发现JAVA的有趣
Day1 继承不是"继承"
1.0 继承的格式

public class FU {
public void method()
{
System.out.println("Good night!");
}
}
public class ZI extends FU {
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZI zi=new ZI();
zi.method();
}
}
打印结果:
Good night!
2.0 继承中成员变量的访问特点

public class FU {
int num=10;
int numfu=100;
public void methodfu()
{
System.out.println(num);
}
}
public class ZI extends FU {
int num=20;
int numzi=200;
public void methodzi()
{
System.out.println(num);
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZI zi=new ZI();
FU fu=new FU();
System.out.println(zi.numfu);//100
System.out.println(zi.numzi);//200
//第一种
System.out.println(zi.num);//20;
System.out.println(fu.num);//10
//第二种
zi.methodzi();//20
fu.methodfu();//10
zi.methodfu();//10
}
}
3.0 区分子类方法中重名的三种

public class ZI extends FU {
int num=20;
public void methodzi()
{
int num=100;
System.out.println(num);//100
System.out.println(this.num);//20
System.out.println(super.num);//10
}
}
4.0 方法的覆盖重写


继承中方法的覆盖重写 (典型事例)
收旧手机!报废手机!手机换盆!换剪子!换菜刀!
public class Oldphone {
public void call()
{
System.out.println("didi~主人的电话来啦");
}
public void send()
{
System.out.println("叮咚! 有一条新信息");
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println("显示来电");
System.out.println("来电铃声");
}
}
public class Newphone extends Oldphone {
@Override
public void show(){
super.show();
System.out.println("显示姓名");
System.out.println("显示头像");
}
}
public class Phone {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Oldphone oldphone=new Oldphone();
Newphone newphone=new Newphone();
System.out.println("老手机的功能:");
oldphone.call();
oldphone.send();
oldphone.show();
System.out.println("=============");
System.out.println("新手机的功能:");
newphone.call();
newphone.send();
newphone.show();
}
}
打印结果:
老手机的功能:
didi~主人的电话来啦
叮咚! 有一条新信息
显示来电
来电铃声
=============
新手机的功能:
didi~主人的电话来啦
叮咚! 有一条新信息
显示来电
来电铃声
显示姓名
显示头像
5.0 继承中构造方法的访问特点

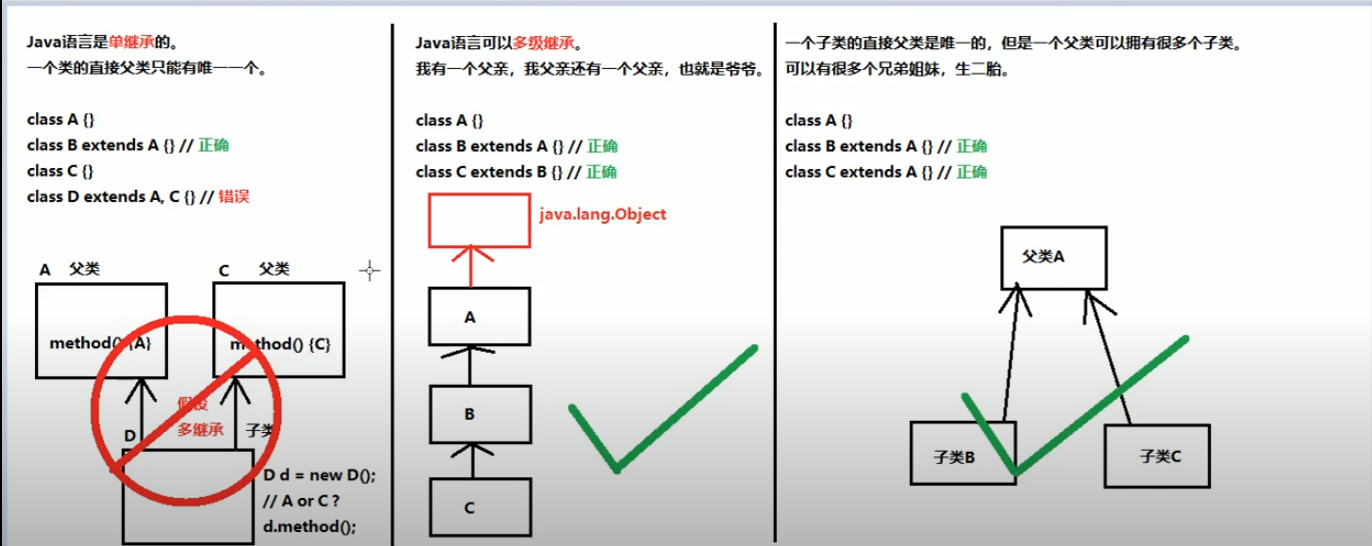
6.0 Java 继承的特点
6.0 继承的案例 (群主发红包啦 快去抢!)
首先 对案例的分析

