2018-09-23 13:25:40
主元素问题是一个非常经典的问题,一般来说,主元素问题指的是数组中元素个数大于一半的数字,显然这个问题可以通过遍历计数解决,时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(n)。这样的算法有两个弊端,一是空间复杂度较高,二是没法处理数据流问题。
因此就有了Boyer-Moore Majority Vote algorithm,这个算法可以用来高效的解决主元素问题,并且空间复杂度降到了O(1),时间复杂度保持不变。
算法的思路就是将不同的元素进行抵消,最后剩余的就是最终的结果。
如果说题目中没有明确说明一定存在主元素,那么还需要额外一次遍历来确认当前的解为主元素。
一、主元素问题
问题描述:

问题求解:
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int candidate = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == candidate) count++;
else if (count == 0) {
candidate = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
else count--;
}
return candidate;
}
二、Follow Up
问题描述:
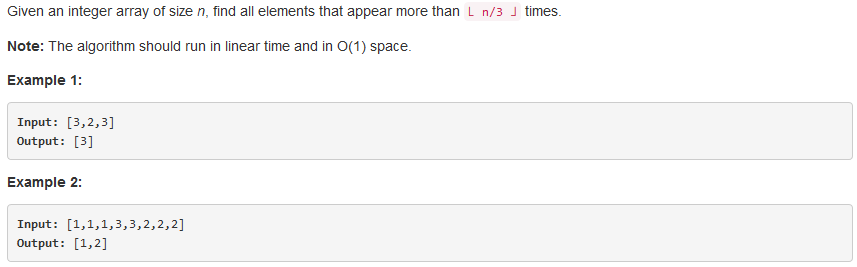
问题求解:
public List<Integer> majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return new ArrayList<>();
int candidate1 = 0;
int candidate2 = 0;
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == candidate1) count1++;
else if (nums[i] == candidate2) count2++;
else if (count1 == 0) {
candidate1 = nums[i];
count1 = 1;
}
else if (count2 == 0) {
candidate2 = nums[i];
count2 = 1;
}
else {
count1--;
count2--;
}
}
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
count1 = 0;
count2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == candidate1) count1++;
else if (nums[i] == candidate2) count2++;
}
if (count1 > nums.length / 3) res.add(candidate1);
if (count2 > nums.length / 3) res.add(candidate2);
return res;
}