今天我们来介绍车牌定位中的一种新方法--文字定位方法(MSER),包括其主要设计思想与实现。接着我们会介绍一下EasyPR v1.5-beta版本中带来的几项改动。
一. 文字定位法
在EasyPR前面几个版本中,最为人所诟病的就是定位效果不佳,尤其是在面对生活场景(例如手机拍摄)时。由于EasyPR最早的数据来源于卡口,因此对卡口数据进行了优化,而并没有对生活场景中图片有较好处理的策略。后来一个版本(v1.3)增加了颜色定位方法,改善了这种现象,但是对分辨率较大的图片处理仍然不好。再加上颜色定位在面对低光照,低对比度的图像时处理效果大幅度下降,颜色本身也是一个不稳定的特征。因此EasyPR的车牌定位的整体鲁棒性仍然不足。
针对这种现象,EasyPR v1.5增加了一种新的定位方法,文字定位方法,大幅度改善了这些问题。下面几幅图可以说明文字定位法的效果。
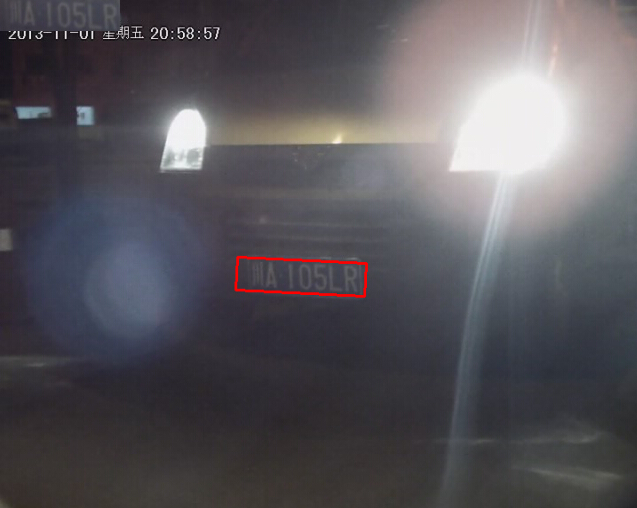
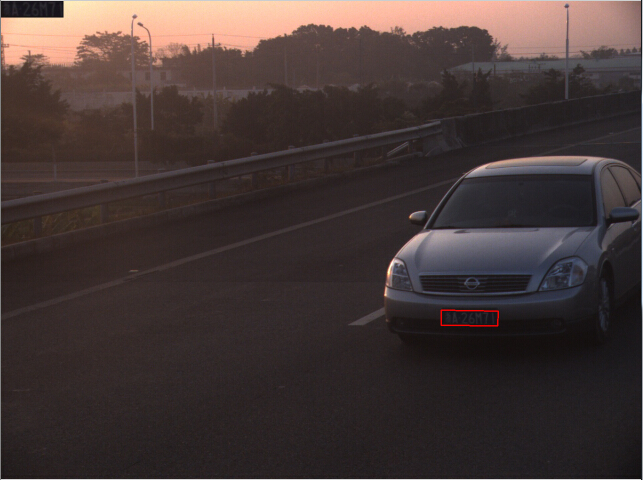


图1 夜间的车牌图像(左) , 图2 对比度非常低的图像(右)

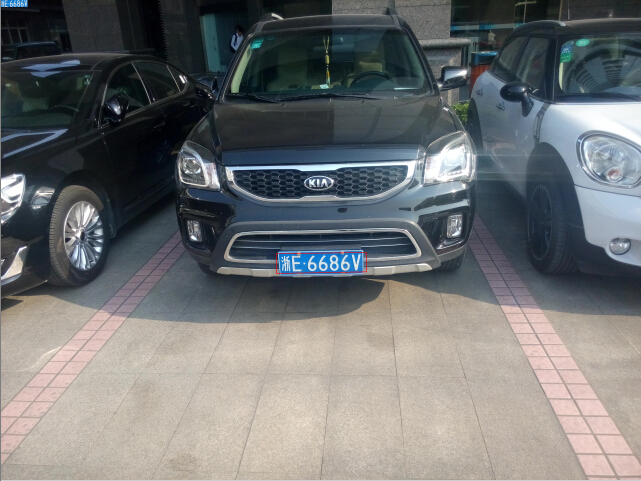
图3 近距离的图像(左) , 图4 高分辨率的图像(右)
图1是夜间的车牌图像,图2是对比度非常低的图像,图3是非常近距离拍摄的图像,图4则是高分辨率(3200宽)的图像。
文字定位方法是采用了低级过滤器提取文字,然后再将其组合的一种定位方法。原先是利用在场景中定位文字,在这里利用其定位车牌。与在扫描文档中的文字不同,自然场景中的文字具有低对比度,背景各异,光亮干扰较多等情况,因此需要一个极为鲁棒的方法去提取出来。目前业界用的较多的是MSER(最大稳定极值区域)方法。EasyPR使用的是MSER的一个改良方法,专门针对文字进行了优化。在文字定位出来以后,一般需要用一个分类器将其中大部分的定位错误的文字去掉,例如ANN模型。为了获得最终的车牌,这些文字需要组合起来。由于实际情况的复杂,简单的使用普通的聚类效果往往不好,因此EasyPR使用了一种鲁棒性较强的种子生长方法(seed growing)去组合。
我在这里简单介绍一下具体的实现。关于方法的细节可以看代码,有很多的注释(代码可能较长)。关于方法的思想可以看附录的两篇论文。

1 //! use verify size to first generate char candidates 2 void mserCharMatch(const Mat &src, std::vector<Mat> &match, std::vector<CPlate>& out_plateVec_blue, std::vector<CPlate>& out_plateVec_yellow, 3 bool usePlateMser, std::vector<RotatedRect>& out_plateRRect_blue, std::vector<RotatedRect>& out_plateRRect_yellow, int img_index, 4 bool showDebug) { 5 Mat image = src; 6 7 std::vector<std::vector<std::vector<Point>>> all_contours; 8 std::vector<std::vector<Rect>> all_boxes; 9 all_contours.resize(2); 10 all_contours.at(0).reserve(1024); 11 all_contours.at(1).reserve(1024); 12 all_boxes.resize(2); 13 all_boxes.at(0).reserve(1024); 14 all_boxes.at(1).reserve(1024); 15 16 match.resize(2); 17 18 std::vector<Color> flags; 19 flags.push_back(BLUE); 20 flags.push_back(YELLOW); 21 22 const int imageArea = image.rows * image.cols; 23 const int delta = 1; 24 //const int delta = CParams::instance()->getParam2i();; 25 const int minArea = 30; 26 const double maxAreaRatio = 0.05; 27 28 Ptr<MSER2> mser; 29 mser = MSER2::create(delta, minArea, int(maxAreaRatio * imageArea)); 30 mser->detectRegions(image, all_contours.at(0), all_boxes.at(0), all_contours.at(1), all_boxes.at(1)); 31 32 // mser detect 33 // color_index = 0 : mser-, detect white characters, which is in blue plate. 34 // color_index = 1 : mser+, detect dark characters, which is in yellow plate. 35 36 #pragma omp parallel for 37 for (int color_index = 0; color_index < 2; color_index++) { 38 Color the_color = flags.at(color_index); 39 40 std::vector<CCharacter> charVec; 41 charVec.reserve(128); 42 43 match.at(color_index) = Mat::zeros(image.rows, image.cols, image.type()); 44 45 Mat result = image.clone(); 46 cvtColor(result, result, COLOR_GRAY2BGR); 47 48 size_t size = all_contours.at(color_index).size(); 49 50 int char_index = 0; 51 int char_size = 20; 52 53 // Chinese plate has max 7 characters. 