抢红包的实现
public class User {
private int money;
private String name;
public User(){};
public User(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println("我叫"+getName()+" 我还有:"+getMoney());
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Owner extends User{
public Owner() {
super();
}
public Owner(int money, String name) {
super(money, name);
}
public ArrayList<Integer> send(int sendmoney,int count)//发多少 发几份
{
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
int totalmoney=super.getMoney();//当前余额
if(totalmoney<sendmoney)
{
System.out.println("余额不足!");
return list;
}
super.setMoney(totalmoney-sendmoney);
int ave=sendmoney/count;
int mod=sendmoney%count;//余数放在最后一个红包
for(int i=0;i<count-1;i++)
{
list.add(ave);
}
list.add(ave+mod);
return list;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class Member extends User {
public Member() {
super();
}
public Member(int money, String name) {
super(money, name);
}
public void receive(ArrayList <Integer> list)
{
int index=new Random().nextInt(list.size());//0~list.size()-1
int datamoney=list.remove(index);
int leftmoney=super.getMoney();//原有的金额
super.setMoney(datamoney+leftmoney);
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Hongbao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Owner owner=new Owner(100,"方时赫");
Member one=new Member(0,"金硕珍");
Member two=new Member(0,"金南俊");
Member three=new Member(0,"闵玧其");
owner.show();
one.show();
two.show();
three.show();
System.out.println("===============");
ArrayList<Integer> list=owner.send(20, 3);
one.receive(list);
two.receive(list);
three.receive(list);
owner.show();
one.show();
two.show();
three.show();
}
}
打印结果:
我叫方时赫 我还有:100
我叫金硕珍 我还有:0
我叫金南俊 我还有:0
我叫闵玧其 我还有:0
===============
我叫方时赫 我还有:80
我叫金硕珍 我还有:6
我叫金南俊 我还有:8
我叫闵玧其 我还有:6
Day3 抽象???
1.0 抽象类的方法

举个列子778吧
public abstract class Animals {
public abstract void eat();
}
public class Dog extends Animals{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("狗吃骨头");
}
}
public class Cat extends Animals{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cat cat=new Cat();
Dog dog=new Dog();
cat.eat();
dog.eat();
}
}
打印结果:
猫吃鱼
狗吃骨头
2.0 抽象类的使用的注意事项


Day 4 欢迎来到接口的世界!
1.0 接口的定义

2.0 接口的抽象方法的定义

3.0 接口的抽象方法的使用

public interface Myinter {
public abstract void method1();
public abstract void method2();
public abstract void method3();
}
public class Interfaced implements Myinter {//实现类
@Override
public void method1() {
System.out.println("这是第一个方法!");
}
@Override
public void method2() {
System.out.println("这是第二个方法!");
}
@Override
public void method3() {
System.out.println("这是第三个方法!");
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Interfaced inte=new Interfaced();
inte.method1();
inte.method2();
inte.method3();
}
}
打印结果:
这是第一个方法!
这是第二个方法!
这是第三个方法!
4.0 接口的默认方法的定义

