Java程序运行过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两类:
§错误(Error):JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况
§违例(Exception): 其它因编程错误或偶然的外在因素导致的一般性问题,例如:
–对负数开平方根
–空指针访问
–试图读取不存在的文件
–网络连接中断
例:
public class ExceptionTest01{ public static void main(String[] args) { String friends[]={"lisa","bily","kessy"}; for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { System.out.println(friends[i]); } System.out.println(" this is the end"); } }
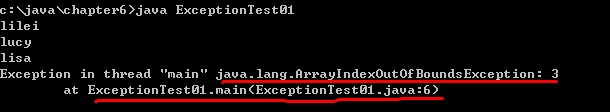
public class ExceptionTest02 { public static void main(String[] args){ String user[] = {"lilei","lucy","lisa"}; try{ for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { System.out.println(user[i]); } }catch(java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){ System.out.println("异常:" + e.getMessage()); } System.out.println("程序结束!"); } }


异常处理块的一般形式
try{ // 要监控错误的代码块 methodGeneratingException(); } catch (Exception e) { // Exception e 的异常处理程序 } finally{ // 在 try 结束前要执行的代码块 cleanup(); }
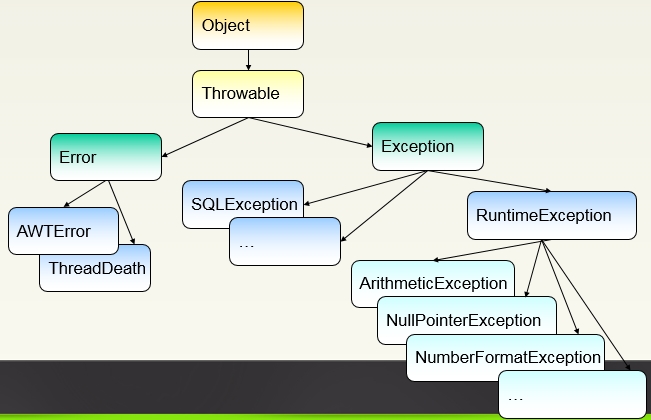
•Throwable 具有两个子类,它们是
–Exception:处理用户程序应当捕获的异常情况
–Error:Error 类的异常为内部错误,因此在正常情况下不期望用户的程序捕获它们
常见 异常类
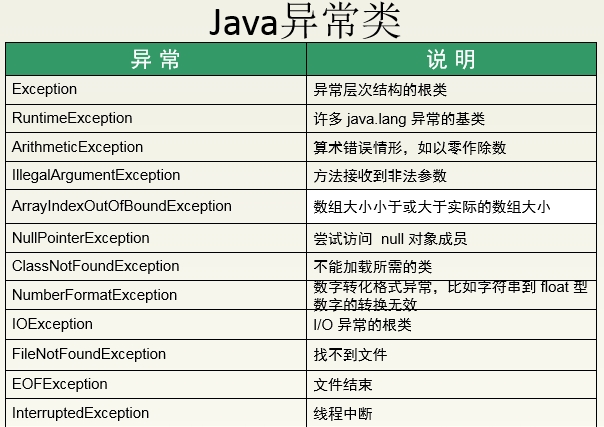
§RuntimeException
–错误的类型转换
–数组下标越界
–空指针访问
§IOExeption
–从一个不存在的文件中读取数据
–越过文件结尾继续读取
–连接一个不存在的URL
捕获异常
捕获异常是通过try-catch-finally语句实现的。
try{ ...... //可能产生异常的代码 }catch( ExceptionName1 e ){ ...... //当产生ExceptionName1型异常时的处置措施 }catch( ExceptionName2 e ){ ...... //当产生ExceptionName2型异常时的处置措施 } {finally{ ...... //无条件执行的语句 } }
§try
捕获异常的第一步是用try{…}语句块选定捕获异常的范围。
§catch
在catch语句块中是对异常对象进行处理的代码,每个try语句块可以伴随一个或多个catch语句,用于处理可能产生的不同类型的异常对象。与其它对象一样,可以访问一个异常对象的成员变量或调用它的方法。
–getMessage( ) 方法,用来得到有关异常事件的信息
–printStackTrace( )用来跟踪异常事件发生时执行堆栈的内容。
当使用多重catch的时候 越外面的 级别越高
如:
try { …… } catch(ClassCastException ex){ …… } catch(NumberFormatException ex){ …… } catch(Exception ex){ …… } // 此句必须放在最后!
§finally
–捕获异常的最后一步是通过finally语句为异常处理提供一个统一的出口,使得在控制流转到程序的其它部分以前,能够对程序的状态作统一的管理。不论在try代码块中是否发生了异常事件,finally块中的语句都会被执行。
–finally语句是任选的
try { startFaucet(); waterLawn(); } catch (BrokenPipeException e){ logProblem(); } finally { stopFaucet(); }
声明抛弃异常
§声明抛弃异常是Java中处理异常的第二种方式
–如果一个方法(中的语句执行时)可能生成某种异常,但是并不能确定如何处理这种异常,则此方法应声明抛弃异常,表明该方法将不对这些异常进行处理,而由该方法的调用者负责处理
public void readFile(String file) throws IOException { …… // 读文件的操作可能产生IOException类型的异常 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); ..…… }
重写方法声明抛弃异常原则
•重写方法不能抛出比被重写方法范围更大的异常类型
public class A { public void methodA() throws IOException { …… } } public class B1 extends TestA { public void methodA() throws FileNotFoundException { …… } } public class B2 extends TestA { public void methodA() throws Exception { …… } }
人工抛出异常
§Java异常类对象除在程序执行过程中出现异常时由系统自动生成并抛出,也可根据需要人工创建并抛出
–首先要生成异常对象,然后通过throw语句实现抛出操作(提交给Java运行环境)。
IOException e =new IOException();
throw e;
–可以抛出的异常必须是Throwable或其子类的实例。下面的语句在编译时将会产生语法错误:
throw new String("want to throw");
•用户自定义异常类MyException,用于描述数据取值范围错误信息:
class MyException extends Exception { private int idnumber; public MyException(String message, int id) { super(message); this.idnumber = id; } public int getId() { return idnumber; } }
用户自定义异常类
public class ExceptionTest05{ public void regist(int num) throws MyException { if (num < 0) { throw new MyException("人数为负值,不合理",3); } System.out.println("登记人数" + num); } public void manager() { try { regist(100); } catch (MyException e) { System.out.print("登记失败,出错种类"+e.getId())); } System.out.print("本次登记操作结束"); } public static void main(String args[]){ ExceptionTest05 t = new ExceptionTest05(); t.manager(); } }
•异常是运行时发生的错误
•可以使用 try、catch、throw、throws 和 finally 来管理 Java 异常处理。要监控的程序语句包含在 try 块内catch 块中的代码用于捕获和处理异常。在方法返回之前绝对必须执行的代码应放置在 finally 块中
•要手动引发异常,使用关键字 throw。任何被抛到方法外部的异常都必须用 throws 子句指定
•多重catch 和嵌套try-catch的使用
•自定义异常的编写和使用