54 const int char_max_count = 7; 55 56 // verify char size and output to rects; 57 for (size_t index = 0; index < size; index++) { 58 Rect rect = all_boxes.at(color_index)[index]; 59 std::vector<Point>& contour = all_contours.at(color_index)[index]; 60 61 // sometimes a plate could be a mser rect, so we could 62 // also use mser algorithm to find plate 63 if (usePlateMser) { 64 RotatedRect rrect = minAreaRect(Mat(contour)); 65 if (verifyRotatedPlateSizes(rrect)) { 66 //rotatedRectangle(result, rrect, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2); 67 if (the_color == BLUE) out_plateRRect_blue.push_back(rrect); 68 if (the_color == YELLOW) out_plateRRect_yellow.push_back(rrect); 69 } 70 } 71 72 // find character 73 if (verifyCharSizes(rect)) { 74 Mat mserMat = adaptive_image_from_points(contour, rect, Size(char_size, char_size)); 75 Mat charInput = preprocessChar(mserMat, char_size); 76 Rect charRect = rect; 77 78 Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / 2, charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / 2); 79 Mat tmpMat; 80 double ostu_level = cv::threshold(image(charRect), tmpMat, 0, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY | CV_THRESH_OTSU); 81 82 //cv::circle(result, center, 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); 83 84 // use judegMDOratio2 function to 85 // remove the small lines in character like "zh-cuan" 86 if (judegMDOratio2(image, rect, contour, result)) { 87 CCharacter charCandidate; 88 charCandidate.setCharacterPos(charRect); 89 charCandidate.setCharacterMat(charInput); 90 charCandidate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level); 91 charCandidate.setCenterPoint(center); 92 charCandidate.setIsChinese(false); 93 charVec.push_back(charCandidate); 94 } 95 } 96 } 97 98 // improtant, use matrix multiplication to acclerate the 99 // classification of many samples. use the character 100 // score, we can use non-maximum superssion (nms) to 101 // reduce the characters which are not likely to be true 102 // charaters, and use the score to select the strong seed 103 // of which the score is larger than 0.9 104 CharsIdentify::instance()->classify(charVec); 105 106 // use nms to remove the character are not likely to be true. 107 double overlapThresh = 0.6; 108 //double overlapThresh = CParams::instance()->getParam1f(); 109 NMStoCharacter(charVec, overlapThresh); 110 charVec.shrink_to_fit(); 111 112 std::vector<CCharacter> strongSeedVec; 113 strongSeedVec.reserve(64); 114 std::vector<CCharacter> weakSeedVec; 115 weakSeedVec.reserve(64); 116 std::vector<CCharacter> littleSeedVec; 117 littleSeedVec.reserve(64); 118 119 //size_t charCan_size = charVec.size(); 120 for (auto charCandidate : charVec) { 121 //CCharacter& charCandidate = charVec[char_index]; 122 Rect rect = charCandidate.getCharacterPos(); 123 double score = charCandidate.getCharacterScore(); 124 if (charCandidate.getIsStrong()) { 125 strongSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate); 126 } 127 else if (charCandidate.getIsWeak()) { 128 weakSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate); 129 //cv::rectangle(result, rect, Scalar(255, 0, 255)); 130 } 131 else if (charCandidate.getIsLittle()) { 132 littleSeedVec.push_back(charCandidate); 133 //cv::rectangle(result, rect, Scalar(255, 0, 255)); 134 } 135 } 136 137 std::vector<CCharacter> searchCandidate = charVec; 138 139 // nms to srong seed, only leave the strongest one 140 overlapThresh = 0.3; 141 NMStoCharacter(strongSeedVec, overlapThresh); 142 143 // merge chars to group 144 std::vector<std::vector<CCharacter>> charGroupVec; 145 charGroupVec.reserve(64); 146 mergeCharToGroup(strongSeedVec, charGroupVec); 147 148 // genenrate the line of the group 149 // based on the assumptions , the mser rects which are 150 // given high socre by character classifier could be no doubtly 151 // be the characters in one plate, and we can use these characeters 152 // to fit a line which is the middle line of the plate. 