1. 走进面前切面编程
编程范式;
面向过程编程,c语言;
面向对象编程;c++,java,c#;
函数式编程;
事件驱动编程;
面向切面编程;
AOP是一种编程范式,不是编程语言;解决特定问题,不能解决所有问题;OOP的补充,不是竞争‘
AOP的初衷:解决代码重复性问题,解决关注点分离;
水平分离;展示层》服务层》持久层;
垂直分离:功能划分 订单库存等;
切面分离:分离功能性需求与非功能性需求;
使用AOP的好处:
集中管理;方便添加删除;增强代码的可读性与可维护性;
AOP的应用场景:
权限控制,缓存控制,事务控制,审计日志,性能监控;分布式追踪;异常处理等;;
支持AOP的编程语言:java,.net,c/c++,ruby python php;
案例:
1.产品管理的服务;
2.产品添加删除的操作只能管理员才能进行;
3.普通实现VSAOP实现;
spring boot 实现;
maven pom 引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
加入product类:
package com.example.aoptest.domain;
public class Product {
private Long id;
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
service层代码:
package com.example.aoptest.service;
import com.example.aoptest.domain.Product;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ProductService {
public void insert(Product product){
System.out.println("insert product");
}
public void delete(Long id){
System.out.println("delete product");
}
}
测试类
package com.example.aoptest.domain;
//模拟用户切换
public class CurrentUserHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> holder = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static String get(){return holder.get() == null?"unknown":holder.get();}
public static void set(String user){holder.set(user);}
}
Service判断
package com.example.aoptest.service; import com.example.aoptest.domain.CurrentUserHolder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component public class AuthService { public void checkAccess(){ String user = CurrentUserHolder.get(); if(!"admin".equals(user)){ throw new RuntimeException("operation not allow"); } } }
普通传统的校验权限的方式:
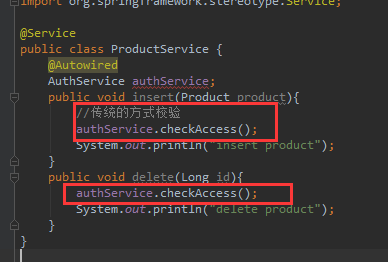
进入测试:

执行验证通过;
总结:
传统硬编码的方式的缺点呢:逻辑复杂度较高;
使用AOP
package com.example.aoptest.security;
import com.example.aoptest.service.AuthService;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component //给spring托管
public class SecurityAspect {
@Autowired
AuthService authService;
//切面,以下表达式有很多种,这里我们用注解的方式
//拦截标注有AdminOnly注解,进行操作;
@Pointcut("@annotation(AdminOnly)")
public void adminOnly(){
}
//执行之前插入一段代码。
@Before("adminOnly()")
public void check(){
authService.checkAccess();
}
}
package com.example.aoptest.security;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //只标注在方法级别
public @interface AdminOnly {
}
修改ProductService
//authService.checkAccess();
test测试 正常情况下失败的;因为没有捕获异常
给ProductService加上注解
package com.example.aoptest.service;
import com.example.aoptest.domain.Product;
import com.example.aoptest.security.AdminOnly;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
AuthService authService;
@AdminOnly
public void insert(Product product){
//传统的方式校验
//authService.checkAccess();
System.out.println("insert product");
}
@AdminOnly
public void delete(Long id){
//authService.checkAccess();
System.out.println("delete product");
}
}
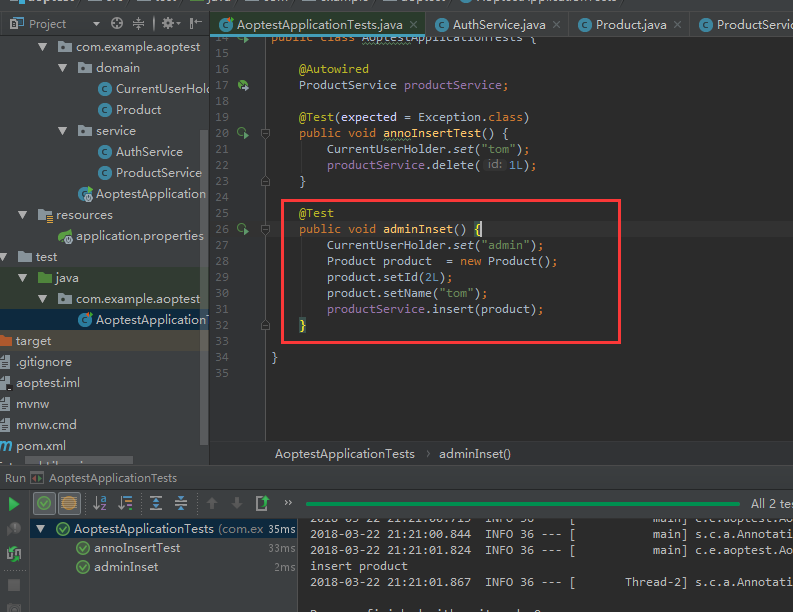
执行测试类,正常通过的。
对比以上两种方式,aop侵入性这种方式更少;
为啥要引入aop的编程范式?
aop的好处及适用场景分别是什么?
aop的两大核心是什么?