webpack是一个静态模块打包器(module bundler),当webpack处理应用程序时,它会递归地构建一个依赖关系图(模块之间有引用依赖。例如:import bar from './bar')
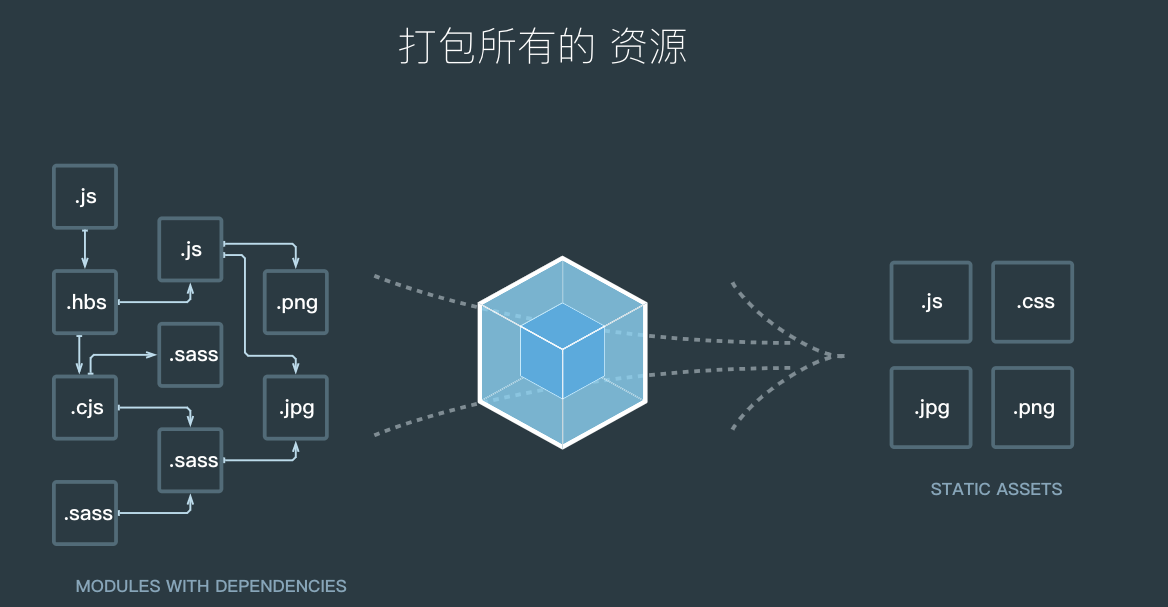
webpack的四个核心概念
核心配置在webpack.config.js文件中
1.入口【entry】
入口起点指示webpack应该使用哪个模块来作为构建其内部依赖图的开始,webpack可配置一个或多个入口起点。默认值是./src
module.exports = { entry: './path/to/my/entry/file.js' };
2.出口【output】
output属性告诉webpack在哪输出它所创建的bundles,以及如何命名这些文件,默认值为./dist。
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
entry: './path/to/my/entry/file.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'my-first-webpack.bundle.js'
}
};
3.loader
loader让webpack能够处理那些非JavaScript文件(webpack自身只能理解JavaScript),loader可以将所有类型文件转换为webpack能够处理的有效模块
test属性,用于表示应该被对应的loader进行转换的某个或某些文件
use属性,表示进行转换时,应该用哪个loader
const path = require('path');
const config = {
output: {
filename: 'my-first-webpack.bundle.js'
},
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.txt$/, use: 'raw-loader' }
]
}
};
module.exports = config;
4.插件plugins(plugin 英 [plʌgɪn] n. 插件;相关插件)
插件的范围:从打包优化和压缩,一直到重新定义环境的变量。插件接口功能极其强大,可以用来处理各种各样的任务。
使用一个插件,你只需要require()它,然后把它添加到plugins数组中。
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin'); // 通过 npm 安装
const webpack = require('webpack'); // 用于访问内置插件
const config = {
module: {
rules: [
{ test: /\.txt$/, use: 'raw-loader' }
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({template: './src/index.html'})
]
};
module.exports = config;