Mysql
一 、用户相关
1.创建用户
1. 创建用户
create user 'lqw'@'ip地址' identified by '密码'
ex:
create user 'lqw'@'%' identified by '123456'
create user 'lqw'@'127.0.%' identified by '123456'
2. 删除用户
drop user 'lqw'@'ip地址';
3.修改用户
rename user 'lqw'@'ip地址' to 'lqw1'@'ip地址';
4. 修改密码
set password 'lqw'@'ip地址' = Password('new_password')
2.权限
1. 赋予权限
权限 人
grant select,insert,update on table.* to 'lqw'@'*';
grant all privileges on table.* to 'lqw'@'*';
2. 取消权限
revoke 权限 on table.* from 'lqw'@'*';
ex:
revoke all privileges on table.* from from 'lqw'@'*';
二 、 数据库的操作
1. 库的操作
1. 创建
create database test;
create database db default charset utf8; 编码默认为utf8
2. 查看数据库
show databases;
3. 删除
drop database ‘name’;
4. 使用
use database
5. 查看当前所在表
select database();
6.数据转存 mysqldump -u 密码 db1 > test.sql -p; # 将db1 的数据保存至test.sql,包含数据和表结构,加 -d 参数,只包含表结构。
数据导入 mysqldump -u 账号 db < db1.sql -p;
2.表的操作
1. 查看表
show tables;
desc table; # 查看表结构
2.创建表
create table t1(id int not null auto_increment primary key,name char(64) default '111') engine = innodb default charset=utf8; id 不能为空,自增,主键。name默认'111',为默认utf8,引擎为innodb;
create table t1(id int auto_increment primary key , name char(18) ) engine=innodb default charset = utf8;
3. 插入表
insert into t1(id,name) values(1,'123')
4. 查看数据
select * from table;
show create table class \G # 查看表结构。
5. 清空表
delete from table where id > 5; # 把内容删掉,自增会在原来的基础上
truncate table t1; # 也会把表清空,自增在
6.删除表
drop table t1;
7 修改:
update 表明 set name = 10 where id > 10;
alter table t1 auto_increment = 100 # 起始自增点。
alter table 表名 add primary key (id); # 添加主键
alter table 表名 change id id int not null auto_increment;# 设置正自增。
tips:
auto_increment 自增,一个表里面只能有一个自增,必须为key
primary key 不能重复,不能为空,加速查找。只能有一个主键。
3.字段类型
1.数字类型:表示的范围 是否有符号 unsigned
tinyint
int
bigint
小数
double
float # float 和double 表示不精准;float短的时候就不精准。double 长的时候不精准
decimal #精准,底层是字符串存的, num decimal(总位数,小数点后最多有多少)
2.字符串
char(10) #会帮你填写空的,速度快,
varchar(10) # 最多帮占4个,节省空间,速度比较慢
优化点:定长的往前放,最高255个字符
text 65535
****** tips :图片、文件、视频,存放文件所在的路径。
3. 时间
datetime yyyy-mm-dd HH:MM:SS
4. 二进制
TinyBlob
Blob
MediumBlob
LongBlob
5. 枚举类型
size ENMU('男','女','不详')
6.集合
craete table t(hobby SET('a','b'))
insert into t(hobby) values(('a,b'))
4.外键
1. 节省空间
2. 和其他表有关联
**要想外键,数据库引擎必须为innodb,外键字段必须唯一索引。可以是多个**
craete table sex(
id int auto_increment primary key,
type char(64),
) engine = innodb default charset=utf8;
第一种:
create table user_info(id
id int auto_increment primary key, name char(64),
sex_id int,
foreign (sex_id) references sex(id),
) engine = innodb default charset=utf8;
第二种:
create table user_info(id
id int auto_increment, name char(64),
sex_id int,
primary key(id) # 支持多列主键。
foreign (sex_id) references sex(id),
) engine = innodb default charset=utf8;
5. 自增步长
1. 基于会话的自增,
show session variables like 'auto_increment';
set session auto_increment_increment = 5 # 在会话中可以
2. 基于全局级别的
