第八章:参数、解包和变量、提示和传递、读取文件、读写文件
我要疯了,写到了习题16,结果网页出现问题,从新写!!!!
----------------------------------<习题13:参数、解包、变量>---------------------------------------
先介绍几个名词:脚本、参数、参数变量、解包、特性、模块
脚本script:我在上一章也多次提到脚本,忘记解释了,其实我也是学到这个习题才注意到脚本的概念。脚本就是你编写的.py程序。
参数argument:例如一个函数运行,需要某些参数,多了不行,少了也不行。
参数变量argv(argument variable):这是一个变量,它可以保存你运行python脚本时传递给Python脚本的参数。它适用于需要用户在输入脚本运行命令时,就要输入不能更改的参数,用以赋值给argv的变量们(第一个除外)
解包unpack:把参数变量argv种的东西解包,并将所有的参数依次赋值给其它变量(该变量的名称可自行设计)
特性、模块module、库library、软件包:它们的概念是一样的,都是Python系统自带的一个软件库,可以用import命令调用。
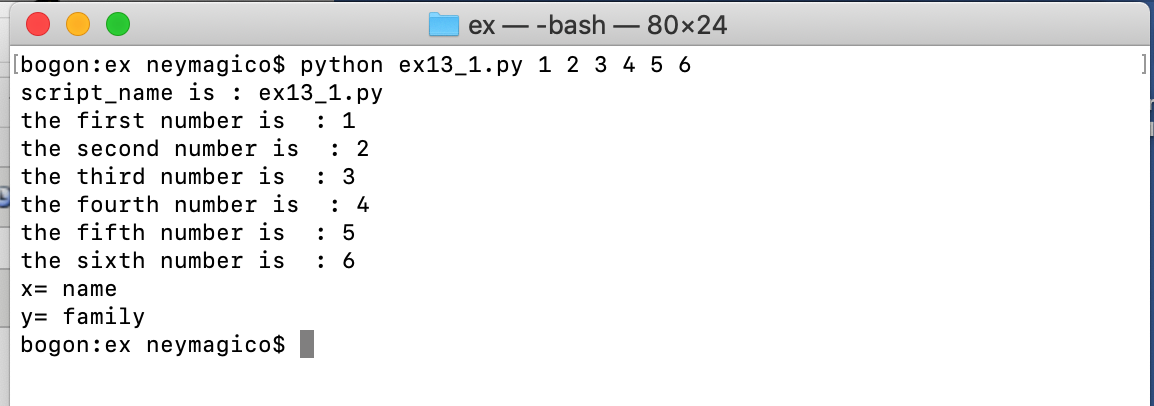
具体如何运用,参考ex13_1.py,代码如下:在该代码中,也可以看到argv和raw_input()的区别

