1.原理
语音操控分为 语音识别和语音朗读两部分。
这两部分本来是需要自然语言处理技能相关知识以及一系列极其复杂的算法才能搞定,可是这篇文章将会跳过此处,如果你只是对算法和自然语言学感兴趣的话,就只有请您移步了,下面没有一个字会讲述到这些内容。
早在上世纪90年代的时候,IBM就推出了一款极为强大的语音识别系统-vio voice , 而其后相关产品层出不穷,不断的进化和演变着。 我们这里将会使用SAPI实现语音模块。
2. 什么是SAPI?
SAPI是微软Speech API , 是微软公司推出的语音接口,而细心的人会发现从WINXP开始,系统上就已经有语音识别的功能了,可是用武之地相当之少,他并没有给出一些人性化的自定义方案,仅有的语音操控命令显得相当鸡胁。 那么这篇文章的任务就是利用SAPI进行个性化的语音识别
代码
前提:打开win7的语音自动识别(控制面板--轻松访问--语音识别)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- codinfg:utf-8 -*-
'''
@author: Jeff LEE
@file: .py
@time: 2018-07-19 11:15
@desc:
'''
from win32com.client import constants
import os
import win32com.client
import pythoncom
speaker = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SPVOICE")
class SpeechRecognition:
def __init__(self, wordsToAdd):
self.speaker = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SpVoice")
self.listener = win32com.client.Dispatch("SAPI.SpSharedRecognizer")
self.context = self.listener.CreateRecoContext()
self.grammar = self.context.CreateGrammar()
self.grammar.DictationSetState(0)
self.wordsRule = self.grammar.Rules.Add("wordsRule", constants.SRATopLevel + constants.SRADynamic, 0)
self.wordsRule.Clear()
[self.wordsRule.InitialState.AddWordTransition(None, word) for word in wordsToAdd]
self.grammar.Rules.Commit()
self.grammar.CmdSetRuleState("wordsRule", 1)
self.grammar.Rules.Commit()
self.eventHandler = ContextEvents(self.context)
self.say("Started successfully")
def say(self, phrase):
self.speaker.Speak(phrase)
class ContextEvents(win32com.client.getevents("SAPI.SpSharedRecoContext")):
def OnRecognition(self, StreamNumber, StreamPosition, RecognitionType, Result):
newResult = win32com.client.Dispatch(Result)
print("你在说 ", newResult.PhraseInfo.GetText())
speechstr=newResult.PhraseInfo.GetText()
# 下面即为语音识别信息对应,打开响应操作
if speechstr=="记事本":
os.system('notepad')
elif speechstr=="写字板":
os.system('write')
elif speechstr=="画图板":
os.system('mspaint')
else:
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
speaker.Speak("语音识别开启")
wordsToAdd = ["记事本", "写字板","画图板",]
speechReco = SpeechRecognition(wordsToAdd)
while True:
pythoncom.PumpWaitingMessages()
调试遇到问题
python调用语音模块时,遇见TypeError:NoneTypetakesnoarguments这种错误类型该如何解决
报错的原因是:不能调用语音开发包
解决方法:(如果你已经安装了pyWin32,它也安装了PythonWin)
1.在python35目录中找到pythonwin文件夹下的pythonwin.exe
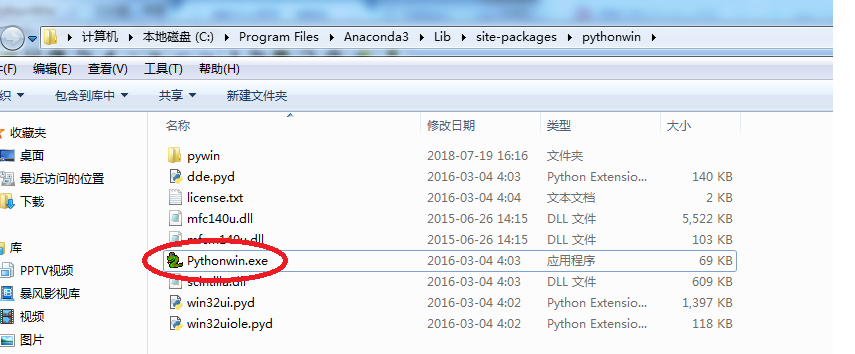
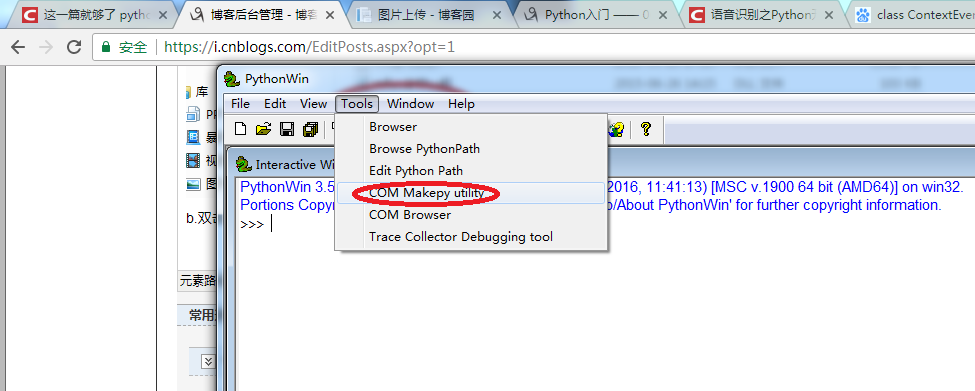
2.双击Pythonwin运行,然后选择工具tools/commakepyutility
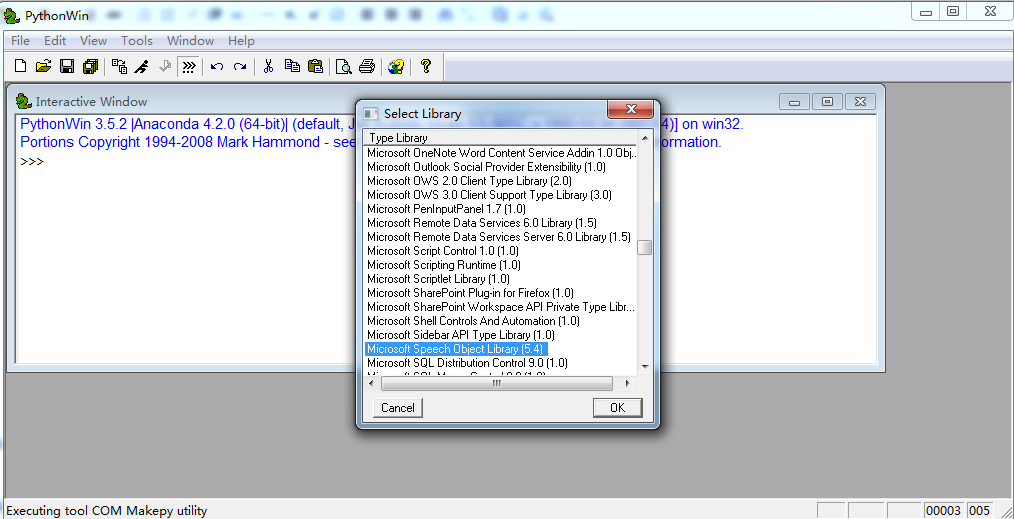
3.然后选择MicrosoftSpeechObjectLibrary5.4,点击OK键
4.运行结果如下,问题解决

后记
推荐一个不错的语音识别文档:https://blog.csdn.net/j2IaYU7Y/article/details/79878310