每次打开会话,都是全局步长的
set global session auto_increment_increment = 5
6.索引相关
0. 唯一索引
create table t1(
id int,
iden unique,
unique (ip,port)。
) # 唯一 加速查找,可以为空,主键不能重复,不能为空。
三 、表库操作
增:
insert into 表名(字段) values ('xxx'),('yyyy');
insert into 表名() select name,age from 表名;
删:
delete from 表名 where id != 5 or id = 5;
改:
update 表名 set name='xxx' where id is not null;
查:
select id as 别名,name from 表名 where id not between 1 and 2;
select id,name,11 from 表名;
select * from table where id <> 1;
四、查询
1.范围
select * from table where id not in (1,2,3);
select * from table where id not between 1 and 6;
select * from table where id not null ;
select * from table where id in (select id from 表;)
tips:
三元表达式
case when 条件 then a else b 满组条件 就是 A 否则 就是 b
if(exp1,exp2,exp3); 如果exp1 为Ture,则为 exp2 否则为exp3;
2.通配符
select * from table where name like '%a%' ;# 包含a的
select * from table where name like '____'; # 四个字符的
3.分组
select dep_id,count(age) from table where id <=5 group by dep_id having max(age)>18;
常见聚合函数:
max,min,count,sum,avg;
分组 可以取得值,分组依据,聚合函数。
having 要用在group之后。
默认分为1组
select count(id) from 表名。
4.连表
1. 笛卡尔积
select * from table,table2;
2.left join
左边都显示
3. right join
右边都显示
4. inner join
存在的都显示
5. 上下连表 union,将上下两表连接在一起
select name from table1
union
select age from table2; # 列数要相同。会去重
select name from table1
union all
select name from table1;#拼在一起不会去重。
5.去重
select distinct name from table #
# 注意点:
id 不能添加进入。
# 也可以通过group by 来去重
6.循环查询
# 循环查询
SELECT DISTINCT out_table.student_id,
(SELECT num from score as inner_table WHERE inner_table.student_id = out_table.student_id AND inner_table.course_id = 1) as 语文,
(SELECT num from score as inner_table WHERE inner_table.student_id = out_table.student_id AND inner_table.course_id = 2) as
英语,
(SELECT num from score as inner_table WHERE inner_table.student_id = out_table.student_id AND inner_table.course_id = 3) as
数学,
(SELECT count(1) from score as inner_table WHERE inner_table.student_id = out_table.student_id and inner_table.course_id in (1,2,3) ),
(SELECT avg(num) from score as inner_table WHERE inner_table.student_id = out_table.student_id and inner_table.course_id in (1,2,3))
from score as out_table;
select id from table; #本质就是循环,id 就是table.id
sqlalchemy:
res = session.query(UserTypes,session.query(Users.id).filter(Users.id ==UserTypes.id).as_scalar()).all()
7.三元表达式
case when 1>2 then 2 else 1 end;
if(1 >2,2,1)
五 sql其他相关
1.视图
假设100 sql,都需要用到一个复查的表,可以用视图;
创建视图
create view test_view as sql语句;
删除视图
drop view 视图名称
修改视图
alter view 名字 as set sql语句
tips:
视图是虚拟表,不要对其增删改查,否则会有问题;
2.触发器
在对表操作时候增删改查,可以关联自定义行为;
delimiter //
create trigger t1 before insert on 表名 for each row
begin
insert into 表名 New(表示新增的数据),old表示旧的数据;
end //
delimiter ;
3.函数
时间函数,将时间转成年月。去官网看
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(date,'%y年%m月'),count(1),group_concat(date_test.id) as 文章 FROM date_test GROUP BY DATE_FORMAT(date,'%y年%m月'); 时间为'2021-01-04 15:15:15'