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 3 from sys import argv 4 5 script_name, a, b, c, d, e, f = argv 6 # argv 的第一个变量不需要赋值,默认是脚本的名称 7 # 所以在运行该脚本时,需要在脚本ex13_1.py后面键入6个参数,分别对应六个变量abcdef 8 # python ex13_1.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 print "script_name is :", script_name #这里的变量名,必须跟参数变量里面的名字一致, 11 print "the first number is :", a 12 print "the second number is :", b 13 print "the third number is :", c 14 print "the fourth number is :", d 15 print "the fifth number is :", e 16 print "the sixth number is :", f 17 18 19 #同样都是需要用户输入参数,对比argv和raw_input()的区别 20 print "x=", 21 x = raw_input() 22 print "y=", 23 y = raw_input() 24 25 26 27 28 # raw_input()和argv的区别是:raw_iput()是在脚本运行的过程中输入参数, 29 # 而argv是在编写运行脚本的命令行时输入参数
终端运行结果如下:
--------------------------------------<习题14:提示和传递>--------------------------------------
该习题就只是简单的介绍一下修改提示符,例如raw_input('>-')中的>-就时修改提示符。ex14.py将该提示符赋值给一个叫prompt的变量,是为了统一修改提示符的格式。需要使用时,就像raw_input(prompt)即可。
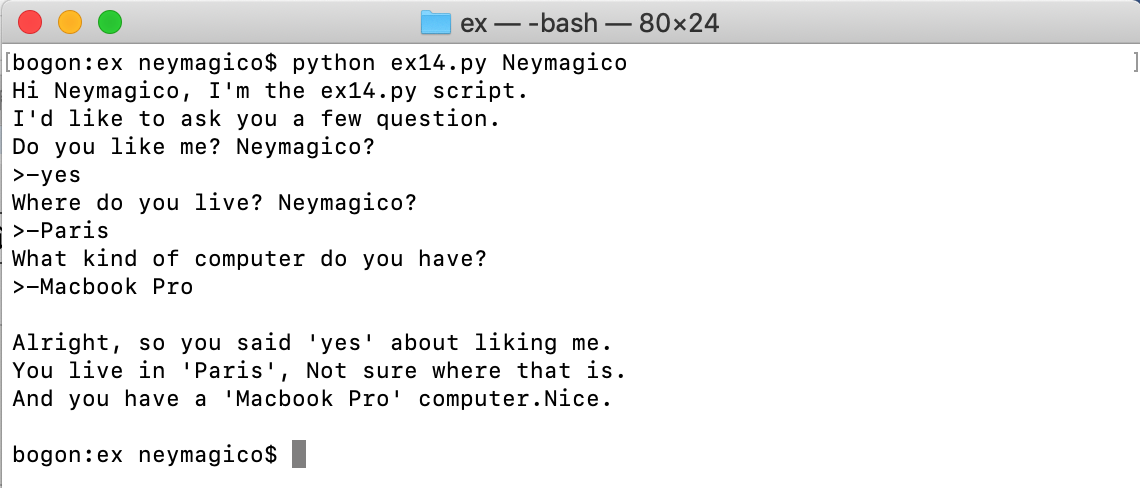
ex14.py的代码如下:

1 # -*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 3 from sys import argv 4 5 script, user_name = argv #在python运行ex14_py是,需要输入一个字符,用于定义user_name 6 prompt = '>-' #raw_input()后面答案的提示符 7 8 print "Hi %s, I'm the %s script." % (user_name, script) 9 print "I'd like to ask you a few question." 10 print "Do you like me? %s?" % user_name # 也可用%r 11 likes = raw_input (prompt) 12 13 print "Where do you live? %s?" % user_name 14 lives = raw_input(prompt) #其实可以直接把该处的prompt该处'>-',该处设置一个prompt,仅仅是为了统一提示符的格式 15 16 print "What kind of computer do you have?" 17 computer = raw_input(prompt) 18 19 # 三个引号是可以定义多行字符串 20 print """ 21 Alright, so you said %r about liking me. 22 You live in %r, Not sure where that is. 23 And you have a %r computer.Nice. 24 """ % (likes, lives, computer)
终端运行结果如下:
--------------------------------------<习题15:读取文件>--------------------------------------
能不能用一段代码来读取你电脑里存的文件呢?答案时肯定的。
首先介绍两个函数和一个符号‘.':txt = open(filename)、 txt.read()
open():打开文件名了,需要在括号内键入文件的名称,而且可以将open()的结果赋值给一个变量,本文是复制给 变量txt。
read(): 读取文件的函数,也可以将读出的结果赋值给一个变量
txt.read()中的小数点'.':它的作用类似于“执行”的意思,变量txt“执行”read()函数
ex15_sample.txt 的内容如下:

1 This is stuff I typed into a file. 2 It is really cool stuff. 3 Lots and lots of fun to have in here.
ex15.py代码如下:

1 # -*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 from sys import argv 3 4 script, filename = argv 5 6 txt = open(filename) #执行 python ex15.py ex15_example.txt, 该文本是提前在目录temp/ex中创建完成的 7 # 是为了将文本“ex15_example.txt"输入到txt=open(),该文本相当于一个参数,并且供下面的%r命令使用 8 9 print "Here's your file %r:" % filename # 10 print txt.read() #txt.read命令,不需要输入参数,直接执行read命令,对象是txt 11 12 print "Type the filename again:" 13 file_again = raw_input(">") #用>字符提示raw_input()的输出结果 14 15 txt_again = open(file_again) 16 17 print txt_again.read() #txt_again.read命令,不需要输入参数,直接执行read命令,对象是txt_again
ex15.py终端运行结果如下:

即然有了open()函数,那有没有close()函数呢? 求助! 求助! 求助! 求助!答案也是肯定的,而且当你不再读或者用某个文本时,用close()函数将其关闭,是一个很好的习惯,至于为什么,我也不太清楚,希望懂得的朋友实例解释一下,谢谢啦。
如果文档用close()函数关闭了,就无法再被read(),否者会报错。见代码ex15_2.py:

1 # -*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 from sys import argv 3 4 script, filename = argv 5 6 txt = open(filename) #执行 python ex15_2.py ex15_example.txt, 该文本是提前在目录temp/ex中创建完成的 7 # 是为了将文本“ex15_example.txt"输入到txt=open(),该文本相当于一个参数,并且供下面的%r命令使用 8 9 print "Here's your file %r:" % filename # 10 print txt.read() #txt.read命令,不需要输入参数,直接执行read命令,对象是txt 11 12 txt.close() #关闭打开的文件 13 14 # print txt.read() 这段代码会报错,因为txt已经执行了close()命令,无法再被读。
求助!求助! 求助! 求助! 这个习题讲的是打开和阅读本地文档,其中有一个前提就是:Python脚本ex15..py必须和文本ex15_sample.txt在同一个目录下,但是如果我想读取其它目录下的文本,该如何操作呢?利用url?
--------------------------------------<习题16:读写文件>--------------------------------------
即然可以读取文件,那一定也可以编辑文件吧?习题16讲的就是如何编辑文件。
先介绍几个函数:close/read/readline/truncate/write(stuff)
close():关闭文件,形式为:txt.close();功能就像是TextWrangler、office软件等的“文件-保存”
read():读取文件内容,方式为:txt.read(),而不能写成read(txt)
readline(): 读取文本文件中的一行
truncate():清空文件内容,形式为:txt.truncate()
write(stuff): 将stuff写入文件,形式为:txt.write(stuff)
利用ex16.py脚本往ex16_sample1.txt里写东西
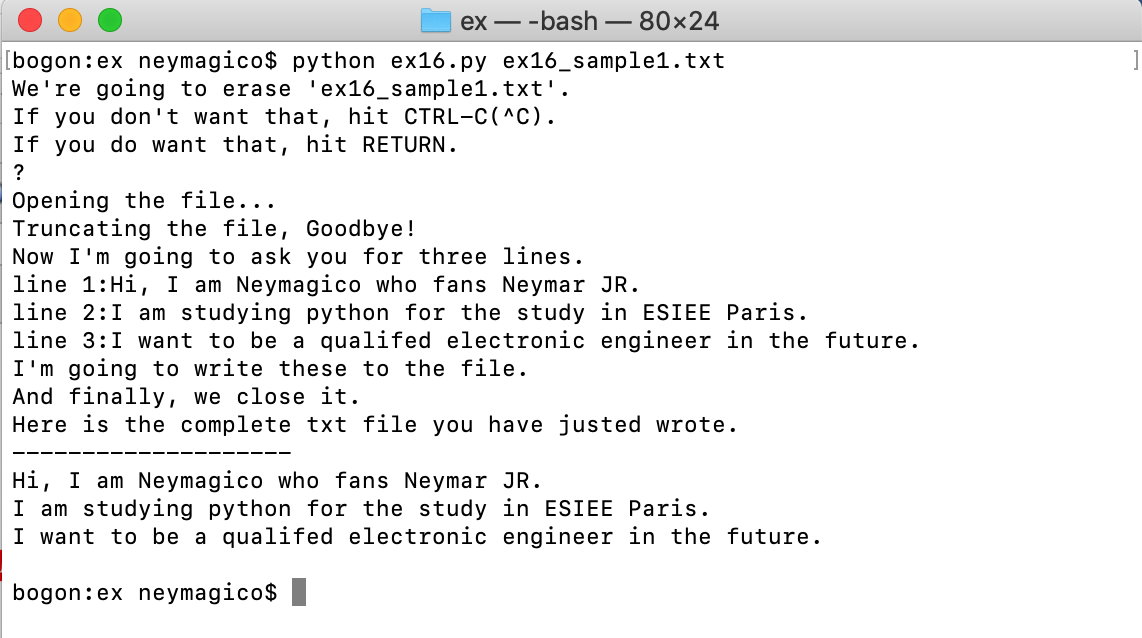
ex16.py代码如下:

