文章目录:
1、C#(.net framework框架)中的事件以及特点
2、事件的组成部分
3、编辑器如何实现事件的
4、显式实现事件
1、C#(.net framework框架)中的事件以及特点
CLR事件模型以委托为基础。使用委托来调用回调方法。声明方式使用event关键字。 事件可以理解为在CLR中使用event关键字修饰的一个委托实例。
事件的特点如下所示:
1)、方法能登记对事件关注
2)、方法能注销对事件的关注
3)、事件发生时,登记了的方法将收到通知
2、事件的组成部分
1)、定义类型容纳所有需要发送给事件通知接收者的附加信息(事件要传递的参数,我是这么理解的)

1 /// <summary> 2 /// 发送给事件接收者的附加信息 3 /// </summary> 4 public class DailyEventArgs : EventArgs 5 { 6 private readonly string _title; 7 private readonly string _body; 8 public DailyEventArgs(string title,string body) 9 { 10 this._title = title; 11 this._body = body; 12 } 13 public string Title { get {return _title; } } 14 public string Body { get { return _body; } } 15 }
这里解释下EventArgs,它由FCL中定义,根据CLR事件约定,所有事件参数均要继承自这个类,且事件的参数类名要以EventArgs结尾。它的定义如下:

2)、定义事件成员
事件成员使用event关键字修饰。我们需要定义事件的可访问级别(默认都是public);委托类型(要调用的方法的原型)。

1 class DailiesEventDemo 2 { 3 //也可以这么定义 4 //public delegate void CustomDelegate(object sender, DailyEventArgs e); 5 //public event CustomDelegate CustomDaily; 6 7 public event EventHandler<DailyEventArgs> NewDaily; 8 9 }
NewDaily是事件的名称,这里使用系统提供的委托EventHandler,EventHandler的定义如下所示,所以我们可以接受的方法原型为void MethodName(Object sender,DailyEventArgs e);

3)、定义负责引发事件的方法来通知事件的的登记对象
按照CLR的约定,我们需要定义一个受保护的虚方法。引发事件时,调用该方法。方法的参数为我们定义的DailyEventArgs对象,方法的默认实现是检查是否有对象登记了对事件的关注,假如有对象登记对事件的关注,引发事件通知登记对象。

1 protected virtual void OnDendDaily(DailyEventArgs e) 2 { 3 //为了线程安全,将委托字段存入一个临时变量中 4 EventHandler<DailyEventArgs> temp = Volatile.Read(ref NewDaily); 5 if (temp != null) 6 temp.Invoke(this, e); 7 }
4)、定义方法将输入转化为期望事件

1 /// <summary> 2 /// 定义方法将输入转化为期望事件 3 /// </summary> 4 /// <param name="title"></param> 5 /// <param name="body"></param> 6 public void SimulateNewDaily(string title,string body) 7 { 8 DailyEventArgs dailyEventArgs = new DailyEventArgs(title, body); 9 OnDendDaily(dailyEventArgs); 10 }
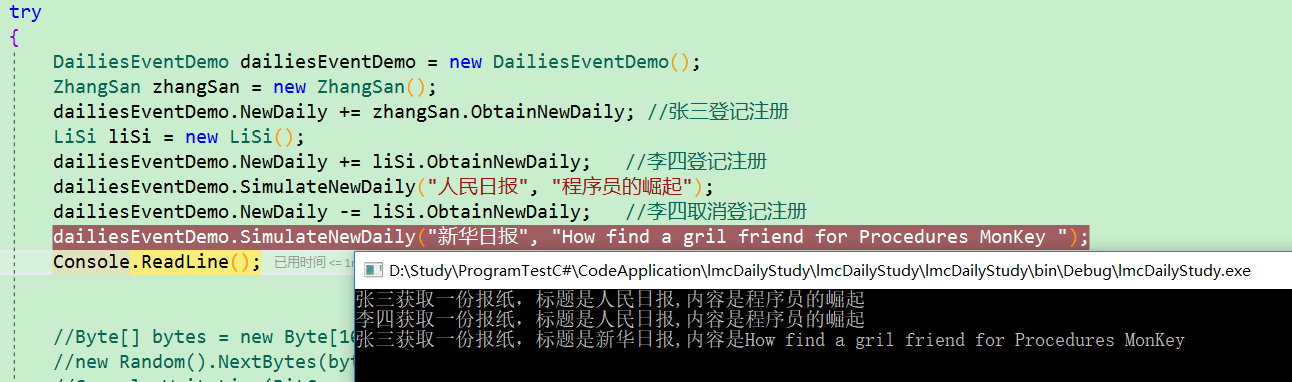
然后让我们定义两个关注类,来登记下事件(C# 用+= 来登记对事件的关注,-=注销对事件的关注),具体代码如下:

1 public class ZhangSan 2 { 3 public void ObtainNewDaily(object sender, DailyEventArgs e) 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine($"张三获取一份报纸,标题是{e.Title},内容是{e.Body}"); 6 } 7 } 8 public class LiSi 9 { 10 public void ObtainNewDaily(object sender, DailyEventArgs e) 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine($"李四获取一份报纸,标题是{e.Title},内容是{e.Body}"); 13 } 14 } 15 static void Main(string[] args) 16 { 17 try 18 { 19 DailiesEventDemo dailiesEventDemo = new DailiesEventDemo(); 20 ZhangSan zhangSan = new ZhangSan(); 21 dailiesEventDemo.NewDaily += zhangSan.ObtainNewDaily; //张三登记注册 22 LiSi liSi = new LiSi(); 23 dailiesEventDemo.NewDaily += liSi.ObtainNewDaily; //李四登记注册 24 dailiesEventDemo.SimulateNewDaily("人民日报", "程序员的崛起"); 25 dailiesEventDemo.NewDaily -= liSi.ObtainNewDaily; //李四取消登记注册 26 dailiesEventDemo.SimulateNewDaily("新华日报", "How find a gril friend for Procedures MonKey ");
3、编辑器实现事件的方式
我们用ILSpy来反编译下我们生成的程序集。
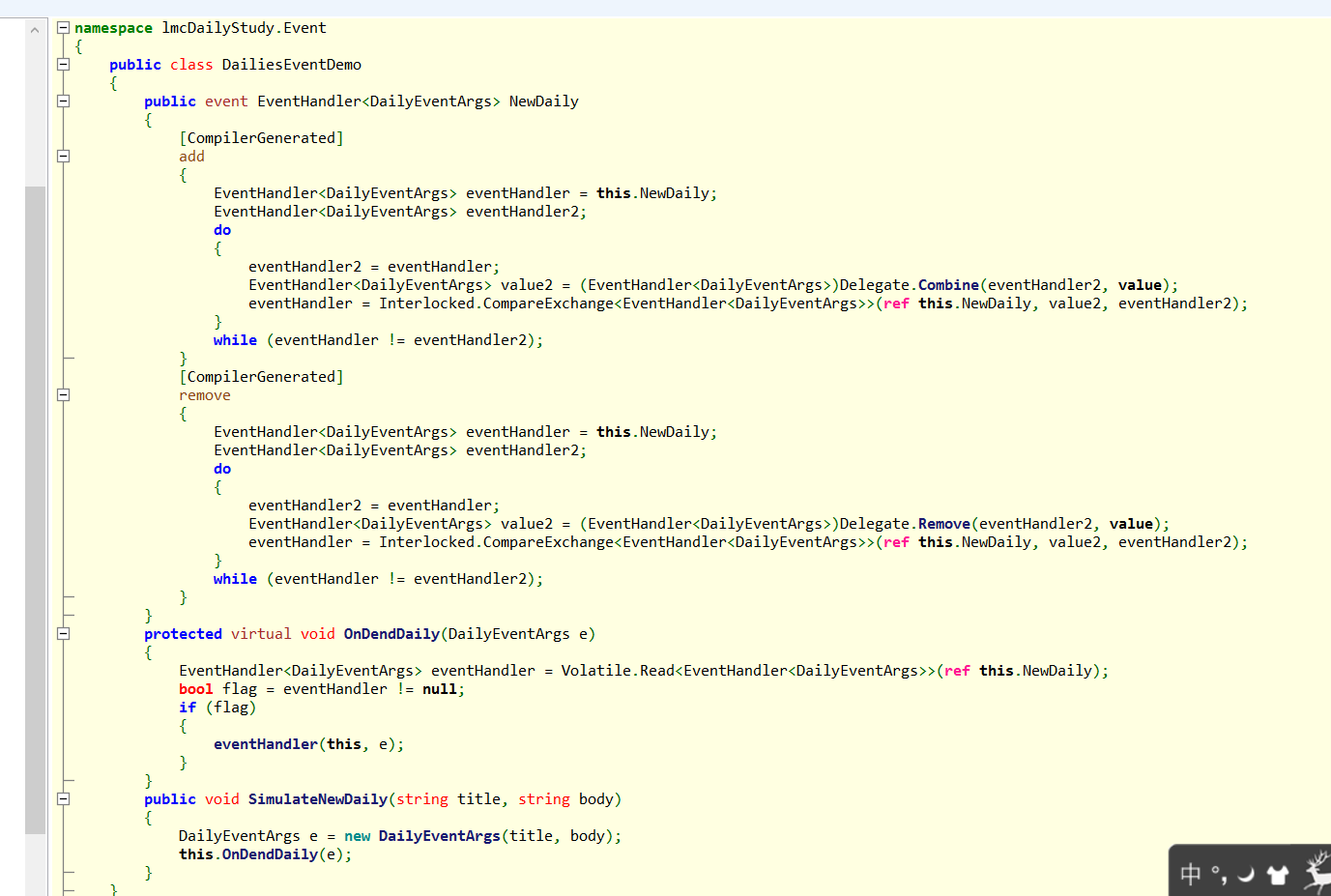
可以看到,public event EventHandler<DailyEventArgs> NewDaily; 被编译器翻译成了一个具有add 和remove方法的对象,add 和remove方法中的 EventHandler<DailyEventArgs> eventHandler = this.NewDaily;拿到当前事件(被event修饰的委托)对象,然后调用 Delegate.Combine() 和 Delegate.Remove()方法添加或者移除委托连中的委托。
4、显式实现事件
上面可以看到,每一个事件都会生成一个委托的实例字段(例如上面的NewDaily),在winform程序中,窗体控件(system.windows.forms.controller)具有70多个事件,为此我们需要准备70多个委托字段,然而我们经常用到的事件也就几个而已,这样就导致了大量的委托实例字段被创建,从而浪费大量内存。 好在我们可以显示实现事件:

