一.输入输出流
流:流就是指一连串流动的字符,以先进先出的方式发送信息的通道。
输出流:写数据。
输入流:读数据。
二.File类
1.构造方法:
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
File(File parent, String child) 根据 parent 抽象路径名和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例。 |
|
File(String pathname) 通过将给定路径名字符串转换为抽象路径名来创建一个新 File 实例。 |
|
File(String parent, String child) 根据 parent 路径名字符串和 child 路径名字符串创建一个新 File 实例。 |
|
File(URI uri) 通过将给定的 file: URI 转换为一个抽象路径名来创建一个新的 File 实例。 |
|
2.主要成员方法:
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
boolean |
canExecute() 测试应用程序是否可以执行此抽象路径名表示的文件。 |
boolean |
canRead() 测试应用程序是否可以读取此抽象路径名表示的文件。 |
boolean |
canWrite() 测试应用程序是否可以修改此抽象路径名表示的文件。 |
int |
compareTo(File pathname) 按字母顺序比较两个抽象路径名。 |
boolean |
createNewFile() 当且仅当不存在具有此抽象路径名指定名称的文件时,不可分地创建一个新的空文件。 |
boolean |
equals(Object obj) 测试此抽象路径名与给定对象是否相等。 |
boolean |
exists() 测试此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录是否存在。 |
String |
getName() 返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件或目录的名称。 |
String |
getParent() 返回此抽象路径名父目录的路径名字符串;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null。 |
File |
getParentFile() 返回此抽象路径名父目录的抽象路径名;如果此路径名没有指定父目录,则返回 null。 |
String |
getPath() 将此抽象路径名转换为一个路径名字符串。 |
long |
getTotalSpace() 返回此抽象路径名指定的分区大小。 |
long |
getUsableSpace() 返回此抽象路径名指定的分区上可用于此虚拟机的字节数。 |
int |
hashCode() 计算此抽象路径名的哈希码。 |
boolean |
isAbsolute() 测试此抽象路径名是否为绝对路径名。 |
boolean |
isDirectory() 测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否是一个目录。 |
boolean |
isFile() 测试此抽象路径名表示的文件是否是一个标准文件。 |
boolean |
isHidden() 测试此抽象路径名指定的文件是否是一个隐藏文件。 |
long |
lastModified() 返回此抽象路径名表示的文件最后一次被修改的时间。 |
long |
length() 返回由此抽象路径名表示的文件的长度。 |
String[] |
list() 返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件和目录。 |
String[] |
list(FilenameFilter filter) 返回一个字符串数组,这些字符串指定此抽象路径名表示的目录中满足指定过滤器的文件和目录。 |
File[] |
listFiles() 返回一个抽象路径名数组,这些路径名表示此抽象路径名表示的目录中的文件。 |
File[] |
listFiles(FileFilter filter) 返回抽象路径名数组,这些路径名表示此抽象路径名表示的目录中满足指定过滤器的文件和目录。 |
File[] |
listFiles(FilenameFilter filter) 返回抽象路径名数组,这些路径名表示此抽象路径名表示的目录中满足指定过滤器的文件和目录。 |
boolean |
mkdir() 创建此抽象路径名指定的目录。 |
boolean |
mkdirs() 创建此抽象路径名指定的目录,包括所有必需但不存在的父目录。 |
String |
toString() 返回此抽象路径名的路径名字符串。 |
例:

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 public class FileDemo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // 创建File对象 9 // 注Linux中目录为/,Windows中为\ 10 // File file=new File("G:\io\test.txt"); 11 // File file=new File("G:\io","test.txt"); 12 File file = new File("G:\io"); 13 File file1 = new File(file, "test.txt"); 14 System.out.println("是否是文件夹" + file.isDirectory()); 15 System.out.println("是否是文件:" + file.isFile()); 16 // 创建文件 17 File file2 = new File("G:\io", "new"); 18 if (!file2.exists()) { 19 file2.mkdir(); 20 // 创建多级目录 21 // file2.mkdirs(); 22 } 23 // 创建文件 24 if (!file1.exists()) { 25 try { 26 file1.createNewFile(); 27 } catch (IOException e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 } 33 }
三.字节字符流
1.字节输入流(InputStream):

