1. 简介
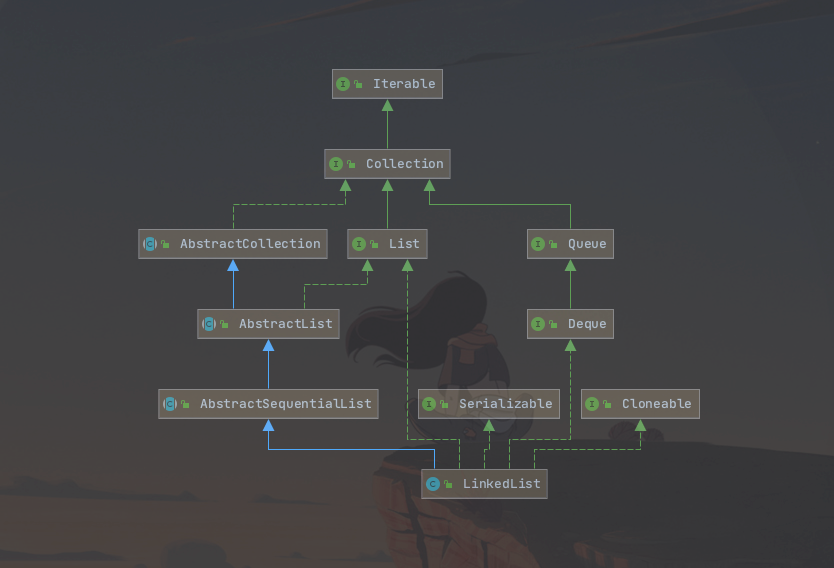
LinkedList 同时实现了List和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作是一个顺序容器,又可以看作是双向队列。
既然是双向列表,那么它的每个数据节点都一定有两个指针,分别指向它的前驱和后继。所以,从LinkedList 链表中的任意一个节点开始,都可以很方便的访问它的前驱和后继节点。
1.1 节点
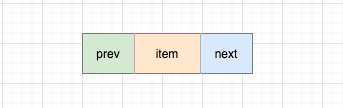
代码实现:
Node 为 LinkedList的静态内部类
// LinkedList.Node
private static class Node<E> {
// 当前节点元素
E item;
// 前驱指针
Node<E> next;
// 后继指针
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
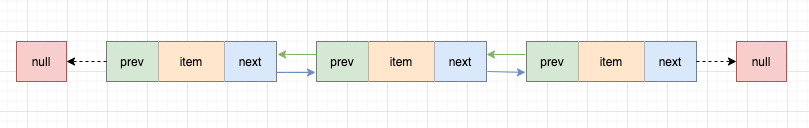
多个节点相连:
每个Node都有指针指向前驱和后继节点,“null”并非Node节点,只不过是firstNode prev 为null,并且 lastNode next 为null。
我们再来看下LinkedList 的几个核心的变量:
// 链表长度
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node. 指向第一个节点
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
* first == null && last == null) :刚初始化还未赋值的状态
* 因为是队列第一个元素,所以 前驱指针为null,item不为null
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
* 因为是最后一个元素,所以 后继指针为null,item不为null
*/
transient Node<E> last;
2. 初始化
首先我们创建一个LinkedList对象:
// Test::main() 构造一个List实例
List<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList 构造方法如下:
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
纳尼? 啥都没干。只是开辟了个堆内存空间而已。。。
如图所示:

3. 添加元素
源码走起:
// 将指定的元素附加到此列表的末尾。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
// 尾部追加
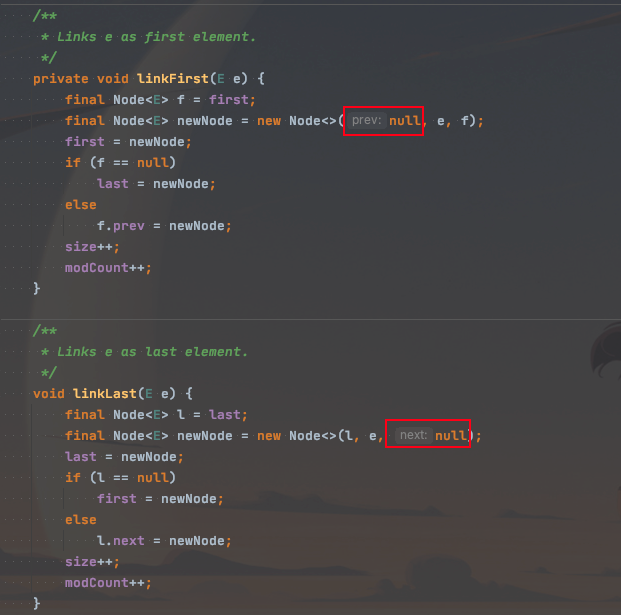
void linkLast(E e) {
// 第一次添加,这里last为null,所以l也为null
final Node<E> l = last;
// 创建一个后继指针为null的node实例
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 赋值给 last 属性
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
// l为null,将创建出来的node再赋值给first
first = newNode;
else
// 如果不是第一次添加,将队尾的node 的后继指针指向 新创建的node
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
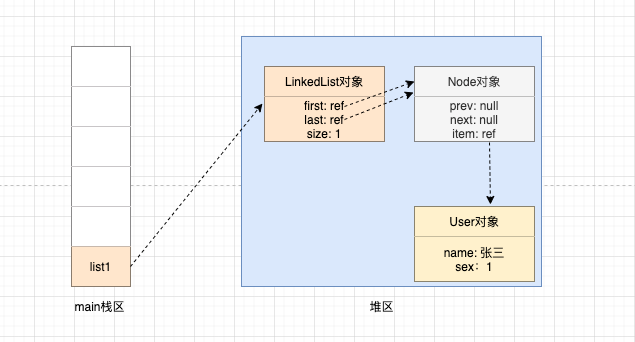
那么我们给list1实例添加一个元素后内存地址会如何变化呢?
