题目链接 : 超级赛亚ACMer
看别人AC代码学会了一个C++STL lower_bound
ForwardIter lower_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last,const _Tp& val)算法返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中的第一个大于等于值val的位置。
ForwardIter upper_bound(ForwardIter first, ForwardIter last, const _Tp& val)算法返回一个非递减序列[first, last)中第一个大于val的位置。
lower_bound和upper_bound如下图所示:
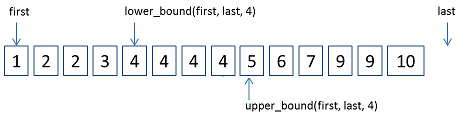
例如 a = [1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4]
int a[10] = {1,2,3,4,4,4,4, 6};
lower_bound(a, a+8, 3) - a = 2, 即下标为2的那个数,要记得减去数组的首地址. 如果lower_bound(a, a+8, 5) - a = 7;
同理upper_bound
本人AC代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1e5+5;
__int64 a[maxn];
int main()
{
//freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
int T, t, n;
__int64 fig, k;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(t = 1; t <= T; t++)
{
scanf("%d %I64d %I64d", &n, &fig, &k);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%I64d", &a[i]);
}
sort(a, a+n);
int i, j;
printf("Case #%d:
", t);
if(a[0] > fig)
{
puts("madan!");continue;
}
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if(a[i] > fig) break;
}
fig = a[i-1];
for(i = i-1; i < n-1;i++)
{
if(fig+k >= a[i] && fig+k < a[i+1])
{
fig = a[i]; k--;
}
}
fig+k >= a[n-1] ? puts("why am I so diao?") : puts("madan!");
}
return 0;
}
使用lower_bound 的代码
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int MAXN = 100000 + 10;
LL dp[MAXN], a[MAXN], add[MAXN];
int n, m, k;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
for(int cas = 1; cas <= T; ++ cas)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
scanf("%I64d", a + i);
}
printf("Case #%d:
", cas);
sort(a, a + n);
if (a[0] > m)
{
puts("madan!");
continue;
}
int pt = lower_bound(a, a + n, m) - a;
if (a[pt] != m) -- pt;
LL st = a[pt];
for (; pt < n; ++ pt)
{
if (k + st >= a[pt] && k + st < a[pt + 1])
{
st = a[pt]; -- k;
}
}
if (st + k >= a[n - 1]) puts("why am I so diao?");
else puts("madan!");
}
return 0;
}