一、<if>
使用<if>可以根据具体情况来拼接SQL语句,使其更加灵活更加适应我们的需求。
<if>的标签体中是需要拼接的语句,满足条件才会将其进行拼接。
<if>标签中的test属性用于判断添加。
例如我们现在有这样一个查询需求,如果客户名不为空则按客户名模糊查询,
如果客户职业不为空,则按职业查询。如果两者都不为空则按客户名和职业查询。
<select id = "findByUsernameOrJobs" resultMap = "re"> select * from t_customer where 1=1 <if test = "username == null and username = '' "> and t_username like concat('%',#{username},'%') </if> <if test = "jobs != null and jobs != '' "> and t_jobs = #{jobs} </if> </select>
<if>元素中满足条件的语句会被拼接入查询语句。
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; public class MybatisTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; //获取配置文件输入流 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //通过配置文件输入流构建sqlSessionFactory, SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream,"my"); //通过sqlSessionFactory获取sqlSession,true代表设置为自动提交。 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true); //执行CustomerMapper.xml文件中,id为xxxCustomer的语句,参数为Integer对象。 Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setUsername("zrx"); List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findByUsernameOrJobs", customer); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(customers); } //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close(); } }

可以看到查询语句拼接了username 和jobs这两个条件。
二、<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>
但有时候我们可能有这样的需求,
如果username不为空则按username查询。
如果usernae为空,jobs不为空,则按jobs查询。
如果jobs为空则查询所有电话不为空的用户。
则使用<if>进行处理是不方便的。
这时我们就可以使用<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>配合完成。
<chosse>类似switch,<when> 类似 case xx:xxxxx:break;<otherwise>类似default:xxx.
但某一个<when>中的test为true时,会拼接该标签中的语句,然后结束<choose>.也就是说所<choose>中
只会执行一个语句。如果所有<when>都不满足,则执行<otherwise>。
CustomerMapper.xml
<select id = "findByUsernameOrJobs" resultMap = "re"> select * from t_customer where 1=1 <choose> <when test = "username != null and username != '' "> and t_username = #{username} </when> <when test = "jobs != null and jobs != '' "> and t_jobs = #{jobs} </when> <otherwise> and t_phone is not null </otherwise> </choose> </select>
测试代码与上例相同。
运行结果:
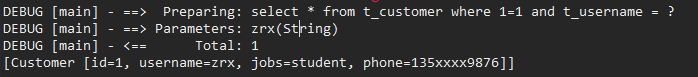
可以看到,查询语句只拼接了username.
三、<where><trim>
上例子中where后面都有一个1==1,
这时因为如果条件不满足时或拼接语句时有一个1==1,不会导致sql语句错误。
如果没有这个1==1,第一个添加满足语句就变成了
select * form t_customer where and username = #{usernmae}.
这样显然是不行的,所以添加了一个1==1避免错误。
当然也有标签可以避免这个问题,那就是<where>标签。
<select id = "findByUsernameOrJobs" resultMap = "re" parameterType="com.mybatis.first.Customer"> select * from t_customer <where> <if test = "username == null and username = '' "> and t_username like concat('%',#{username},'%') </if> <if test = "jobs != null and jobs != '' "> and t_jobs = #{jobs} </if> </where> </select>
使用where标签,只有在<where>标签类的有满足语句才会添加where关键字,且会去掉多余的'and' 和'or'。
测试: (拼接where关键字及语句、去取多余and)
Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setJobs("student"); customer.setUsername("zrx"); List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findByUsernameOrJobs", customer); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(customers); }