User user = new User("张三", 1);
LinkedList<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list1.add(user);
如图所示:
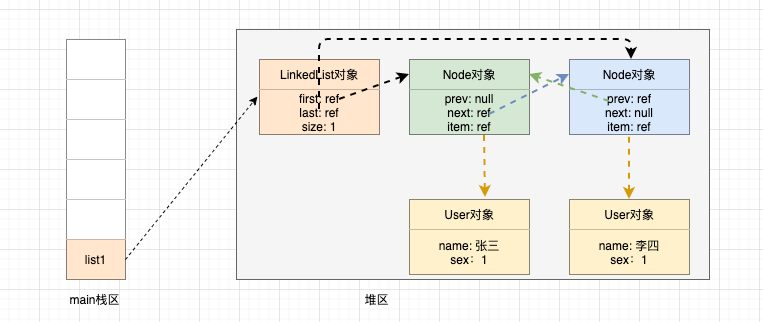
此时我们再添加一个元素呢?
User user = new User("张三", 1);
User user1 = new User("李四", 1);
LinkedList<User> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
list1.add(user);
list1.add(user1);
如图所示:
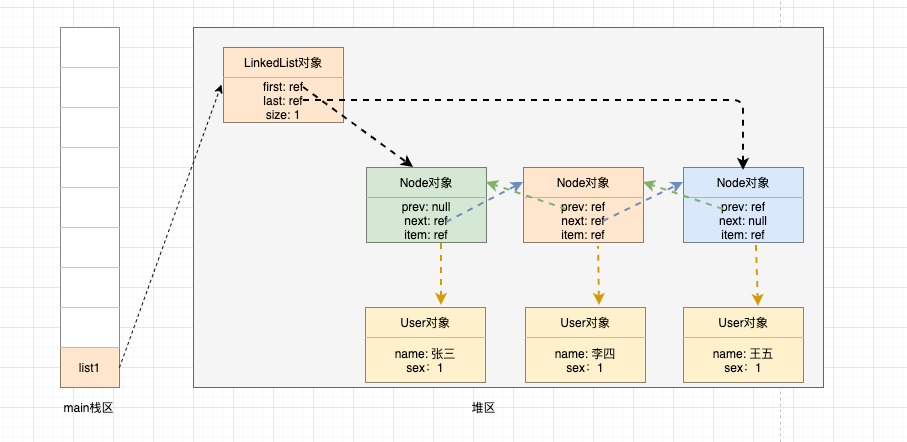
再添加一个王五对象:
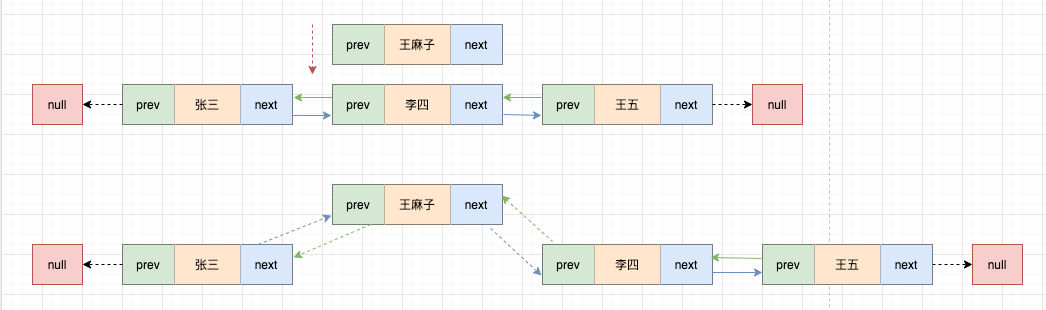
那如果我们是插入元素,不是尾部追加,会是什么情况?
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查索引下标 index >= 0 && index < size
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
// 如果index == size 那么尾部追加
linkLast(element);
else
// 插入元素
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// 获取之前index所在位置node的前驱
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
// 创建一个node。前驱 == 之前index所在位置node的前驱,后继 == 之前index所在位置的node
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
// 之前index所在位置node的前驱指向 新创建的node
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 查找指定索引位置的node。4.0有讲,这里不再赘述
Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
其原理如图所示:
4. 获取元素
因为LinkedList本身就是个双端队列,所以LinkedList支持从双端获取元素,即:firstNode 和 lastNode。
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
我们再来看下get()方法:
public E get(int index) {
// 检查索引下标 index >= 0 && index < size
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// 如果索引 < size / 2 , 右移一位相当于除以2
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
// 从链表的最左端一直 遍历到 index为止
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
// 从链表的最右端 遍历到 index为止
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
啊哈,所以说为什么LinkedList查找元素慢了,原来是从离 index 最近的一端 一直遍历到 index 位置为止。
5. 删除元素
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
* 移除此列表中指定位置的元素。将任何后续元素向左移动(从它们的索引中减去一个)。返回从列表中删除的元素
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
// 将删除node前驱的后继指针指向删除node的后继
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
// 将删除node后继的前驱指针指向删除node的前驱
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
// 设置为null 为了让GC清除被删除的node
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}