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 from sys import argv #从sys软件包中调取参数变量argv使用。 3 4 script, filename = argv #给argv解压, 5 # 并且在运行python ex16.py ex16_sample1.txt时,赋予filename以参数ex16_sample1.txt 6 7 print "We're going to erase %r." %filename 8 print "If you don't want that, hit CTRL-C(^C)." 9 print "If you do want that, hit RETURN." 10 11 raw_input("?") 12 13 print "Opening the file..." 14 target = open(filename,'w') #赋予变量target以ex16_sample1.txt 15 16 print "Truncating the file, Goodbye!" 17 target.truncate()# 清空文档target中的内容 18 19 20 print "Now I'm going to ask you for three lines." 21 22 line1 = raw_input("line 1:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line1 23 line2 = raw_input("line 2:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line2 24 line3 = raw_input("line 3:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line3 25 26 print "I'm going to write these to the file." 27 28 target.write(line1)# 将line1写入target文本中 29 target.write(" ")# 重起一行 30 target.write(line2)# 将line2写入target文本中 31 target.write(" ")# 重起一行 32 target.write(line3)# 将line3写入target文本中 33 target.write(" ")# 重起一行 34 35 print "And finally, we close it." 36 target.close() #关闭target文本 37 38 39 # 是为了输出你刚刚写的txt文档 40 txt = open(filename, 'r') #文档必须先被open(),并且将open后的文件赋予变量,然后才能read()这个变量 41 print "Here is the complete txt file you have justed wrote." 42 print "-"*20 #这个命令行,仅仅是为了终端运行时看起来更清晰 43 print txt.read() 44 txt.close
终端运行结果如下:
附加练习1:编写ex16_2.py,要求使用raw_input()和argv两种方式来读取刚刚写的文本ex16_sample1.txt,代码如下:

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 #本程序是为了读文本ex16_sample1.txt 3 4 print "filename" 5 filename = raw_input() 6 7 txt = open(filename) 8 9 print "You can find your file here:" 10 print txt.read() 11 12 txt.close() 13 14 15 # 利用argv获取文本或文件名,必须在整个脚本运行开始的第一条命令行中输入文件名 16 from sys import argv 17 18 19 script, filename = argv 20 21 txt = open(filename) 22 23 print "It's your file:" 24 print txt.read() 25 26 txt.close()
附加练习2:编写ex16_3.py,要求简化write()命令这段代码, 代码如下:

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 from sys import argv #从sys软件包中调取参数变量argv使用。 3 4 script, filename = argv #给argv解压, 5 # 并且在运行python ex16.py ex16_sample.txt时,赋予filename以参数ex16_sample1.txt 6 7 print "We're going to erase %r." %filename 8 print "If you don't want that, hit CTRL-C(^C)." 9 print "If you do want that, hit RETURN." 10 11 raw_input("?") 12 13 print "Opening the file..." 14 target = open(filename,'w') #赋予变量target以ex16_sample1.txt,并且w表示时只写模式 15 16 print "Truncating the file, Goodbye!" 17 target.truncate()# 清空文档target中的内容 18 19 20 print "Now I'm going to ask you for three lines." 21 22 line1 = raw_input("line 1:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line1 23 line2 = raw_input("line 2:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line2 24 line3 = raw_input("line 3:")# 输入字符串,用于定义line3 25 26 print "I'm going to write these to the file." 27 28 contxt = "%r %r %r" %(line1, line2, line3) 29 30 target.write(contxt) # 将line1写入target文本中 31 32 print "And finally, we close it." 33 34 target.close() #关闭target文本 35 36 # 是为了输出你刚刚写的txt文档 37 txt = open(filename, 'r') #文档必须先被open(),并且将open后的文件赋予变量,然后才能read()这个变量 38 print "Here is the complete txt file you have justed wrote." 39 print "-"*20 #这个命令行,仅仅是为了终端运行时看起来更清晰 40 print txt.read() 41 txt.close
不知道大家有没有注意到,在这个习题的所有代码当中,都没有readline()函数,我在第一次学这个时候,也把这个忽略了,在这里把它补上。
我用的是习题15和ex15_sample.txt:

