
nodesSeen.add(curr);
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr;
}
}
Python 实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
curr = head
nodes_seen = set()
while curr:
if curr in nodes_seen:
return curr
nodes_seen.add(curr)
curr = curr.next
return curr
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:(O(n))
- 空间复杂度:(O(n))
解法二:双指针
思路
和 LeetCode 第 141 题一样,如果不想占用额外的空间的话,可以采用双指针的方式。
假设链表的起始节点为 A,环的入口节点为 B,两个指针(快慢指针)相交节点为 C,AB 两点之间的长度为 (x),BC 两点之间的长度为 (y),CB 两点之间的长度为 (z)。慢指针 slow 走过的长度为 (x+y),快指针 fast 为了“赶上”慢指针,应该走过的长度为 (x + y + z + y),同时,由于快指针的速度是慢指针的两倍,因此相同时间内,快指针走过的路程应该是慢指针(走过的路程)的两倍,即
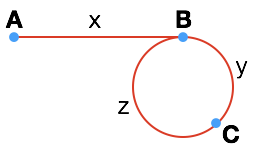
[x + y + z + y = 2 (x + y)
]
化简得,
[x = z
]
因此,如果此时有另外一个慢指针 slow2 从起始节点 A 出发,则两个慢指针会在节点 B (环的入口)相遇。
Java 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
ListNode slow2 = head;
while (slow != slow2) {
slow = slow.next;
slow2 = slow2.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
// Runtime: 1 ms
// Your runtime beats 100.00 % of python submissions.
Python 实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
slow2 = head
while slow != slow2:
slow = slow.next
slow2 = slow2.next
return slow
return None
# Runtime: 44 ms
# Your runtime beats 99.73 % of python submissions.
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:(O(n)),其中 (n) 表示链表的长度。最坏的情况下(链表有环),需要迭代的次数为 (x + y + z = n) 次,因此时间复杂度为 (O(n))
- 空间复杂度:(O(1)),只需要存储 3 个引用