本文主要介绍下spring data jpa,主要聊聊为何要使用它进行开发以及它的基本使用。本文主要是入门介绍,并在最后会留下完整的demo供读者进行下载,从而了解并且开始使用spring data jpa。
(1)spring data jpa是什么?
小菜认为,spring data jpa,一、首先他不是ORM框架,跟hibernate不是同一个东西,hibernate是JPA标准的一个实现;二、它是对JPA进行了封装,并且提供一些基础的操作方法供开发者使用从而简化数据访问层的开发,我们使用spring data jpa 的目的就是为了简化开发。
(2)spring data jpa 对持久层的简化
spring data jpa主要是对持久层进行简化,主要体现在于:只要声明持久层的接口,无需编写具体的逻辑实现。这个原理是:根据方法名字进行解析,从而获取这个方法要执行的操作。例如,findByUserName(String name),我们可以看到他要做的就是根据用户名进行查询。spring data jpa提供了丰富的根据关键字组合进行查询,比如 like 、 not null、by等,如图:
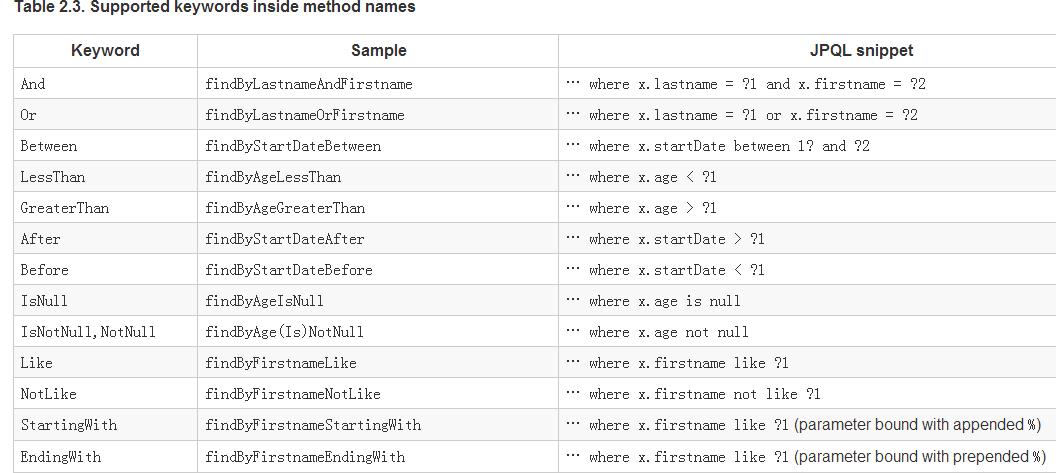
所以我们的持久层就会显得非常精简,先看看一个简单的持久层:
1 package com.lcy.web.systemuser.model;
2
3 import java.util.List;
4
5 import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
6 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor;
7 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
8 import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
9 import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
10 import org.springframework.data.repository.PagingAndSortingRepository;
11 import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
12 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
13
14 import com.lcy.web.systemuser.pojo.User;
15 @Repository
16 public interface UserRepository extends CrudRepository < User, Long > ,PagingAndSortingRepository<User,Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor <User>{
17
18
19 @Query(value="select user from User user where competence=0",nativeQuery=false)
20 public List<User> getSystemUsers(Pageable pageable);
21
22 @Query(value="select user from User user where competence=?1")
23 public List<User> getNormalUsers(Integer status);
24 /**
25 * nativeQuery=true 表示采用原生SQL语句进行操作
26 */
27 @Query(value="select * from cms_user where competence=?1",nativeQuery=true)
28 public List<User> getNormalUsersInNativeQuery(Integer status);
29
30 @Modifying //表示修改操作,记得加事务
31 @Query(value="update User user set user.userName=?1 where user.userName=?2 ")
32 public void updateNameByName(String newName,String oldName);
33 public User findByUserNameLike(String userName);
34 }
内容不说,只要看看几点因素,我们看到持久层只是一个接口,具体的方法的实现逻辑都省略到掉了,@Repository注解声明是持久层,主要看看它继承的三个类:
CrudRepository :提供基础的增删改查操作;
PagingAndSortingRepository:分页和排序的操作、
JpaSpecificationExecutor :组合查询条件,提供原生SQL查询
(3)spring data JPA的几个常用的功能:增删改查、自定义SQL语句操作、分页查询
3.1 增删改查
持久层继承CrudRepository,CrudRepository提供了基础的增删改查操作,所以无需在持久层再次编写方法,直接调用即可完成基础的操作,比如:
|
1
2
|
1 userRepository.findAll();2 userRepository.findOne(id); |
3.2自定义SQL语句操作
实际开发中有很多时候还是根据具体的需要进行一些自定义的查询方法或者其他操作,这时候需要开发人员去编写相关的SQL语句,spring data jpa提供了原生SQL语句操作还有面向对象的SQL操作
|
1
|
比如: |
1 @Query(value="select user from User user where competence=?1") 2 public List<User> getNormalUsers(Integer status); 3 /** 4 * nativeQuery=true 表示采用原生SQL语句进行操作 5 */ 6 @Query(value="select * from cms_user where competence=?1",nativeQuery=true) 7 public List<User> getNormalUsersInNativeQuery(Integer status);
3.3 分页查询
关键类:Sort、Pageable和Specification,说明:Sort是排序条件组合,Pageable是分页的信息组合(当前页数、每页记录数等),Specification是查询条件的组合。
例如:
1 //1. 排序
2 Sort sort=new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id");
3 //2.分页条件
4 Pageable pageable=new PageRequest(0, 2, sort);
5 //3.查询条件组合
6 Specification<User> s=new Specification<User>() {
7 @Override
8 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<User> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query,
9 CriteriaBuilder builder) {
10 Path<String> name=root.get("userName");
11 Path<User> competence=root.get("competence");
12 query.where(builder.like(name, "%K%"),builder.equal(competence, "1"));
13 return null;
14 }
15 };
16 //执行
17 Page<User> users=userRepository.findAll(s,pageable);
分页写的一些基础使用的代码,在实际开发中是不会这样写的,不够通用导致代码重复,当然目前已经有了相关的开源项目已经做得很好了,比如江南白衣的springside里面就有对分页做了很好的封装,使用起来非常方便。
简单的spring data jpa就介绍到这里,纯属入门介绍,要深入学习还是看官方文档比较好:
下面是参考资料:
spring data jpa的官方文档:http://docs.spring.io/spring-data/data-jpa/docs/current/reference/html/