1.1InputStream:
成员方法:
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
int |
available() 返回此输入流下一个方法调用可以不受阻塞地从此输入流读取(或跳过)的估计字节数。 |
void |
close() 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源。 |
void |
mark(int readlimit) 在此输入流中标记当前的位置。 |
boolean |
markSupported() 测试此输入流是否支持 mark 和 reset 方法。 |
abstract int |
read() 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节。 |
int |
read(byte[] b) 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节,并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。如果返回值为-1,则表示已经达到文件末尾。 |
int |
read(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组。 |
void |
reset() 将此流重新定位到最后一次对此输入流调用 mark 方法时的位置。 |
long |
skip(long n) 跳过和丢弃此输入流中数据的 n 个字节。 |
例:

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 public class FileInputDemo { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 try { 10 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("G:\io\test.txt"); 11 //int n=fis.read(); 12 int n=0; 13 // while (n!=-1){ 14 // System.out.print((char)n); 15 // n=fis.read(); 16 // } 17 //一个一个读 18 while((n=fis.read())!=-1){ 19 System.out.print((char)n); 20 } 21 //fis.close(); 22 //利用数组读取 23 byte[] b=new byte[100]; 24 fis.read(b,0,5); 25 System.out.println(new String(b)); 26 fis.close(); 27 28 29 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 35 } 36 }
2.字节输出流(OutputStream):
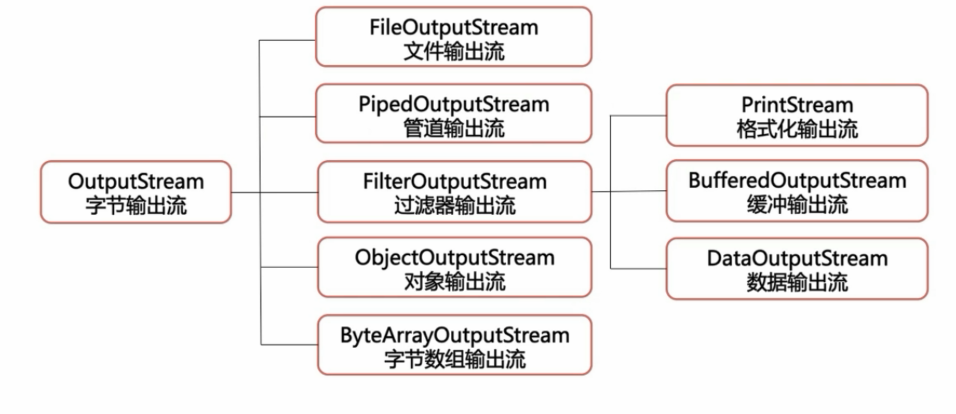
成员方法:
| 方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
void |
close() 关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源。 |
void |
flush() 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节。 |
void |
write(byte[] b) 将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流。 |
void |
write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流。 |
abstract void |
write(int b) 将指定的字节写入此输出流。 |

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 4 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 public class FileOutputDemo { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 try { 12 //true参数,表示在后面追加 13 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("G:\io\test.txt",true); 14 fos.write(10); 15 fos.write('h'); 16 fos.close(); 17 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 catch(IOException e){ 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 25 26 } 27 28 }

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 8 public class FileCopy { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // 文件拷贝 12 try { 13 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.png"); 14 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("testcopy.png"); 15 int n = 0; 16 byte[] b = new byte[1024]; 17 //可能复制的文件更大,因为最后一次可能没有1024 18 while ((n = fis.read(b)) != -1) { 19 //fos.write(b); 20 //n就是实际读的字节数 21 fos.write(b,0,n); 22 } 23 fis.close(); 24 fos.close(); 25 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 26 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 catch(IOException e){ 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 33 } 34 35 }
3.缓冲流:(提高性能)
BufferedInputStream:
BufferedInputStream 为另一个输入流添加一些功能,即缓冲输入以及支持 mark 和 reset 方法的能力。
BufferedOutputStream:
该类实现缓冲的输出流。通过设置这种输出流,应用程序就可以将各个字节写入底层输出流中,而不必针对每次字节写入调用底层系统。