153 std::vector<CPlate> plateVec; 154 plateVec.reserve(16); 155 for (auto charGroup : charGroupVec) { 156 Rect plateResult = charGroup[0].getCharacterPos(); 157 std::vector<Point> points; 158 points.reserve(32); 159 160 Vec4f line; 161 int maxarea = 0; 162 Rect maxrect; 163 double ostu_level_sum = 0; 164 165 int leftx = image.cols; 166 Point leftPoint(leftx, 0); 167 int rightx = 0; 168 Point rightPoint(rightx, 0); 169 170 std::vector<CCharacter> mserCharVec; 171 mserCharVec.reserve(32); 172 173 // remove outlier CharGroup 174 std::vector<CCharacter> roCharGroup; 175 roCharGroup.reserve(32); 176 177 removeRightOutliers(charGroup, roCharGroup, 0.2, 0.5, result); 178 //roCharGroup = charGroup; 179 180 for (auto character : roCharGroup) { 181 Rect charRect = character.getCharacterPos(); 182 cv::rectangle(result, charRect, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1); 183 plateResult |= charRect; 184 185 Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / 2, charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / 2); 186 points.push_back(center); 187 mserCharVec.push_back(character); 188 //cv::circle(result, center, 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2); 189 190 ostu_level_sum += character.getOstuLevel(); 191 192 if (charRect.area() > maxarea) { 193 maxrect = charRect; 194 maxarea = charRect.area(); 195 } 196 if (center.x < leftPoint.x) { 197 leftPoint = center; 198 } 199 if (center.x > rightPoint.x) { 200 rightPoint = center; 201 } 202 } 203 204 double ostu_level_avg = ostu_level_sum / (double)roCharGroup.size(); 205 if (1 && showDebug) { 206 std::cout << "ostu_level_avg:" << ostu_level_avg << std::endl; 207 } 208 float ratio_maxrect = (float)maxrect.width / (float)maxrect.height; 209 210 if (points.size() >= 2 && ratio_maxrect >= 0.3) { 211 fitLine(Mat(points), line, CV_DIST_L2, 0, 0.01, 0.01); 212 213 float k = line[1] / line[0]; 214 //float angle = atan(k) * 180 / (float)CV_PI; 215 //std::cout << "k:" << k << std::endl; 216 //std::cout << "angle:" << angle << std::endl; 217 //std::cout << "cos:" << 0.3 * cos(k) << std::endl; 218 //std::cout << "ratio_maxrect:" << ratio_maxrect << std::endl; 219 220 std::sort(mserCharVec.begin(), mserCharVec.end(), 221 [](const CCharacter& r1, const CCharacter& r2) { 222 return r1.getCharacterPos().tl().x < r2.getCharacterPos().tl().x; 223 }); 224 225 CCharacter midChar = mserCharVec.at(int(mserCharVec.size() / 2.f)); 226 Rect midRect = midChar.getCharacterPos(); 227 Point midCenter(midRect.tl().x + midRect.width / 2, midRect.tl().y + midRect.height / 2); 228 229 int mindist = 7 * maxrect.width; 230 std::vector<Vec2i> distVecVec; 231 distVecVec.reserve(32); 232 233 Vec2i mindistVec; 234 Vec2i avgdistVec; 235 236 // computer the dist which is the distacne between 237 // two near characters in the plate, use dist we can 238 // judege how to computer the max search range, and choose the 239 // best location of the sliding window in the next steps. 