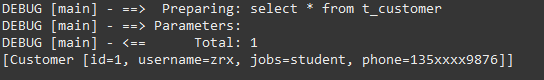
(没有满足条件语句,不添加where关键字)
List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findByUsernameOrJobs", null);
<trim>也可以实现<where>的效果,而且比<where>更灵活。
<trim>中有四个属性
prefix :代表要添加的前缀;prefix = "where"代表添加前缀 “where”。
prefixOverrides:代表要删除的前缀,例如prefixOverrides = “and“.代表删除前缀and。
suffix:代表要添加的后缀;
suffixOverrides :代表要删除的后缀。
使用<trim> 代替<where>
<select id = "findByUsernameOrJobs" resultMap = "re" parameterType="com.mybatis.first.Customer" flushCache = "true"> select * from t_customer <trim prefix = "where" prefixOverrides="and"> <if test = "username != null and username != '' "> and t_username like concat('%',#{username},'%') </if> <if test = "jobs != null and jobs != '' "> and t_jobs = #{jobs} </if> </trim> </select> <!--添加前缀where 同时去掉第一个and-->

运行结果与<where>标签相同。
四、<set>
有时只需要更新某一个字段,这时就可以使用<set>标签和<if>标签来实现生成对应的SQL语句。
<update id = "updateDy" parameterType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer"> update t_customer <set> <if test = "username != null and username != '' "> t_username = #{username}, </if> <if test = "jobs != null and jobs != '' "> t_jobs = #{jobs}, </if> <if test = "phone != null and phone != '' "> t_phone = #{phone}, </if> </set> where t_id = #{id} </update>
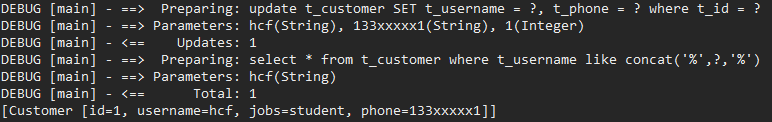
Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setId(1); customer.setUsername("hcf"); customer.setPhone("133xxxxx1"); //更新表中id为1的数据的username和phone。 int num = sqlSession.update("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.updateDy", customer); //查询 List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findByUsernameOrJobs", customer); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(customers); } //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close();
更新前:

更新后:
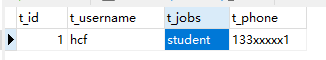
生成的更新语句中只拼接了属性不为空的选项,属性为空的选项(jobs)没有拼接入语句中。
这样可以动态的对需要更新的属性进行更新,而不是对其全部更新。
<set>还去除了最后的“,”。(t_phone = #{phone},)后面的","被去除了。
同样<set>可以用<trim>来实现,只需要添加前缀set,和去除后缀“,”即可。
五、<foreach>
例如我们需要查询id为1~10的客户,这个用手写也可以,但如果是需要查询id为1-1000的客户,这个手写的工作量就比较打了。
这时我们可以采用<foreach>元素来实现这个功能。
例如我们先构建一个list,通过for循环添加1000个元素到list中,然后将list传递给sql语句,再使用foreach读取每一个元素,最后根据元读取素拼接成语句。
<foreach>属性:
item:可以看做一个临时变量,用于存放迭代目标中单个元素的值。
index:当前元素在集合中的下标,如果是字典类型则代表key。
collection:指传递过来的集合类型。
open,close:代表开始和结束符号。
separator:代表元素分隔符。
<select id="findByDyID" resultMap = "re" parameterType = "List"> select * from t_customer where t_id in <foreach collection="list" item = "id" index = "index" open = "(" separator = "," close = ")" > #{id} </foreach> </select>
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) { list.add(i); } List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findByDyID", list); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(customers); } //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close();

六、<bind>
<bind>元素可以通过一个OGNL表达式来创建一个上下文变量。
<!-- 根据用户名模糊查询 --> <select id = "findCustomerByName" parameterType = "com.mybatis.first.Customer" resultMap = "re"> <bind name="bindFindByName" value="'%' + _parameter.getUsername() + '%'"/> select * from t_customer where t_username like #{bindFindByName} </select>
其中_parameter.getUsername是获取customer对象中的username属性值,也可以直接写username.
Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setId(1); customer.setUsername("h"); customer.setPhone("133xxxxx1"); //查询 List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.mybatis.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName", customer); for(Customer temp : customers) { System.out.println(temp); } //如果没有设置自动提交,使用insert、update、delete时需要使用sqlSession.commit()手动提交。 sqlSession.close();