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 4 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 7 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 10 public class BufferFileDemo { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 FileOutputStream fos; 15 try { 16 fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); 17 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos); 18 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("test.txt"); 19 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis); 20 bos.write('h'); 21 bos.write(22); 22 //flush(),close()任意一个方法,强制清空缓冲区(缓冲区未满),写入文件 23 bos.flush(); 24 System.out.println(bis.read()); 25 System.out.println((char)bis.read()); 26 fos.close(); 27 bos.close(); 28 fis.close(); 29 bis.close(); 30 31 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 32 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 } 35 catch (IOException e){ 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 }
4.字符流:
4.1字符输入流:
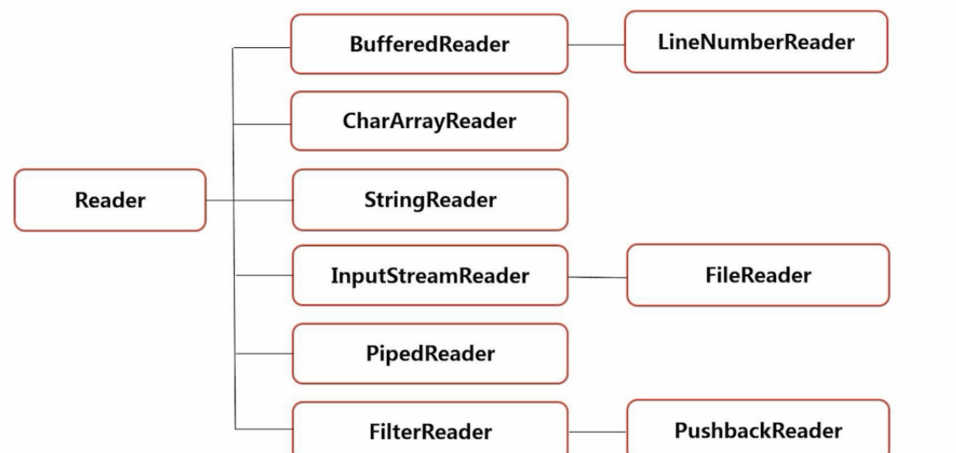
4.2字符输出流:
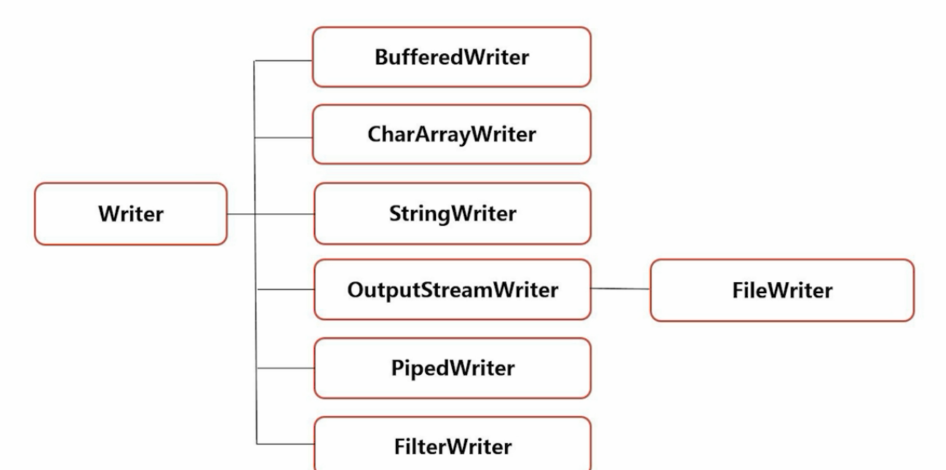
4.3字节流和字符流的区别:
用途不同 https://blog.csdn.net/lwang_it/article/details/78886186
4.4字节字符转换流:
注保持读写数据编码一致,防止乱码。