按照年月分组。
delimiter //
create function f1(
i1 int,
i2 int)
returns int
Begin
declare num int default 0;
set num = i1+i2;
return(num);
end //
delimiter ;
4.存储过程
4.1 一般版本
保存在mysql的一个别名,一坨代码,想干嘛就干嘛。
别名(),用于替代程序员写sql语句。直接调用就行了。
delimiter //
create procedure p1()
Begin
select * from student;
END //
delimiter ;
pymsql中调用存储过程 res = cursor.callproc('p1')
4.2参数版本
# 传参数 in out inout 三种。
delimiter //
create procedure p2(
in n1 int,
out n2 int
)
Begin
select * from test where id > n1;
set n2 = 999
END //
delimiter ;
'''
pymysql 获取存储过程结果
res = cursor.callproc('p2',args=(2,45))
print(cursor.fetchall()) #先获取结果
cursor.execute('select @_p2_0,@_p2_1')
print(cursor.fetchall()) 在获取 out
'''
状态表示可以存储过程执行的状态。
4.3 事务版本
delimiter //
create procedure p7(
out status int
)
BEGIN
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER for SQLEXCEPTION --有问题执行这个
BEGIN
set status = 1;
ROLLBACK;
END;
START TRANSACTION; --开始事务
SELECT * FROM test1;
COMMIT;
set status = 2;
END //
delimiter ;
4.4 循环
//创建存储过程前先检查是否存在,存在就删除,这个可以忽略
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS staff_zt_test;
//存储过程
CREATE PROCEDURE staff_zt_test()
BEGIN
//该变量用于标识是否还有数据需遍历
DECLARE flag INT DEFAULT 0;
//创建一个变量用来存储遍历过程中的值
DECLARE id BIGINT(40);
//查询出需要遍历的数据集合
DECLARE idList CURSOR FOR (SELECT id FROM table WHERE a = 1);
//查询是否有下一个数据,没有将标识设为1,相当于hasNext
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET flag = 1;
//打开游标
OPEN idList;
//取值设置到临时变量中
FETCH idList INTO id;
//遍历未结束就一直执行
WHILE flag != 1 DO
-- targetSQL //你想要执行的目标功能,这里可以写多个SQL
// 注意
//这里有一个坑,目标语句引用临时变量,实测发现不需要加@符号,但是搜索到的结果都是例如:@id ,这样来使用,实测发现无法取到数据
// 注意
update XXX from table2 where key_id = id;
//一定要记得把游标向后移一位,这个坑我替各位踩过了,不需要再踩了
FETCH idList INTO id;
END WHILE;
CLOSE idList;
END;
4.5 动态执行sql 防止sql注入
delimiter //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_sql(
in id int
)
Begin
set @nid = nid;
Prepare prod from 'sql语句’;
Execute prod using @nid;
Deallocate prepare prod;
End //
delimiter ;
六 、索引
1.索引的意义
1.对列进行约束
2.对列进行创建‘字典’,加速查找
如 unique 对字段约束成唯一,primiary key 非空且唯一
2.mysql索引的类别
1. hash索引,类似于字典,会维护一个hash表,根据hash值去查找,单行查找很快,范围查找就很慢;
2. btree索引,维护成一个树,对于范围查找比较快;
聚簇索引:聚簇索引只可能是主键,或者所有组成唯一键的所有列都为NOT NULL的第一个唯一索引,或者隐式创建的聚簇索引这三种情况;
非聚簇索引:又叫辅助索引,辅助索引,每个辅助索引的每条记录都包含主键,也包含非聚簇索引指定的列,辅助索引应该短一点,在查询普通索引时,会有回表这个操作,如下图
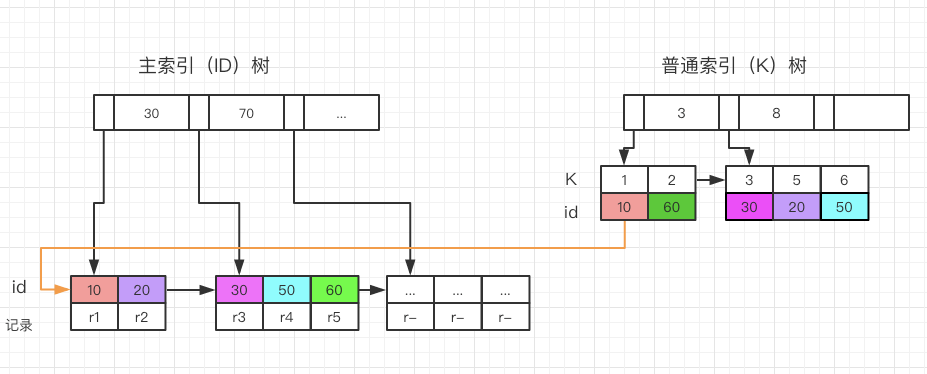
3.索引的创建
create index '索引名' on 表(字段)
drop index '索引名' on 表
4.索引的名词
- like '%xx'
select * from tb1 where name like '%cn';
- 使用函数
select * from tb1 where reverse(name) = 'dada';
- or
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or email = 'seven@live.com';
特别的:当or条件中有未建立索引的列才失效,以下会走索引
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or name = 'seven';
select * from tb1 where nid = 1 or email = 'seven@live.com' and name = 'alex'
- 类型不一致
如果列是字符串类型,传入条件是必须用引号引起来,不然...