240 for (size_t mser_i = 0; mser_i + 1 < mserCharVec.size(); mser_i++) { 241 Rect charRect = mserCharVec.at(mser_i).getCharacterPos(); 242 Point center(charRect.tl().x + charRect.width / 2, charRect.tl().y + charRect.height / 2); 243 244 Rect charRectCompare = mserCharVec.at(mser_i + 1).getCharacterPos(); 245 Point centerCompare(charRectCompare.tl().x + charRectCompare.width / 2, 246 charRectCompare.tl().y + charRectCompare.height / 2); 247 248 int dist = charRectCompare.x - charRect.x; 249 Vec2i distVec(charRectCompare.x - charRect.x, charRectCompare.y - charRect.y); 250 distVecVec.push_back(distVec); 251 252 //if (dist < mindist) { 253 // mindist = dist; 254 // mindistVec = distVec; 255 //} 256 } 257 258 std::sort(distVecVec.begin(), distVecVec.end(), 259 [](const Vec2i& r1, const Vec2i& r2) { 260 return r1[0] < r2[0]; 261 }); 262 263 avgdistVec = distVecVec.at(int((distVecVec.size() - 1) / 2.f)); 264 265 //float step = 10.f * (float)maxrect.width; 266 //float step = (float)mindistVec[0]; 267 float step = (float)avgdistVec[0]; 268 269 //cv::line(result, Point2f(line[2] - step, line[3] - k*step), Point2f(line[2] + step, k*step + line[3]), Scalar(255, 255, 255)); 270 cv::line(result, Point2f(midCenter.x - step, midCenter.y - k*step), Point2f(midCenter.x + step, k*step + midCenter.y), Scalar(255, 255, 255)); 271 //cv::circle(result, leftPoint, 3, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2); 272 273 CPlate plate; 274 plate.setPlateLeftPoint(leftPoint); 275 plate.setPlateRightPoint(rightPoint); 276 277 plate.setPlateLine(line); 278 plate.setPlatDistVec(avgdistVec); 279 plate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level_avg); 280 281 plate.setPlateMergeCharRect(plateResult); 282 plate.setPlateMaxCharRect(maxrect); 283 plate.setMserCharacter(mserCharVec); 284 plateVec.push_back(plate); 285 } 286 } 287 288 // use strong seed to construct the first shape of the plate, 289 // then we need to find characters which are the weak seed. 290 // because we use strong seed to build the middle lines of the plate, 291 // we can simply use this to consider weak seeds only lie in the 292 // near place of the middle line 293 for (auto plate : plateVec) { 294 Vec4f line = plate.getPlateLine(); 295 Point leftPoint = plate.getPlateLeftPoint(); 296 Point rightPoint = plate.getPlateRightPoint(); 297 298 Rect plateResult = plate.getPlateMergeCharRect(); 299 Rect maxrect = plate.getPlateMaxCharRect(); 300 Vec2i dist = plate.getPlateDistVec(); 301 double ostu_level = plate.getOstuLevel(); 302 303 std::vector<CCharacter> mserCharacter = plate.getCopyOfMserCharacters(); 304 mserCharacter.reserve(16); 305 306 float k = line[1] / line[0]; 307 float x_1 = line[2]; 308 float y_1 = line[3]; 309 310 std::vector<CCharacter> searchWeakSeedVec; 311 searchWeakSeedVec.reserve(16); 312 313 std::vector<CCharacter> searchRightWeakSeed; 314 searchRightWeakSeed.reserve(8); 315 std::vector<CCharacter> searchLeftWeakSeed; 316 searchLeftWeakSeed.reserve(8); 317 318 std::vector<CCharacter> slideRightWindow; 319 slideRightWindow.reserve(8); 320 std::vector<CCharacter> slideLeftWindow; 321 slideLeftWindow.reserve(8); 322 323 // draw weak seed and little seed from line; 324 // search for mser rect 325 if (1 && showDebug) { 326 std::cout << "search for mser rect:" << std::endl; 327 } 328 329 if (0 && showDebug) { 330 std::stringstream ss(std::stringstream::in | std::stringstream::out); 331 ss << "resources/image/tmp/" << img_index << "_1_" << "searcgMserRect.jpg"; 332 imwrite(ss.str(), result); 333 } 334 if (1 && showDebug) { 335 std::cout << "mserCharacter:" << mserCharacter.size() << std::endl; 336 } 337 338 // if the count of strong seed is larger than max count, we dont need 339 // all the next steps, if not, we first need to search the weak seed in 340 // the same line as the strong seed. The judge condition contains the distance 341 // between strong seed and weak seed , and the rect simily of each other to improve 342 // the roubustnedd of the seed growing algorithm. 343 if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) { 344 double thresh1 = 0.15; 345 double thresh2 = 2.0; 346 searchWeakSeed(searchCandidate, searchRightWeakSeed, thresh1, thresh2, line, rightPoint, 347 maxrect, plateResult, result, CharSearchDirection::RIGHT); 348 if (1 && showDebug) { 349 std::cout << "searchRightWeakSeed:" << searchRightWeakSeed.size() << std::endl; 350 } 351 for (auto seed : searchRightWeakSeed) { 352 cv::rectangle(result, seed.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1); 353 mserCharacter.push_back(seed); 354 } 355 356 searchWeakSeed(searchCandidate, searchLeftWeakSeed, thresh1, thresh2, line, leftPoint, 357 maxrect, plateResult, result, CharSearchDirection::LEFT); 358 if (1 && showDebug) { 359 std::cout << "searchLeftWeakSeed:" << searchLeftWeakSeed.size() << std::endl; 360 } 361 for (auto seed : searchLeftWeakSeed) { 362 cv::rectangle(result, seed.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1); 363 mserCharacter.push_back(seed); 364 } 365 } 366 367 // sometimes the weak seed is in the middle of the strong seed. 368 // and sometimes two strong seed are actually the two parts of one character. 369 // because we only consider the weak seed in the left and right direction of strong seed. 370 // now we examine all the strong seed and weak seed. not only to find the seed in the middle, 371 // but also to combine two seed which are parts of one character to one seed. 372 // only by this process, we could use the seed count as the condition to judge if or not to use slide window. 373 float min_thresh = 0.3f; 374 float max_thresh = 2.5f; 375 reFoundAndCombineRect(mserCharacter, min_thresh, max_thresh, dist, maxrect, result); 376 377 // if the characters count is less than max count 378 // this means the mser rect in the lines are not enough. 379 // sometimes there are still some characters could not be captured by mser algorithm, 380 // such as blur, low light ,and some chinese characters like zh-cuan. 381 // to handle this ,we use a simple slide window method to find them. 382 if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) { 383 if (1 && showDebug) { 384 std::cout << "search chinese:" << std::endl; 385 std::cout << "judege the left is chinese:" << std::endl; 386 } 387 388 // if the left most character is chinese, this means 389 // that must be the first character in chinese plate, 390 // and we need not to do a slide window to left. So, 391 // the first thing is to judge the left charcater is 392 // or not the chinese. 