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 8 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 9 10 public class ReaderDemo { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 try { 14 //注读写数据时要保证编码一致,防止乱码 15 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("test.txt"); 16 InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis); 17 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("test2.txt"); 18 OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"utf-8"); 19 int n=0; 20 char[] cbuf=new char[10]; 21 // while((n=fis.read())!=-1){ 22 // System.out.println((char)n); 23 // } 24 while((n=isr.read(cbuf))!=-1){ 25 String str=new String(cbuf,0,n); 26 System.out.println(str); 27 osw.write(cbuf,0,n); 28 osw.flush(); 29 } 30 fis.close(); 31 fos.close(); 32 isr.close(); 33 osw.close(); 34 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 35 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 36 e.printStackTrace(); 37 } 38 catch(IOException e){ 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 }
4.5字符缓冲流:
(1)BufferedReader():从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。
(2)BufferedWriter():将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.BufferedReader; 4 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 5 import java.io.FileInputStream; 6 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 7 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 8 import java.io.IOException; 9 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 10 import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; 11 12 public class ReaderDemo { 13 14 public static void main(String[] args) { 15 try { 16 //注读写数据时要保证编码一致,防止乱码 17 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("test.txt"); 18 InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis); 19 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(isr); 20 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("test2.txt"); 21 OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(fos); 22 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(osw); 23 int n=0; 24 char[] cbuf=new char[10]; 25 // while((n=fis.read())!=-1){ 26 // System.out.println((char)n); 27 // } 28 while((n=br.read(cbuf))!=-1){ 29 String str=new String(cbuf,0,n); 30 System.out.println(str); 31 bw.write(cbuf,0,n); 32 bw.flush(); 33 } 34 fis.close(); 35 fos.close(); 36 isr.close(); 37 osw.close(); 38 br.close(); 39 bw.close(); 40 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 41 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } 44 catch(IOException e){ 45 e.printStackTrace(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 }
四.序列化
1.ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream:
ObjectOutputStream 和 ObjectInputStream 分别与 FileOutputStream 和 FileInputStream 一起使用时,可以为应用程序提供对对象图形的持久存储。ObjectInputStream 用于恢复那些以前序列化的对象。其他用途包括使用套接字流在主机之间传递对象,或者用于编组和解组远程通信系统中的实参和形参。

1 package com.swpu; 2 3 import java.io.FileInputStream; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.io.ObjectInputStream; 8 import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; 9 import java.io.Serializable; 10 //实现Serializable接口(序列化接口) 11 class Good implements Serializable{ 12 String num; 13 String name; 14 float price; 15 public Good(String num,String name,float price){ 16 this.num=num; 17 this.name=name; 18 this.price=price; 19 } 20 public String getNum() { 21 return num; 22 } 23 public void setNum(String num) { 24 this.num = num; 25 } 26 public String getName() { 27 return name; 28 } 29 public void setName(String name) { 30 this.name = name; 31 } 32 public float getPrice() { 33 return price; 34 } 35 public void setPrice(float price) { 36 this.price = price; 37 } 38 @Override 39 public String toString() { 40 return "Good: ["+"num:"+num+",name:"+name+",price:"+price+"]"; 41 } 42 43 } 44 public class FileStreamDemo { 45 46 public static void main(String[] args) { 47 Good good=new Good("k1212","手机",2000); 48 FileOutputStream fos; 49 try { 50 fos = new FileOutputStream("test.txt"); 51 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos); 52 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("test.txt"); 53 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis); 54 //注意读的顺序和写的顺序要一致 55 oos.writeObject(good); 56 oos.writeBoolean(true); 57 oos.flush(); 58 try { 59 Good goodaf=(Good)ois.readObject(); 60 System.out.println(goodaf); 61 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 62 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 fos.close(); 66 fis.close(); 67 oos.close(); 68 ois.close(); 69 70 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 71 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 72 e.printStackTrace(); 73 } 74 catch (IOException e){ 75 e.printStackTrace(); 76 } 77 } 78 79 }