select * from tb1 where name = 999;
- !=
select * from tb1 where name != 'alex'
特别的:如果是主键,则还是会走索引
select * from tb1 where nid != 123
- >
select * from tb1 where name > 'alex'
特别的:如果是主键或索引是整数类型,则还是会走索引
select * from tb1 where nid > 123
select * from tb1 where num > 123
- order by
select email from tb1 order by name desc;
当根据索引排序时候,选择的映射如果不是索引,则不走索引
特别的:如果对主键排序,则还是走索引:
select * from tb1 order by nid desc;
- 组合索引最左前缀
如果组合索引为:(name,email)
name and email -- 使用索引
name -- 使用索引
email -- 不使用索引
七 、额外
1.注意事项
避免使用select *
- count(1)或count(列) 代替 count(*)
- 创建表时尽量时 char 代替 varchar
- 表的字段顺序固定长度的字段优先
- 组合索引代替多个单列索引(经常使用多个条件查询时)
- 尽量使用短索引
- 使用连接(JOIN)来代替子查询(Sub-Queries)
- 连表时注意条件类型需一致
- 索引散列值(重复少)不适合建索引,例:性别不适合
2.分页
select * from tb1 where nid < 1000 order by nid desc limit 10;
select * from tb1 where nid > 1000 limit 10;
3.执行计划explain
explain + 查询SQL - 用于显示SQL执行信息参数,根据参考信息可以进行SQL优化
+----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
+----+-------------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+------+------+-------------+
| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | NULL |
| 2 | DERIVED | tb1 | range | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 8 | NULL | 9 | Using where |
select_type
查询类型
SIMPLE 简单查询
PRIMARY 最外层查询
SUBQUERY 映射为子查询
DERIVED 子查询
UNION 联合
UNION RESULT 使用联合的结果
...
table
正在访问的表名
type
查询时的访问方式,性能:all < index < range < index_merge < ref_or_null < ref < eq_ref < system/const
ALL 全表扫描,对于数据表从头到尾找一遍
select * from tb1;
特别的:如果有limit限制,则找到之后就不在继续向下扫描
select * from tb1 where email = 'seven@live.com'
select * from tb1 where email = 'seven@live.com' limit 1;
虽然上述两个语句都会进行全表扫描,第二句使用了limit,则找到一个后就不再继续扫描。
INDEX 全索引扫描,对索引从头到尾找一遍
select nid from tb1;
RANGE 对索引列进行范围查找
select * from tb1 where name < 'alex';
PS:
between and
in
> >= < <= 操作
注意:!= 和 > 符号
INDEX_MERGE 合并索引,使用多个单列索引搜索
select * from tb1 where name = 'alex' or nid in (11,22,33);
REF 根据索引查找一个或多个值
select * from tb1 where name = 'seven';
EQ_REF 连接时使用primary key 或 unique类型
select tb2.nid,tb1.name from tb2 left join tb1 on tb2.nid = tb1.nid;
CONST 常量
表最多有一个匹配行,因为仅有一行,在这行的列值可被优化器剩余部分认为是常数,const表很快,因为它们只读取一次。
select nid from tb1 where nid = 2 ;
SYSTEM 系统
表仅有一行(=系统表)。这是const联接类型的一个特例。
select * from (select nid from tb1 where nid = 1) as A;
possible_keys
可能使用的索引
key
真实使用的
key_len
MySQL中使用索引字节长度
rows
mysql估计为了找到所需的行而要读取的行数 ------ 只是预估值
extra
该列包含MySQL解决查询的详细信息
“Using index”
此值表示mysql将使用覆盖索引,以避免访问表。不要把覆盖索引和index访问类型弄混了。
“Using where”
这意味着mysql服务器将在存储引擎检索行后再进行过滤,许多where条件里涉及索引中的列,当(并且如果)它读取索引时,就能被存储引擎检验,因此不是所有带where子句的查询都会显示“Using where”。有时“Using where”的出现就是一个暗示:查询可受益于不同的索引。
“Using temporary”
这意味着mysql在对查询结果排序时会使用一个临时表。
“Using filesort”
这意味着mysql会对结果使用一个外部索引排序,而不是按索引次序从表里读取行。mysql有两种文件排序算法,这两种排序方式都可以在内存或者磁盘上完成,explain不会告诉你mysql将使用哪一种文件排序,也不会告诉你排序会在内存里还是磁盘上完成。
“Range checked for each record(index map: N)”
这个意味着没有好用的索引,新的索引将在联接的每一行上重新估算,N是显示在possible_keys列中索引的位图,并且是冗余的。
4.慢日志查询
slow_query_log = OFF 是否开启慢日志记录
long_query_time = 2 时间限制,超过此时间,则记录
slow_query_log_file = /usr/slow.log 日志文件
log_queries_not_using_indexes = OFF 未使用索引的搜索是否记录
注:查看当前配置信息:
show variables like '%query%'
修改当前配置:
set global 变量名 = 值;
5.ondelete
set null 置为空,要可以为空
cascade 删除
no action restrict 有的话不允许删除