1 This is stuff I typed into a file. 2 It is really cool stuff. 3 Lots and lots of fun to have in here.
我自己又写了一个脚本ex15_3.py,里面解释了4种读取文本每一行的方法,代码如下:

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 3 #整行读取文本的方法 4 5 6 from sys import argv 7 8 script_name, file_name = argv 9 10 print " I am going to read the file ex15_sample.txt line by line" 11 12 txt = open(file_name, 'r') 13 L = txt.readlines() 14 15 #方法1,该方法不完全正确 16 print L # 读出的结果是全部的内容,是一个列表,列表的元素个数为文本的行数 #['This is stuff I typed into a file. ', 'It is really cool stuff. ', 'Lots and lots of fun to have in here.'] 17 print "-"*30 18 19 20 #方法2 因为上面说过txt.readlines()是一个列表,所以用下面的方法 21 print L[0], L[1], L[2] 22 print "-"*30 23 24 25 #方法3 26 for line in open(file_name): 27 print line 28 29 print "-"*30 30 31 #方法4 32 txt = open(file_name, 'r') 33 M = txt.readline() #这里定义变量M,M知识txt中的一句 34 while M: #这是一个死循环,会一直运行这个while语句 35 print M, #输出打印处一句 36 M = txt.readline() #此处的M其实是第二次读取txt里的第二句,往下循环就是第三次
终端运行结果如下:

下面要介绍一下常见的打开方式,我相信大家在看到open(file_name, 'r') 时已经注意到此处的'r'了,它是什么意思呢?它规定了文件打开的方式。
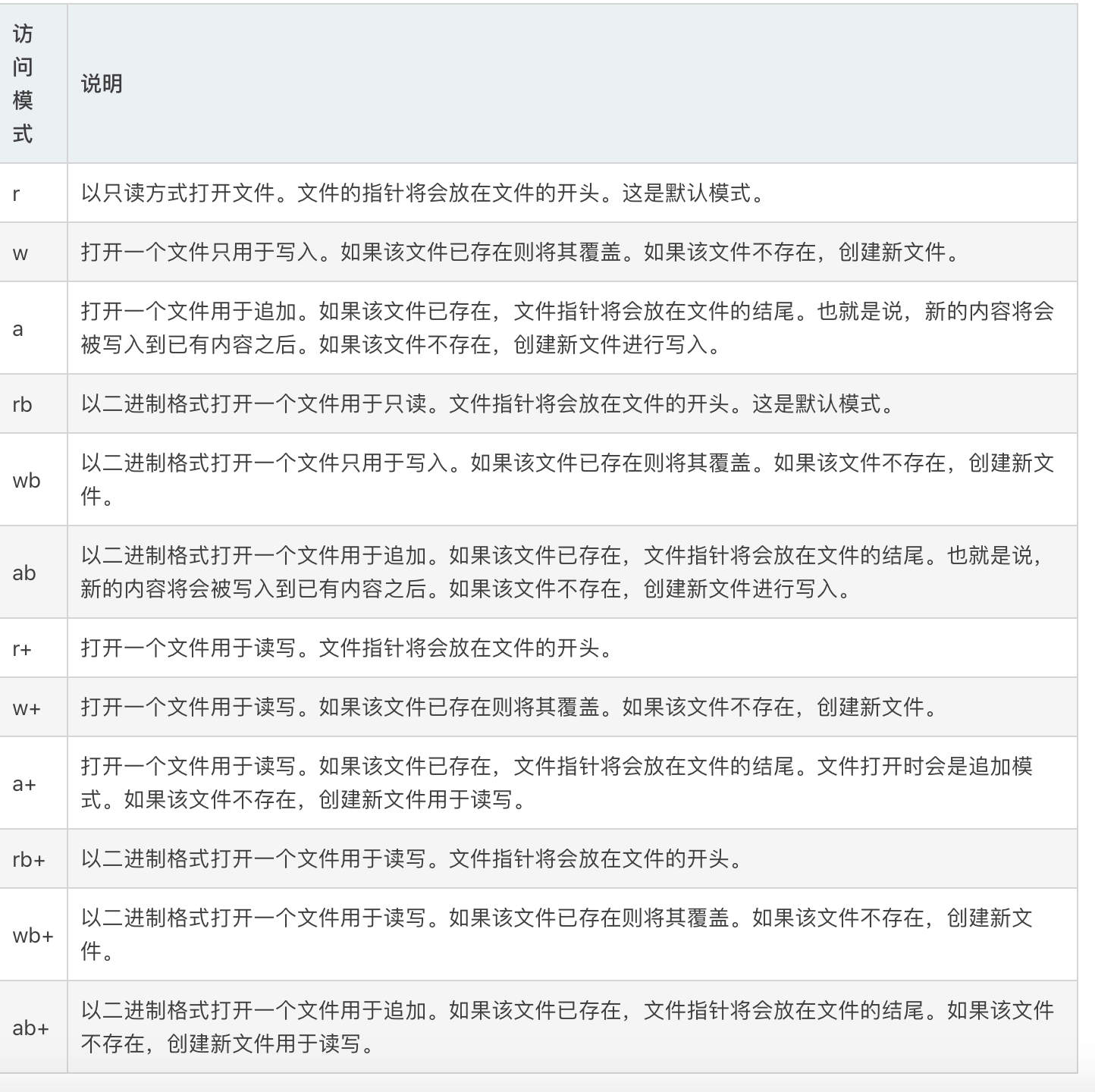
常见的文件打开方式如下:
'r': open for reading (default) 默认的只读模式
'w': open for wiritting 需要先将文本内容情况后,才可以写!
'a': open for writting, appending, to the end of the file if it exists 可写可增加模式,只能写在文件的末位
'b': binary mode 二进制式模式
't': text mode(default) 默认的文本模式
'+': open a disk for updating (reading and writting)
'u': universal newline mode(for backwards compatiblity, shouldn't be used in new code)
常见的文件打开方式组合:借用CSDN网站的文档,其网址为:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_26442553/article/details/81626442
--------------------------------------<习题17:复制文本内容>----------------------------------
介绍一个函数:exits(stuff), 如果stuff存在,则该函数反馈True,否者反馈False
做这个习题,需要先创建两个新的txt文本,一个是ex17_from_file.txt,其内容自己定义,我写的如下:

1 'she is so beautiful!' 2 'she is so kind!' 3 'she is the one!'
另一个为ex17_to_file.txt,其内容为空白,我们会通过ex17.py将ex17_from_file.txt的内容复制到ex17_to_file.txt里。代码如下:

1 #-*-coding:utf-8-*- 2 from sys import argv 3 from os.path import exists #命令exists是为了验证文件是否存在,如果存在,则反馈True,反之False 4 5 script, from_file, to_file = argv 6 7 print "Copying from %s to %s " % (from_file, to_file) 8 print " " 9 #we could do these two on one line too, how ? 10 #写成这样即可取代下面两行代码 indata = open(from_flie).read() 11 in_file = open(from_file) # 将from_file.txt打开,并定义称为一个变量,命名位in_file 12 indata = in_file.read() #将from_file中的原字符串提取出来,形成一个变量indata 13 14 print "The original file is : " 15 print indata 16 17 print "The input file is %d bytes long" % len(indata) 18 19 print "Does the output file exist? %r" % exists(to_file) #如何to_file存在,则exists(to_file)反馈True 20 print "Ready, hit RETURN to continue, CTRL-C to abort." 21 raw_input('?') 22 23 out_file = open(to_file, 'w') #这个out_file不可以用read(),因为它的打开方式是w 24 out_file.write(indata) 25 out_file.close() 26 in_file.close() 27 28 #这是为了输出被复制内容的空白文件ex17_to_file.txt 29 new_file = raw_input('file_name:') #在这里输入ex17_to_file.txt 30 txt = open(new_file) 31 print "This is editted ex17_to_file.txt" 32 print txt.read() 33 34 #in_file, out_file, indata 都是中间变量,是为了能够更加清晰体现程序的原理。
终端运行结果如下:

注意:上面截屏的下方,我用到 bogon:ex neymagico$ cat ex17_to_file.txt,这命令行可以直接打印文本的内容,因此也可以上了ex17..py的最后一段代码。
第九章预告:Python里的函数
