1、SQL的分类

2、mysql常用方法

3、逻辑运算
提出一个问题Select * from users where id=1 and 1=1; 这条语句为什么能够选择出id=1的内容,and 1=1 到底起作用了没有?
这里就要清楚sql 语句执行顺序了。同时这个问题我们在使用万能密码的时候会用到。
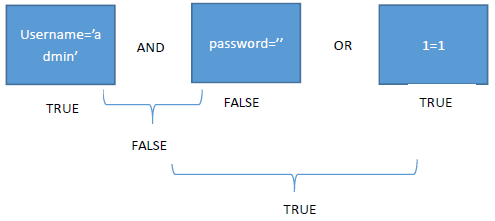
Select * from admin where username=’admin’ and password=’admin’
我们可以用’or 1=1# 作为密码输入。原因是为什么?这里涉及到一个逻辑运算,当使用上述所谓的万能密码后,构成的sql 语句为:
Select * from admin where username=’admin’ and password=’’or 1=1#’
Explain:上面的这个语句执行后,我们在不知道密码的情况下就登录到了admin 用户了。
原因是在where 子句后, 我们可以看到三个条件语句username=’admin’ and password=’’or 1=1三个条件用and 和or 进行连接。在sql 中,我们and 的运算优先级大于or 的元算优先级。因此可以看到第一个条件(用a 表示)是真的,第二个条件(用b 表示)是假的,a and b = false,第一个条件和第二个条件执行and 后是假,再与第三个条件or 运算,因为第三个条件1=1 是恒成立的,所以结果自然就为真了。因此上述的语句就是恒真了。
4、sql注入流程
启动数据库,检索数据库实例;
Show databases;
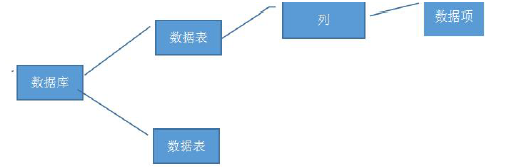
5、使用information_schema
Mysql 有一个系统数据库information_schema,存储着所有的数据库的相关信息,一般的,我们利用该表可以进行一次完整的注入。以下为一般的流程。
猜数据库
select schema_name from information_schema.schemata;
猜某库的数据表
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema="xxxxx";
猜某表的所有列
Select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name="xxxxx";
获取某列的内容
Select *** from ****
实例:
select schema_name from information_schema.schemata select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema="security" Select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name="users" use security; select password from users where username = 'admin';
存放数据库实例的表:information_schema.schemata其中数据库实例的字段名: schema_name
存放数据表的表:information_schema.tables其中数据库实例的字段名:table_schema,表名字段:table_name
存放数据列的表:information_schema.columns表名字段:table_name
6、union
union可以联合2个sql查询语句,要求这2条sql查询语句返回的结果列数相同。
select * from users where id= '1' union select 1,2,3

select * from users where id= '1' --查询结果是,

select 1,2,3 --查询结果是,
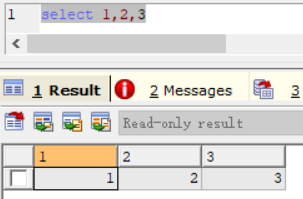

当其中一个查询语句的结果为空时(不是报错),则只显示另外一条sql查询

7、order by
order by 2
对查询的结果,按照第2列升序排序,
order by 2 desc
对查询的结果,按照第2列降序排序。
作用可以判断,原SQL查询语句有多少列,一旦order by后面的数据大于查询的列,就会报错,由此可以判断原SQL查询的是多少列数据。
+用于代替空格