1 public sealed class EventKey { } 2 public sealed class EventSet { 3 //私有字典维护EventKey => delegate 的映射 4 private readonly Dictionary<EventKey, Delegate> m_events = new Dictionary<EventKey, Delegate>(); 5 6 //添加EventKey => delegate映射 或者将委托和现有的EventKey合并 7 public void Add(EventKey eventKey,Delegate handler) 8 { 9 Monitor.Enter(m_events); 10 Delegate d; 11 m_events.TryGetValue(eventKey, out d); 12 m_events[eventKey] = Delegate.Combine(d, handler); 13 Monitor.Exit(m_events); 14 } 15 16 //从EvetnKey 删除委托,并且在删除最后一个委托时候删除映射关系 17 public void Remove(EventKey eventKey, Delegate handler) 18 { 19 Monitor.Enter(m_events); 20 Delegate d; 21 if(m_events.TryGetValue(eventKey, out d)) 22 { 23 d = Delegate.Remove(d, handler); 24 if (d != null) 25 m_events[eventKey] = d; 26 else 27 m_events.Remove(eventKey); 28 } 29 Monitor.Exit(m_events); 30 } 31 public void Raise(EventKey eventKey,Object sender,EventArgs e) 32 { 33 Delegate d; 34 Monitor.Enter(m_events); 35 m_events.TryGetValue(eventKey, out d); 36 Monitor.Exit(m_events); 37 if(d!=null) 38 { 39 d.DynamicInvoke(new Object[] { sender, e }); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 public class FooEventArgs : EventArgs { } 44 public class TryWithLostOfEvents 45 { 46 //定义私有实例字段来引用集合 47 //集合用于管理一组 事件/委托 对 48 //EventSet类型不是不是FCL的一部分,他是我自己的类型 49 private readonly EventSet m_eventSet = new EventSet(); 50 //受保护属性识破爱生类能访问集合 51 protected EventSet EventSet { get { return m_eventSet; } } 52 // 支持Foo事件的代码,定义Foo事件的必要成员,构造静态制度对象标识事件;每个对象都有自己的哈希码,一边在对象的集合中查找这个事件的委托链表 53 protected static readonly EventKey s_fooEventKey = new EventKey(); 54 //定义访问器方法,用于集合中CRUD 55 public event EventHandler<FooEventArgs> Foo 56 { 57 add { m_eventSet.Add(s_fooEventKey, value); } 58 remove { m_eventSet.Remove(s_fooEventKey, value); } 59 } 60 //调用事件的虚方法 61 protected virtual void OnFoo(FooEventArgs e) 62 { 63 m_eventSet.Raise(s_fooEventKey,this, e); 64 } 65 //定义将输入转换成这个事件的方法 66 public void SimulateFoo() { OnFoo(new FooEventArgs()); } 67 }
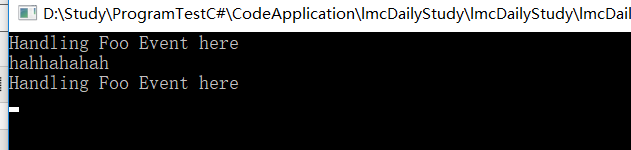
来运行一下

1 TryWithLostOfEvents tryWithLostOfEvents = new TryWithLostOfEvents(); 2 tryWithLostOfEvents.Foo += TryWithLostOfEvents_Foo; //TryWithLostOfEvents_Foo登记对事件的订阅 3 tryWithLostOfEvents.Foo += fun1; // fun1登记对事件的订阅 4 tryWithLostOfEvents.SimulateFoo(); 5 tryWithLostOfEvents.Foo -= fun1; // fun1注销对事件的订阅 6 tryWithLostOfEvents.SimulateFoo();