393 bool leftIsChinese = false; 394 if (1) { 395 std::sort(mserCharacter.begin(), mserCharacter.end(), 396 [](const CCharacter& r1, const CCharacter& r2) { 397 return r1.getCharacterPos().tl().x < r2.getCharacterPos().tl().x; 398 }); 399 400 CCharacter leftChar = mserCharacter[0]; 401 402 //Rect theRect = adaptive_charrect_from_rect(leftChar.getCharacterPos(), image.cols, image.rows); 403 Rect theRect = leftChar.getCharacterPos(); 404 //cv::rectangle(result, theRect, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 1); 405 406 Mat region = image(theRect); 407 Mat binary_region; 408 409 ostu_level = cv::threshold(region, binary_region, 0, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY | CV_THRESH_OTSU); 410 if (1 && showDebug) { 411 std::cout << "left : ostu_level:" << ostu_level << std::endl; 412 } 413 //plate.setOstuLevel(ostu_level); 414 415 Mat charInput = preprocessChar(binary_region, char_size); 416 if (0 /*&& showDebug*/) { 417 imshow("charInput", charInput); 418 waitKey(0); 419 destroyWindow("charInput"); 420 } 421 422 std::string label = ""; 423 float maxVal = -2.f; 424 leftIsChinese = CharsIdentify::instance()->isCharacter(charInput, label, maxVal, true); 425 //auto character = CharsIdentify::instance()->identifyChinese(charInput, maxVal, leftIsChinese); 426 //label = character.second; 427 if (0 /* && showDebug*/) { 428 std::cout << "isChinese:" << leftIsChinese << std::endl; 429 std::cout << "chinese:" << label; 430 std::cout << "__score:" << maxVal << std::endl; 431 } 432 } 433 434 // if the left most character is not a chinese, 435 // this means we meed to slide a window to find the missed mser rect. 436 // search for sliding window 437 float ratioWindow = 0.4f; 438 //float ratioWindow = CParams::instance()->getParam3f(); 439 float threshIsCharacter = 0.8f; 440 //float threshIsCharacter = CParams::instance()->getParam3f(); 441 if (!leftIsChinese) { 442 slideWindowSearch(image, slideLeftWindow, line, leftPoint, dist, ostu_level, ratioWindow, threshIsCharacter, 443 maxrect, plateResult, CharSearchDirection::LEFT, true, result); 444 if (1 && showDebug) { 445 std::cout << "slideLeftWindow:" << slideLeftWindow.size() << std::endl; 446 } 447 for (auto window : slideLeftWindow) { 448 cv::rectangle(result, window.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1); 449 mserCharacter.push_back(window); 450 } 451 } 452 } 453 454 // if we still have less than max count characters, 455 // we need to slide a window to right to search for the missed mser rect. 456 if (mserCharacter.size() < char_max_count) { 457 // change ostu_level 458 float ratioWindow = 0.4f; 459 //float ratioWindow = CParams::instance()->getParam3f(); 460 float threshIsCharacter = 0.8f; 461 //float threshIsCharacter = CParams::instance()->getParam3f(); 462 slideWindowSearch(image, slideRightWindow, line, rightPoint, dist, plate.getOstuLevel(), ratioWindow, threshIsCharacter, 463 maxrect, plateResult, CharSearchDirection::RIGHT, false, result); 464 if (1 && showDebug) { 465 std::cout << "slideRightWindow:" << slideRightWindow.size() << std::endl; 466 } 467 for (auto window : slideRightWindow) { 468 cv::rectangle(result, window.getCharacterPos(), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1); 469 mserCharacter.push_back(window); 470 } 471 } 472 473 // computer the plate angle 474 float angle = atan(k) * 180 / (float)CV_PI; 475 if (1 && showDebug) { 476 std::cout << "k:" << k << std::endl; 477 std::cout << "angle:" << angle << std::endl; 478 } 479 480 // the plateResult rect need to be enlarge to contains all the plate, 481 // not only the character area. 482 float widthEnlargeRatio = 1.15f; 483 float heightEnlargeRatio = 1.25f; 484 RotatedRect platePos(Point2f((float)plateResult.x + plateResult.width / 2.f, (float)plateResult.y + plateResult.height / 2.f), 485 Size2f(plateResult.width * widthEnlargeRatio, maxrect.height * heightEnlargeRatio), angle); 486 487 // justify the size is likely to be a plate size. 488 if (verifyRotatedPlateSizes(platePos)) { 489 rotatedRectangle(result, platePos, Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1); 490 491 plate.setPlatePos(platePos); 492 plate.setPlateColor(the_color); 493 plate.setPlateLocateType(CMSER); 494 495 if (the_color == BLUE) out_plateVec_blue.push_back(plate); 496 if (the_color == YELLOW) out_plateVec_yellow.push_back(plate); 497 } 498 499 // use deskew to rotate the image, so we need the binary image. 500 if (1) { 501 for (auto mserChar : mserCharacter) { 502 Rect rect = mserChar.getCharacterPos(); 503 match.at(color_index)(rect) = 255; 504 } 505 cv::line(match.at(color_index), rightPoint, leftPoint, Scalar(255)); 506 } 507 } 508 509 if (0 /*&& showDebug*/) { 510 imshow("result", result); 511 waitKey(0); 512 destroyWindow("result"); 513 } 514 515 if (0) { 516 imshow("match", match.at(color_index)); 517 waitKey(0); 518 destroyWindow("match"); 519 } 520 521 if (0) { 522 std::stringstream ss(std::stringstream::in | std::stringstream::out); 523 ss << "resources/image/tmp/plateDetect/plate_" << img_index << "_" << the_color << ".jpg"; 524 imwrite(ss.str(), result); 525 } 526 } 527 528 529 }
首先通过MSER提取区域,提取出的区域进行一个尺寸判断,滤除明显不符合车牌文字尺寸的。接下来使用一个文字分类器,将分类结果概率大于0.9的设为强种子(下图的绿色方框)。靠近的强种子进行聚合,划出一条线穿过它们的中心(图中白色的线)。一般来说,这条线就是车牌的中间轴线,斜率什么都相同。之后,就在这条线的附近寻找那些概率低于0.9的弱种子(蓝色方框)。由于车牌的特征,这些蓝色方框应该跟绿色方框距离不太远,同时尺寸也不会相差太大。蓝色方框实在绿色方框的左右查找的,有时候,几个绿色方框中间可能存在着一个方库,这可以通过每个方框之间的距离差推出来,这就是橙色的方框。全部找完以后。绿色方框加上蓝色与橙色方框的总数代表着目前在车牌区域中发现的文字数。有时这个数会低于7(中文车牌的文字数),这是因为有些区域即便通过MSER也提取不到(例如非常不稳定或光照变化大的),另外很多中文也无法通过MSER提取到(中文大多是不连通的,MSER提取的区域基本都是连通的)。所以下面需要再增加一个滑动窗口(红色方框)来寻找这些缺失的文字或者中文,如果分类器概率大于某个阈值,就可以将其加入到最终的结果中。最后,把所有文字的位置用一个方框框起来,就是车牌的区域。
想要通过中间图片进行调试程序的话,首先依次根据函数调用关系plateMserLocate->mserSearch->mserCharMatch在core_func.cpp找到位置。在函数的最后,把图片输出的判断符改为1。然后在resources/image下面依次新建tmp与plateDetect目录(跟代码中的一致),接下来再运行时在新目录里就可以看到这些调试图片。(EasyPR里还有很多其他类似的输出代码,只要按照代码的写法创建文件夹就可以看到输出结果了)。
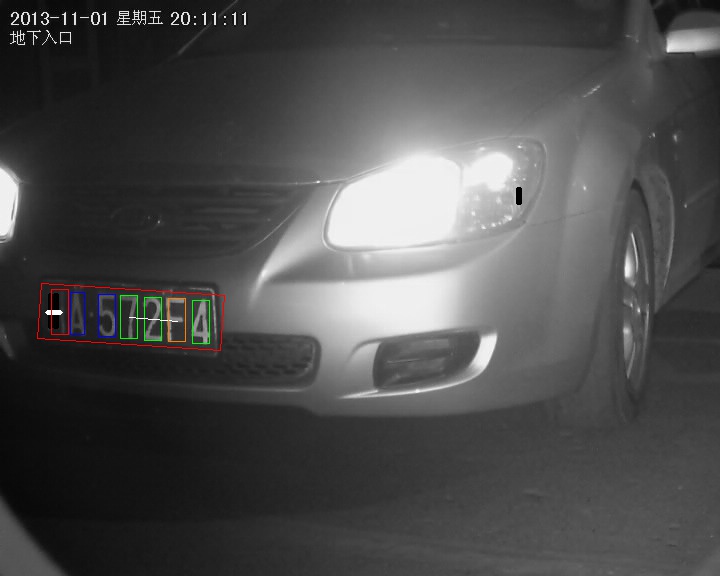

图5 文字定位的中间结果(调试图像)
二. 更加合理准确的评价指标
原先的EasyPR的评价标准中有很多不合理的地方。例如一张图片中找到了一个疑似的区域,就认为是定位成功了。或者如果一张图片中定位到了几个车牌,就用差距率最小的那个作为定位结果。这些地方不合理的地方在于,有可能找到的疑似区域根本不是车牌区域。另外一个包含几个车牌的图片仅仅用最大的一个作为结果,明显不合理。
因此新评价指标需要考虑定位区域和车牌区域的位置差异,只有当两者接近时才能认为是定位成功。另外,一张图片如果有几个车牌,对应的就有几个定位区域,每个区域与车牌做比对,综合起来才能作为定位效果。因此需要加入一个GroundTruth,标记各个车牌的位置信息。新版本中,我们标记了251张图片,其中共250个车牌的位置信息。为了衡量定位区域与车牌区域的位置差的比例,又引入了ICDAR2003的评价协议,来最终计算出定位的recall,precise与fscore值。
车牌定位评价中做了大改动。字符识别模块则做了小改动。首先是去除了“平均字符差距”这个意义较小的指标。转而用零字符差距,一字符差距,中文字符正确替代,这三者都是比率。零字符差距(0-error)指的是识别结果与车牌没有任何差异,跟原先的评价协议中的“完全正确率”指代一样。一字符差距(1-error)指的是错别仅仅只有1个字符或以下的,包括零字符差距。注意,中文一般是两个字符。中文字符正确(Chinese-precise)指代中文字符识别正确的比率。这三个指标,都是越大越好,100%最高。
为了实际看出这些指标的效果,拿通用测试集里增加的50张复杂图片做对此测试,文字定位方法在这些数据上的表现的差异与原先的SOBEL,COLOR定位方法的区别可以看下面的结果。
SOBEL+COLOR:
总图片数:50, Plates count:52, 定位率:51.9231%
Recall:46.1696%, Precise:26.3273%, Fscore:33.533%.
