GET 和 POST 是我们最常用的两种请求方式,今天结合前端 axios 请求库来讲一讲,如何在 golang 服务中,正确接收这两种请求的参数信息。
一、搭建一个简单的服务
首先,我们来创建一个最简单的静态页面,将 axios 引进来:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
GET & POST
</body>
</html>
接下来,我们写一个简单的 golang 服务程序,在浏览器端访问这个服务时,将上面的静态页面内容返回给浏览器:
package main
import (
"log"
"fmt"
"net/http"
"html/template"
)
// 返回静态页面
func handleIndex(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
t, _ := template.ParseFiles("index.html")
t.Execute(writer, nil)
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", handleIndex)
fmt.Println("Running at port 3000 ...")
err := http.ListenAndServe(":3000", nil)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("ListenAndServe: ", err.Error())
}
}
运行上面程序,然后在浏览器中访问 localhost:3000,就可以看到一个简单的静态页面了。
二、处理 GET 请求
接下来,我们就在静态页面中添加一个 GET 请求:
<script>
axios.get('/testGet', {
params: {
id: 1,
}
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});
</script>
对应地,服务端也要添加这个请求路径的处理函数:
// 处理GET请求
func handleGet(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
query := request.URL.Query()
// 第一种方式
// id := query["id"][0]
// 第二种方式
id := query.Get("id")
fmt.Printf("GET: id=%s
", id)
fmt.Fprintf(writer, `{"code":0}`)
}
func main() {
// ...
http.HandleFunc("/testGet", handleGet)
// ...
}
重新运行程序,访问页面,服务端控制台打印如下:
GET: id=1
在接收到请求参数后,我们会返回一个 {"code":0} 的响应结果,浏览器端收到响应后,会将其转为 JS 对象,控制台打印如下:
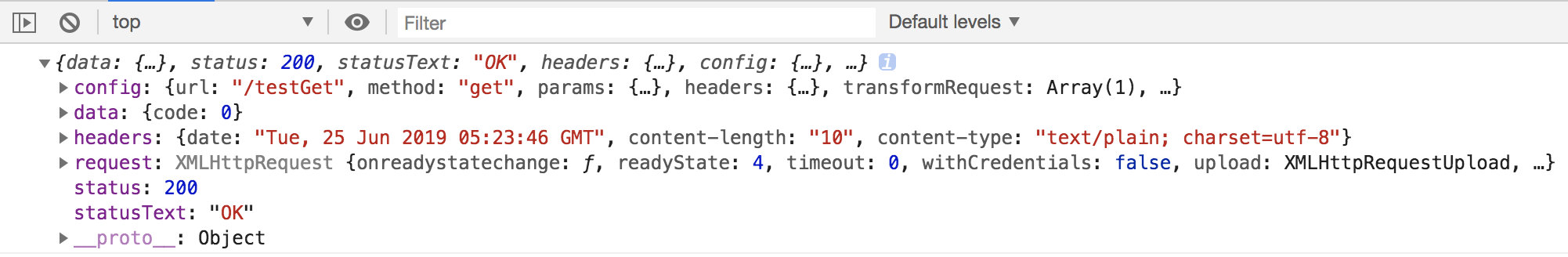
三、处理 POST 请求
在开发中,常用的 POST 请求有两种,分别是 application/json 和 application/x-www-form-urlencoded,下面就来介绍一下这两种类型的处理方式。
先说第一种,在使用 axios 发起请求时,默认就是 application/json 类型,我们来添加一个这样的请求:
// POST数据
const postData = {
username: 'admin',
password: '123',
};
axios.post('/testPostJson', postData).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});
同样地,我们需要在 golang 服务中添加处理函数:
// 引入encoding/json包
import (
// ...