5.0 接口的默认方法的使用

public interface Myinter {
public abstract void method1();
public abstract void method2();
public abstract void method3();
public default void method4()
{
System.out.println("新增加的方法!");
}
}
public class Interfaced implements Myinter {//实现类
@Override
public void method1() {
System.out.println("这是第一个方法!");
}
@Override
public void method2() {
System.out.println("这是第二个方法!");
}
@Override
public void method3() {
System.out.println("这是第三个方法!");
}
@Override
public void method4() {
System.out.println("这是覆盖重写的 方法!");
}
}
public class Practice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Interfaced inte=new Interfaced();
inte.method1();
inte.method2();
inte.method3();
inte.method4();
}
}
打印结果:
这是第一个方法!
这是第二个方法!
这是第三个方法!
这是覆盖重写的 方法!
6.0 接口的静态方法的定义

7.0 接口的静态方法的使用

public interface Myinter {
public static void methodstatic()
{
System.out.println("这是一个静态方法");
}
}
public class Myinterface implements Myinter {
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//错误写法 Myinterface.methodstatic();
Myinter.methodstatic();
}
}
打印结果:
这是一个静态方法
8.0 接口的私有方法的定义

public interface Myinter {
public default void method1()
{
System.out.println("这是一个默认方法1");
method3();
}
public default void method2()
{
System.out.println("这是一个默认方法2");
method3();
}
private void method3()
{
System.out.println("AAA");
System.out.println("BBB");
System.out.println("CCC");
}
}
public interface Myinter {
public static void method1()
{
System.out.println("这是一个默认方法1");
method3();
}
public static void method2()
{
System.out.println("这是一个默认方法2");
method3();
}
private static void method3()
{
System.out.println("AAA");
System.out.println("BBB");
System.out.println("CCC");
}
}
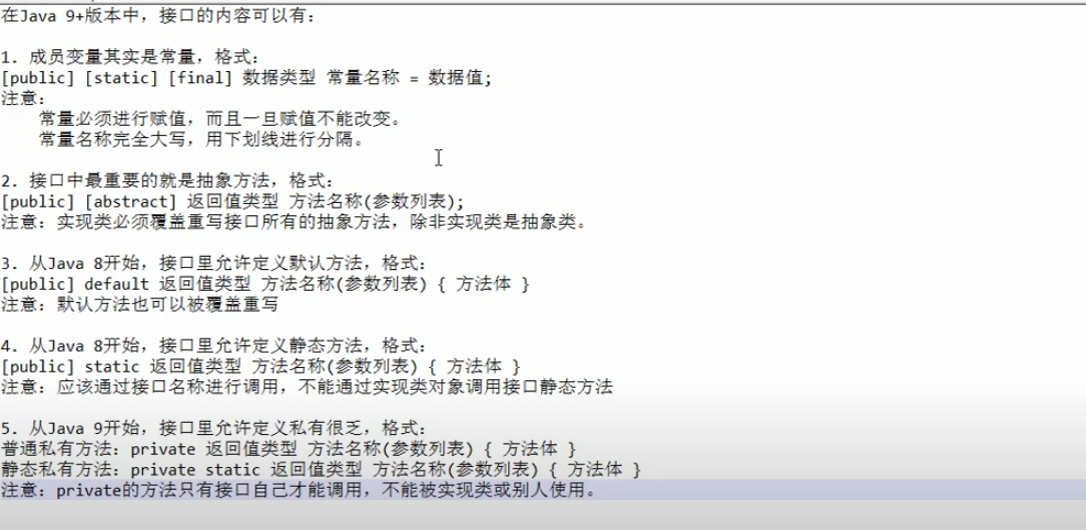
9.0 接口中常量定义和使用

10.0 接口的小结
11.0 继承父类并实现多个接口

12.0 接口的多继承