0-error:12.5%, 1-error:12.5%, Chinese-precise:37.5%
CMSER:
总图片数:50, Plates count:52, 定位率:78.8462%
Recall:70.6192%, Precise:70.1825%, Fscore:70.4002%.
0-error:59.4595%, 1-error:70.2703%, Chinese-precise:70.2703%
可以看出定位率提升了接近27个百分点,定位Fscore与中文识别正确率则提升了接近1倍。
三. 非极大值抑制
新版本中另一个较大的改动就是大量的使用了非极大值抑制(Non-maximum suppression)。使用非极大值抑制有几个好处:1.当有几个定位区域重叠时,可以根据它们的置信度(也是SVM车牌判断模型得出的值)来取出其中最大概率准确的一个,移除其他几个。这样,不同定位方法,例如Sobel与Color定位的同一个区域,只有一个可以保留。因此,EasyPR新版本中,最终定位出的一个车牌区域,不再会有几个框了。2.结合滑动窗口,可以用其来准确定位文字的位置,例如在车牌定位模块中找到概率最大的文字位置,或者在文字识别模块中,更准确的找到中文文字的位置。
非极大值抑制的使用使得EasyPR的定位方法与后面的识别模块解耦了。以前,每增加定位方法,可能会对最终输出产生影响。现在,无论多少定位方法定位出的车牌都会通过非极大值抑制取出最大概率的一个,对后面的方法没有一点影响。
另外,如今setMaxPlates()这个函数可以确实的作用了。以前可以设置,但没效果。现在,设置这个值为n以后,当在一副图像中检测到大于n个车牌区域(注意,这个是经过非极大值抑制后的)时,EasyPR只会输出n个可能性最高的车牌区域。
四. 字符分割与识别部分的强化
新版本中字符分割与识别部分都添加了新算法。例如使用了spatial-ostu替代普通的ostu算法,增加了图像分割在面对光照不均匀的图像上的二值化效果。


图6 车牌图像(左),普通大津阈值结果(中),空间大津阈值结果(右)
同时,识别部分针对中文增加了一种adaptive threshold方法。这种方法在二值化“川”字时有比ostu更好的效果。通过将两者一并使用,并选择其中字符识别概率最大的一个,显著提升了中文字符的识别准确率。在识别中文时,增加了一个小型的滑动窗口,以此来弥补通过省份字符直接查找中文字符时的定位不精等现象。
五. 新的特征与SVM模型,新的中文识别ANN模型
为了强化车牌判断的鲁棒性,新版本中更改了SVM模型的特征,使用LBP特征的模型在面对低对比度与光照的车牌图像中也有很好的判断效果。为了强化中文识别的准确率,现在单独为31类中文文字训练了一个ANN模型ann_chinese,使用这个模型在分类中文是的效果,相对原先的通用模型可以提升近10个百分点。
六. 其他
几天前EasyPR发布了1.5-alpha版本。今天发布的beta版本相对于alpha版本,增加了Grid Search功能, 对文字定位方法的参数又进行了部分调优,同时去除了一些中文注释以提高window下的兼容性,除此之外,在速度方面,此版本首次使用了多线程编程技术(OpenMP)来提高算法整体的效率等,使得最终的速度有了2倍左右的提升。
下面说一点新版本的不足:目前来看,文字定位方法的鲁棒性确实很高,不过遗憾的速度跟颜色定位方法相比,还是慢了接近一倍(与Sobel定位效率相当)。后面的改善中,考虑对其进行优化。另外,字符分割的效果实际上还是可以有更多的优化算法选择的,未来的版本可以考虑对其做一个较大的尝试与改进。
对EasyPR做下说明:EasyPR,一个开源的中文车牌识别系统,代码托管在github和gitosc。其次,在前面的博客文章中,包含EasyPR至今的开发文档与介绍。
版权说明:
本文中的所有文字,图片,代码的版权都是属于作者和博客园共同所有。欢迎转载,但是务必注明作者与出处。任何未经允许的剽窃以及爬虫抓取都属于侵权,作者和博客园保留所有权利。
参考文献:
1.Character-MSER : Scene Text Detection with Robust Character Candidate Extraction Method, ICDAR2015
2.Seed-growing : A robust hierarchical detection method for scene text based on convolutional neural networks, ICME2015