"encoding/json"
)
// 处理application/json类型的POST请求
func handlePostJson(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
// 根据请求body创建一个json解析器实例
decoder := json.NewDecoder(request.Body)
// 用于存放参数key=value数据
var params map[string]string
// 解析参数 存入map
decoder.Decode(¶ms)
fmt.Printf("POST json: username=%s, password=%s
", params["username"], params["password"])
fmt.Fprintf(writer, `{"code":0}`)
}
func main() {
// ...
http.HandleFunc("/testPostJson", handlePostJson)
// ...
}
再次运行程序,访问页面,服务端控制台打印如下:
POST json: username=admin, password=123
如果我们使用 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 这样的请求类型,就需要在发送请求时,额外添加一些配置信息:
// POST数据
const postData = {
username: 'admin',
password: '123',
};
axios.post('/testPostForm', postData, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8',
},
transformRequest: [(data) => {
const pairs = [];
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
pairs.push(`${key}=${data[key]}`);
});
return pairs.join('&');
}]
}).then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});
对应的服务端 golang 处理函数如下:
// 处理application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型的POST请求
func handlePostForm(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
request.ParseForm()
// 第一种方式
// username := request.Form["username"][0]
// password := request.Form["password"][0]
// 第二种方式
username := request.Form.Get("username")
password := request.Form.Get("password")
fmt.Printf("POST form-urlencoded: username=%s, password=%s
", username, password)
fmt.Fprintf(writer, `{"code":0}`)
}
func main() {
// ...
http.HandleFunc("/testPostForm", handlePostForm)
// ...
}
最后运行程序并访问,服务端控制台打印如下:
POST form-urlencoded: username=admin, password=123
四、返回JSON对象数据
前面我们的处理函数中,都返回了一个简单的 JSON 字符串,实际开发中,往往是一些数据对象,我们需要将这些数据对象以 JSON 的形式返回,下面我们就来添加一段代码:
type Person struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
type Response struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
Data Person `json:"data"`
}
// 返回数据对象的JSON数据
func handleResponseJson(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
res := Response{
0,
"success",
Person{
"Jack",
20,
},
}
json.NewEncoder(writer).Encode(res)
}
func main() {
// ...
http.HandleFunc("/handleResponseJson", handleResponseJson)
// ...
}
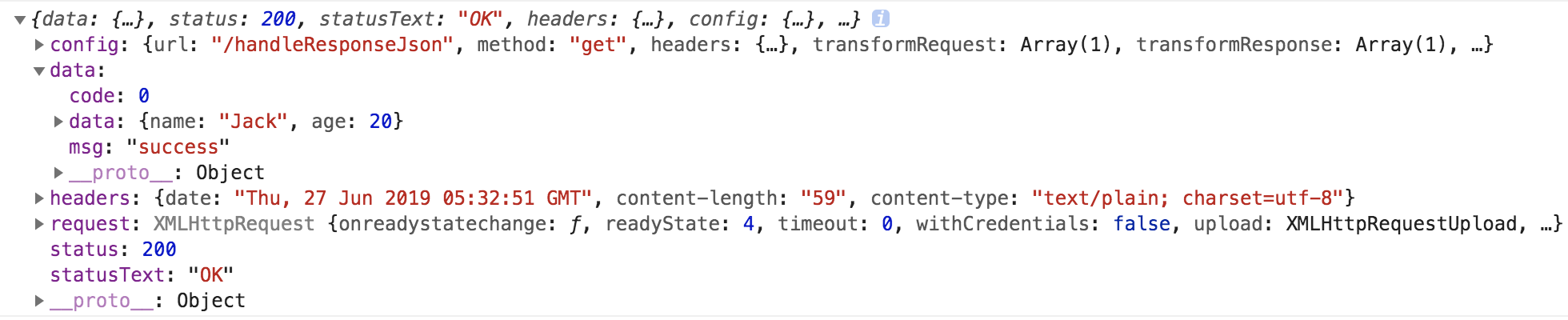
接着,我们使用 axios 测试一下这个服务:
axios.get('/handleResponseJson').then((response) => {
console.log(response);
});
访问页面,浏览器控制台打印结果如下: